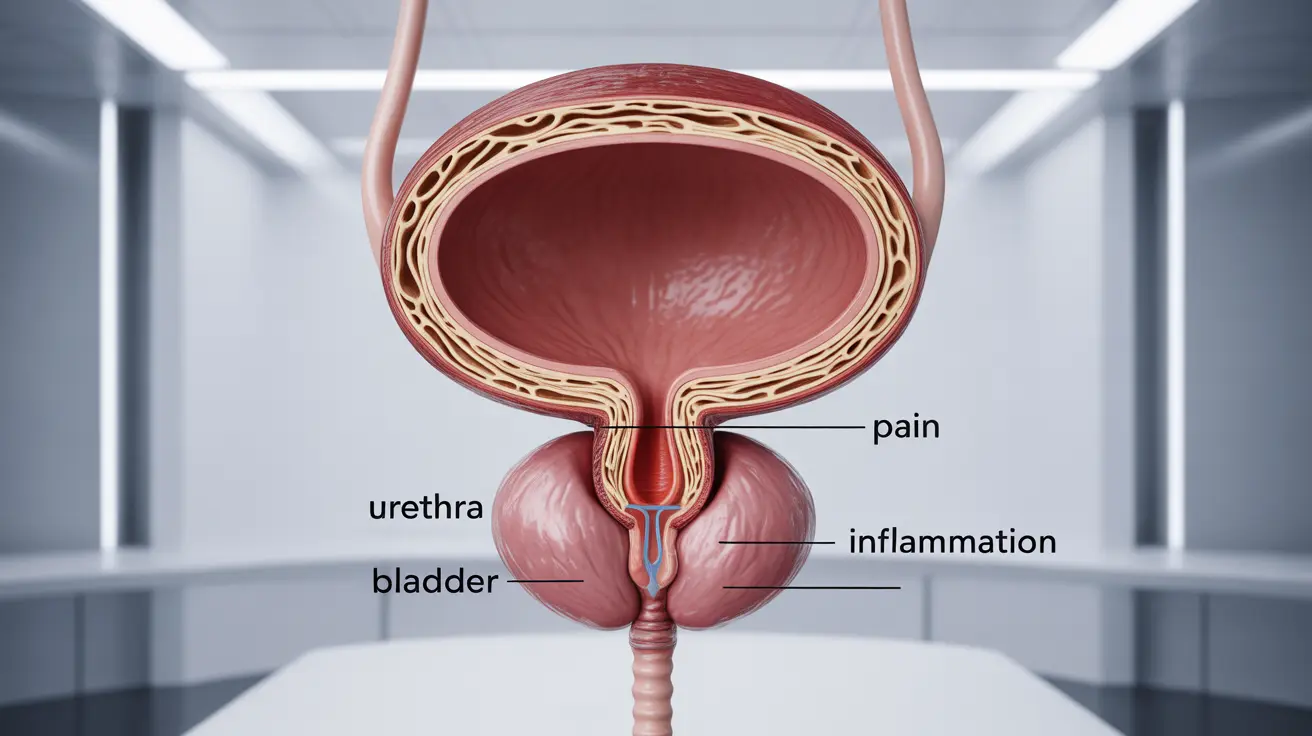
Cystitis in men, though less common than in women, is a significant urinary tract condition that requires proper understanding and timely treatment. This inflammation of the bladder can cause considerable discomfort and, if left untreated, may lead to more serious complications. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options is crucial for managing this condition effectively.
While men are generally less susceptible to cystitis due to their longer urethra, certain risk factors can increase their likelihood of developing this condition. This comprehensive guide will explore everything you need to know about cystitis in men, from recognition to recovery.
Common Symptoms and Warning Signs
Recognizing cystitis symptoms early is crucial for prompt treatment. Men experiencing cystitis typically notice several distinct symptoms:
- Frequent urination
- Burning or pain during urination
- Lower abdominal pain or pressure
- Cloudy or strong-smelling urine
- Blood in urine
- Low-grade fever
- General feeling of discomfort
These symptoms can vary in intensity and may develop gradually or appear suddenly. It's important to seek medical attention if these symptoms persist for more than 24 hours.
Diagnosis Process
Healthcare providers use several methods to diagnose cystitis in men accurately:
Physical Examination and Medical History
Your doctor will conduct a thorough physical examination and discuss your medical history, including any previous urinary tract issues or underlying conditions.
Diagnostic Tests
- Urinalysis
- Urine culture
- Blood tests
- Imaging studies (in some cases)
- Cystoscopy (if recurring episodes)
Treatment Approaches
Treatment for cystitis in men typically involves a multi-faceted approach:
Medical Treatments
The primary treatment usually includes:
- Antibiotics specific to the causing bacteria
- Pain relief medication
- Anti-inflammatory drugs
- Increased fluid intake
Supportive Care
Additional measures to support recovery include:
- Adequate rest
- Avoiding irritants
- Using warm compresses
- Maintaining proper hydration
Prevention Strategies
Several preventive measures can help reduce the risk of developing cystitis:
- Maintaining good hygiene
- Staying well-hydrated
- Urinating regularly
- Avoiding holding urine for long periods
- Managing underlying health conditions
- Regular exercise
- Proper dietary choices
Risk Factors and Complications
Understanding risk factors is crucial for prevention. Key risk factors include:
- Age (older men are more susceptible)
- Enlarged prostate
- Catheter use
- Compromised immune system
- Diabetes
- Previous urinary tract procedures
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the common symptoms of cystitis in men and how can I recognize them?
Common symptoms include frequent urination, burning sensation during urination, lower abdominal pain, cloudy or strong-smelling urine, and sometimes blood in the urine. These symptoms typically develop over a short period and can cause significant discomfort.
- How is cystitis diagnosed in men and what tests are usually done?
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, urinalysis, and urine culture. Your healthcare provider may also order blood tests or imaging studies if needed. In cases of recurring cystitis, a cystoscopy might be recommended to examine the bladder's interior.
- What are the most effective treatment options for bacterial cystitis in men?
The most effective treatment usually involves a course of antibiotics specific to the causing bacteria. This may be complemented with pain relief medication, increased fluid intake, and rest. The treatment duration typically ranges from 3-7 days, depending on severity.
- Can lifestyle changes or home remedies help prevent cystitis in men?
Yes, several lifestyle changes can help prevent cystitis, including staying well-hydrated, practicing good hygiene, urinating regularly, and avoiding holding urine for long periods. Some men also benefit from cranberry supplements, though evidence for their effectiveness is mixed.
- What are the main risk factors that increase the chance of developing cystitis in men?
The main risk factors include age (particularly over 50), enlarged prostate, use of urinary catheters, compromised immune system, diabetes, and previous urinary tract procedures or infections. Managing these risk factors can help reduce the likelihood of developing cystitis.