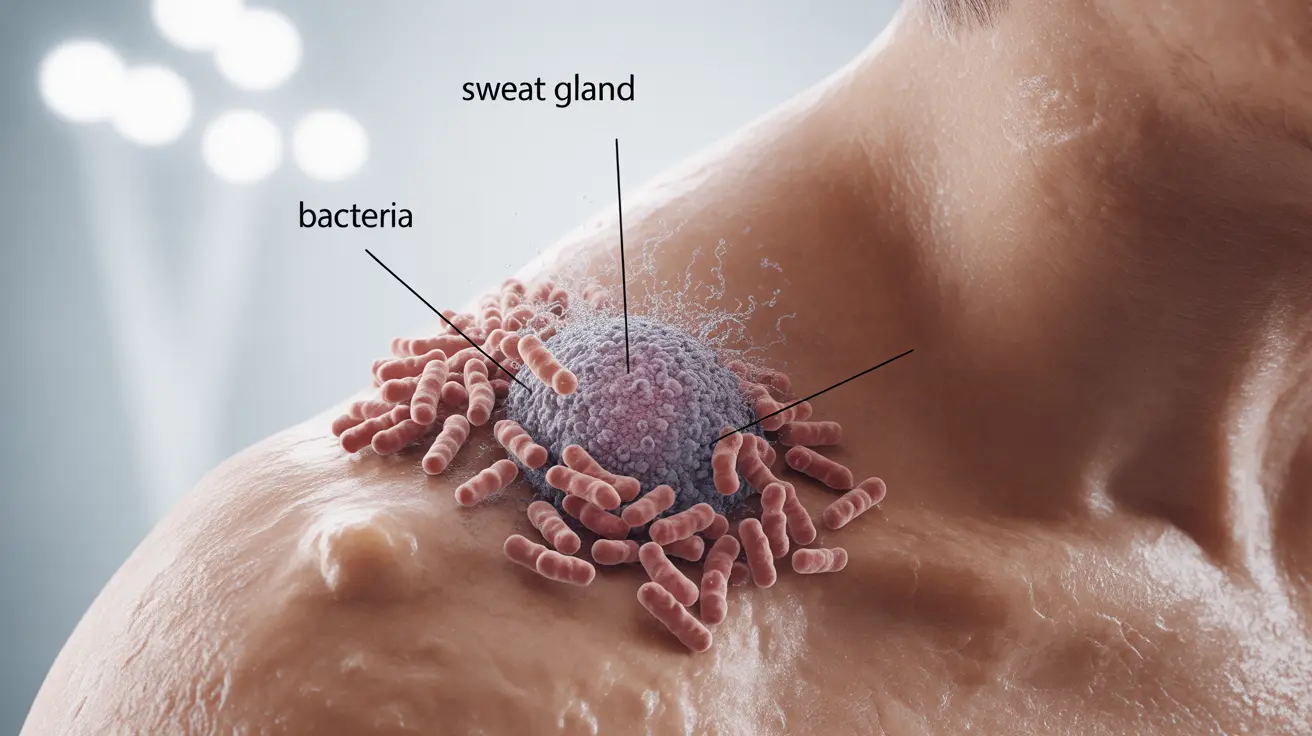
Bromhidrosis, commonly known as body odor disorder, is a medical condition characterized by the production of an unpleasant or offensive body odor. This condition occurs when bacteria break down proteins in sweat, leading to distinct malodorous compounds. While body odor is natural to some degree, bromhidrosis represents a more significant concern that can impact both physical health and social well-being.
Understanding this condition is crucial for proper diagnosis and management, as it affects many individuals worldwide and can significantly impact quality of life. This comprehensive guide will explore the causes, symptoms, and various treatment approaches for bromhidrosis.
What Causes Bromhidrosis?
Bromhidrosis develops through a complex interaction between sweat glands, bacteria, and various biological and environmental factors. The primary causes include:
- Bacterial breakdown of sweat components
- Excessive sweating (hyperhidrosis)
- Poor personal hygiene
- Certain dietary choices
- Underlying medical conditions
The condition primarily affects areas with a high concentration of apocrine sweat glands, such as the armpits, groin, and feet. These glands produce a protein-rich type of sweat that bacteria particularly favor.
Risk Factors and Contributing Elements
Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing bromhidrosis or make existing symptoms worse:
- Obesity
- Certain medications
- Hormonal changes
- Genetic predisposition
- Specific medical conditions
- Climate and environmental factors
Identifying Symptoms and Diagnosis
The primary symptom of bromhidrosis is persistent, unpleasant body odor that doesn't respond to regular hygiene practices. Healthcare providers typically diagnose the condition through:
- Physical examination
- Medical history review
- Assessment of hygiene practices
- Evaluation of underlying conditions
- Possible skin cultures in some cases
Treatment Approaches and Management
Managing bromhidrosis often requires a multi-faceted approach that may include:
Medical Interventions
- Prescription-strength antiperspirants
- Topical antibacterial medications
- Oral medications when necessary
- Botox injections in severe cases
Lifestyle Modifications
- Enhanced personal hygiene routines
- Dietary adjustments
- Proper clothing choices
- Regular exercise with appropriate cleanup
Prevention Strategies
Preventing or reducing bromhidrosis symptoms involves several key practices:
- Regular bathing with antibacterial soap
- Wearing breathable, natural-fiber clothing
- Maintaining a healthy diet
- Managing weight
- Using appropriate antiperspirants
- Keeping skin dry and clean
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the definition of bromhidrosis and how does it cause body odor?
Bromhidrosis is a medical condition characterized by offensive body odor resulting from bacterial breakdown of sweat proteins. The condition occurs when bacteria on the skin metabolize compounds in sweat, particularly from apocrine glands, producing volatile organic compounds that create an unpleasant smell.
What are the common causes and risk factors of bromhidrosis?
Common causes include bacterial overgrowth, excessive sweating, poor hygiene, and certain medical conditions. Risk factors include obesity, hormonal changes, genetic predisposition, and specific dietary habits that can influence body odor.
How is bromhidrosis diagnosed and what symptoms should I look for?
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination and medical history review. The main symptom is persistent, unusual body odor that doesn't improve with regular hygiene. Healthcare providers may also look for signs of excessive sweating or underlying skin conditions.
What are the most effective treatments and management options for bromhidrosis?
Effective treatments include prescription-strength antiperspirants, antibacterial medications, and proper hygiene practices. In some cases, medical interventions like Botox injections or oral medications may be necessary. A comprehensive approach often yields the best results.
How can bromhidrosis be prevented or reduced through hygiene and lifestyle changes?
Prevention strategies include maintaining excellent personal hygiene, using appropriate antiperspirants, wearing breathable clothing, maintaining a healthy diet, and managing weight. Regular bathing with antibacterial soap and keeping skin dry are essential preventive measures.