When discussing conditions that affect the brain and behavior, one common question often arises: is dementia considered a mental illness? This important distinction impacts how we understand, diagnose, and treat this complex condition that affects millions of people worldwide.
Understanding whether dementia is classified as a mental illness or a neurological disorder is crucial for both healthcare providers and families seeking appropriate care and support for their loved ones. Let's explore this topic in detail to provide clarity and insight.
The Classification of Dementia
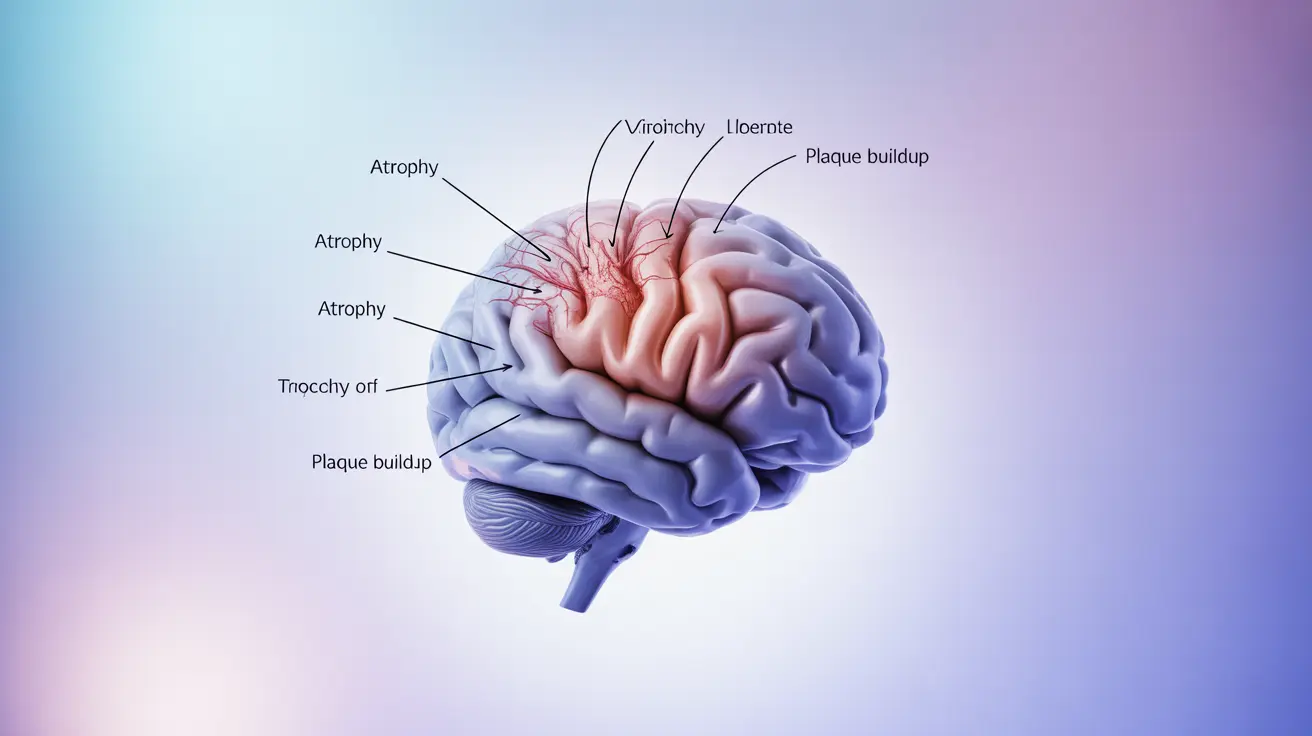
Dementia is primarily classified as a neurological disorder, not a mental illness. It involves progressive damage to brain cells that leads to cognitive decline, affecting memory, thinking, and behavior. Unlike mental illnesses, which typically involve chemical imbalances or psychological factors, dementia results from physical changes in the brain's structure and function.
Key Differences Between Dementia and Mental Illness
Physical Brain Changes
Dementia involves visible changes in brain tissue, including the death of nerve cells and loss of brain mass. These changes can be observed through brain imaging. Mental illnesses, however, typically don't show such structural changes and are more related to chemical and functional aspects of the brain.
Progression and Treatment
While mental illnesses can often be managed effectively with medication and therapy, dementia is generally progressive and irreversible. Current treatments focus on slowing progression and managing symptoms rather than curing the condition.
The Connection Between Mental Health and Dementia
Although dementia isn't classified as a mental illness, there are important connections between mental health and dementia that shouldn't be overlooked:
- Mental health conditions can sometimes mimic dementia symptoms
- Depression and anxiety commonly co-occur with dementia
- Chronic mental health issues may increase dementia risk
- Stress and emotional well-being can impact cognitive function
Diagnosis and Assessment
Proper diagnosis requires comprehensive evaluation by healthcare professionals. This typically includes:
- Cognitive testing
- Medical history review
- Brain imaging
- Mental health assessment
- Blood tests to rule out other conditions
Treatment Approaches
Treatment strategies differ significantly from those used for mental illnesses:
- Medication to manage specific symptoms
- Cognitive stimulation therapy
- Lifestyle modifications
- Environmental adaptations
- Caregiver support and education
Frequently Asked Questions
- Is dementia classified as a mental illness or a neurological disorder?
Dementia is classified as a neurological disorder, not a mental illness. It involves physical changes in the brain's structure and function, leading to progressive cognitive decline.
- What are the main differences between dementia and mental illnesses like depression or anxiety?
The key differences include: dementia shows physical brain changes visible on scans, is generally progressive and irreversible, and primarily affects cognitive function. Mental illnesses typically involve chemical imbalances, can often be effectively treated, and may not show structural brain changes.
- How can I tell if memory problems are due to dementia or a mental health condition?
Professional evaluation is essential for accurate diagnosis. Dementia typically shows progressive decline in multiple cognitive areas, while memory issues related to mental health conditions may be more temporary and often improve with treatment of the underlying condition.
- Does having a mental illness increase the risk of developing dementia later in life?
Some studies suggest that certain mental health conditions, particularly depression and anxiety, may increase the risk of developing dementia. However, this doesn't mean that having a mental illness will definitely lead to dementia.
- What treatments are available specifically for dementia compared to those for mental illnesses?
Dementia treatments focus on managing symptoms and slowing progression through medications, cognitive therapy, and lifestyle modifications. Mental illness treatments typically involve psychotherapy, medication to regulate brain chemistry, and counseling, with better potential for symptom resolution.
Understanding the distinction between dementia and mental illness is crucial for ensuring proper diagnosis, treatment, and support. While they may share some symptoms and can co-exist, recognizing their fundamental differences helps in providing appropriate care and management strategies for affected individuals.