Bad breath, medically known as halitosis, can be more than just a social concern for people with diabetes. Understanding the relationship between diabetes and bad breath is crucial, as it can sometimes indicate serious underlying health issues that require immediate attention.
This comprehensive guide explores how diabetes can lead to bad breath, the warning signs to watch for, and effective management strategies to help maintain fresh breath and overall oral health.
Understanding the Diabetes-Bad Breath Connection
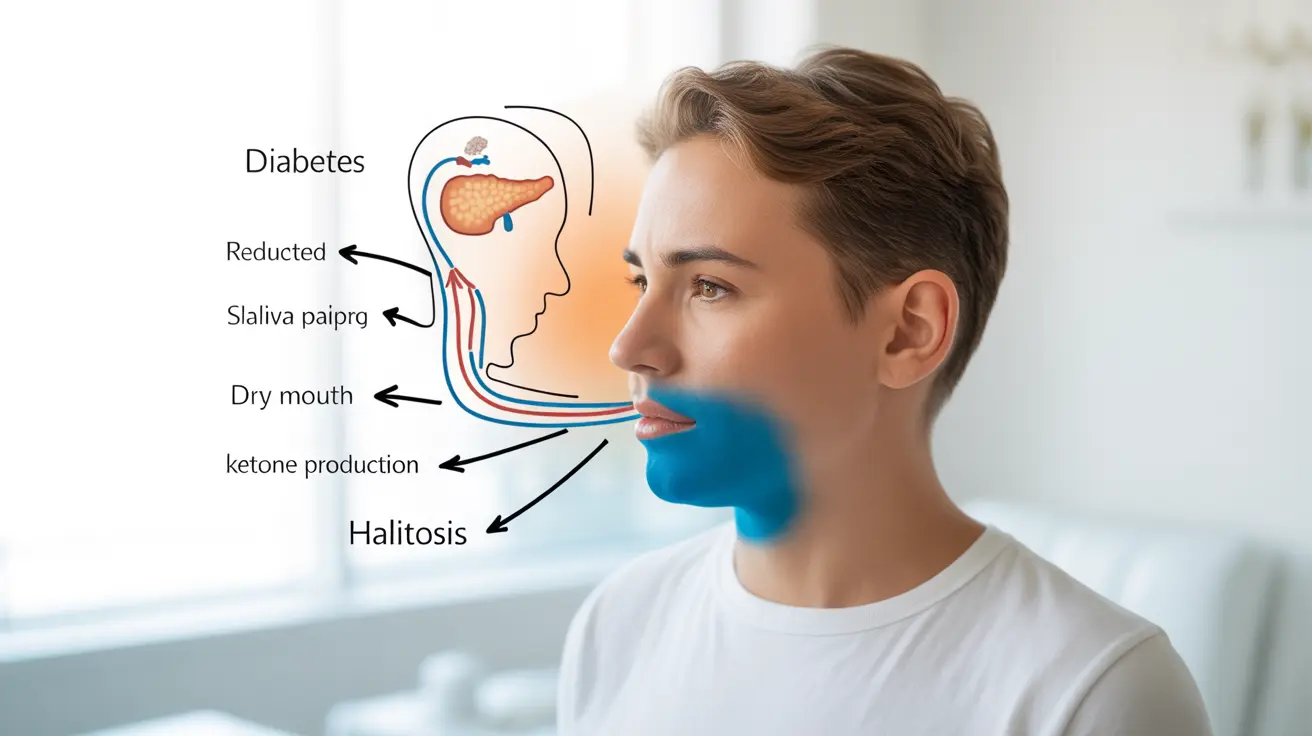
Diabetes can contribute to bad breath through several distinct mechanisms. When blood sugar levels aren't properly controlled, various physiological changes occur that can affect breath odor and oral health.
High Blood Sugar and Dry Mouth
People with diabetes often experience xerostomia, or dry mouth, due to decreased saliva production. This reduction in saliva creates an environment where bacteria can thrive, leading to unpleasant breath odors and increased risk of oral health problems.
The Role of Ketones
When the body can't properly use glucose for energy, it begins breaking down fat cells for fuel. This process produces ketones, which can create a distinctive fruity or acetone-like breath odor – a condition particularly associated with diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA).
Diabetes-Related Gum Disease and Bad Breath
High blood sugar levels can weaken the body's ability to fight bacterial infections, making people with diabetes more susceptible to periodontal disease. This connection creates a challenging cycle that can significantly impact breath quality.
How Gum Disease Develops
Elevated blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the gums. This impaired circulation makes it harder for the body to heal and fight infections, leading to:
- Gingivitis (early-stage gum disease)
- Periodontitis (advanced gum disease)
- Persistent bad breath
- Tooth decay and potential tooth loss
Warning Signs and Risk Factors
Several key indicators may suggest diabetes-related breath problems:
- Sweet, fruity, or acetone-like breath odor
- Persistent dry mouth
- Bleeding or swollen gums
- Frequent oral infections
- White patches on the tongue or cheeks
Managing Diabetes-Related Bad Breath
Effective management of diabetes-related bad breath requires a multi-faceted approach focusing on both blood sugar control and oral hygiene.
Blood Sugar Management
Maintaining stable blood glucose levels is crucial for preventing diabetes-related breath problems. This includes:
- Regular blood sugar monitoring
- Following prescribed medication schedules
- Maintaining a balanced diet
- Regular exercise
- Staying well-hydrated
Oral Hygiene Practices
A thorough oral care routine is essential and should include:
- Brushing teeth at least twice daily
- Daily flossing
- Regular dental check-ups
- Using alcohol-free mouthwash
- Cleaning dentures properly (if applicable)
Frequently Asked Questions
Does diabetes cause bad breath and what are the main reasons for it? Yes, diabetes can cause bad breath primarily through three mechanisms: high blood sugar leading to dry mouth, the production of ketones during diabetic ketoacidosis, and increased susceptibility to gum disease.
Why does diabetic ketoacidosis cause a fruity or acetone-like smell on the breath? When the body can't use glucose properly, it breaks down fat for energy, producing ketones as a byproduct. These ketones are released through breathing and create a characteristic fruity or acetone-like smell.
How can gum disease related to diabetes lead to persistent bad breath? Diabetes can weaken the body's ability to fight bacteria and reduce blood flow to the gums, leading to periodontal disease. The bacterial buildup and tissue breakdown associated with gum disease create persistent unpleasant odors.
What are the warning signs of diabetic ketoacidosis linked to bad breath? Key warning signs include fruity-smelling breath, excessive thirst, frequent urination, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and confusion. These symptoms require immediate medical attention.
How can people with diabetes prevent or manage bad breath effectively? Prevention and management strategies include maintaining good blood sugar control, practicing thorough oral hygiene, staying hydrated, having regular dental check-ups, and using sugar-free gum or mints to stimulate saliva production.