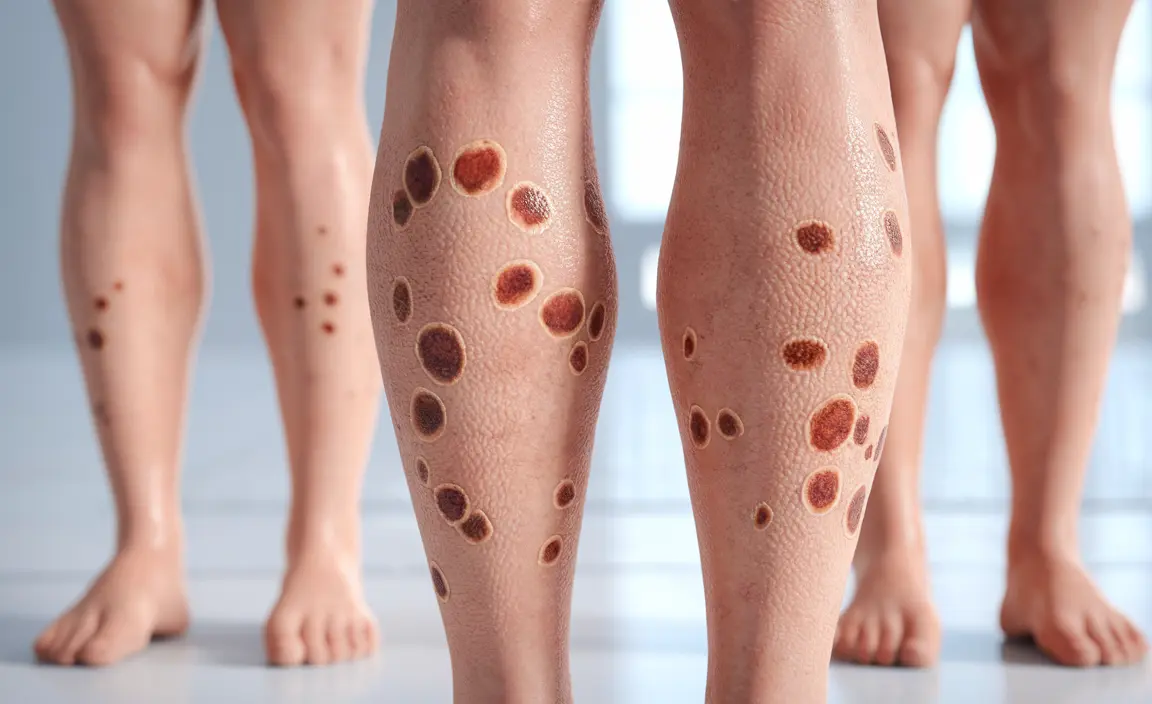
Diabetic dermopathy is a common skin condition that affects many people living with diabetes. These characteristic skin lesions, while harmless, can be a visible indicator of underlying diabetes-related changes in the body. Understanding this condition is crucial for both diabetes management and peace of mind.
This comprehensive guide explores what diabetic dermopathy looks like, why it occurs, and how it can be managed effectively. While the condition itself doesn't require specific treatment, recognizing its appearance and implications can help in overall diabetes care.
What Is Diabetic Dermopathy?
Diabetic dermopathy presents as small, round or oval, brownish patches on the skin. These spots typically appear on the shins but can occasionally develop on other parts of the body. The lesions are usually flat, don't cause pain or itching, and can sometimes have a slightly scaly appearance.
The condition is so common among people with diabetes that it's sometimes referred to as "shin spots" or "pigmented pretibial patches." Understanding its characteristics can help distinguish it from other skin conditions that may require different approaches to treatment.
Causes and Risk Factors
The development of diabetic dermopathy is closely linked to several diabetes-related factors:
- Changes in small blood vessels
- Trauma to the affected areas
- Long-term blood sugar fluctuations
- Reduced blood circulation
People who have had diabetes for many years or those with poorly controlled blood sugar levels are more likely to develop these skin changes. The condition is particularly common in individuals over 50 years of age and those with other diabetes-related complications.
Diagnosis and Identification
Healthcare providers typically diagnose diabetic dermopathy through visual examination and medical history review. The distinctive appearance and location of the lesions, combined with a history of diabetes, usually make the diagnosis straightforward. However, other conditions may need to be ruled out, including:
- Fungal infections
- Allergic reactions
- Age spots
- Other diabetes-related skin conditions
Management and Care
While there isn't a specific treatment required for diabetic dermopathy, several approaches can help manage the condition:
Blood Sugar Control
Maintaining stable blood sugar levels through proper diabetes management is the most important step in preventing new lesions and managing existing ones. This includes regular monitoring, medication adherence, and lifestyle modifications.
Skin Protection
Protecting the skin from injury can help prevent new lesions from forming. This involves:
- Wearing protective clothing during activities
- Moisturizing the skin regularly
- Avoiding trauma to the shins and legs
- Using sunscreen when exposed to UV rays
Prevention and Long-term Outlook
While diabetic dermopathy can't always be prevented, good diabetes management can reduce the risk of developing new lesions. The spots typically don't cause any medical complications and may fade over time, though some may remain permanently.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does diabetic dermopathy look like and where on the body does it usually appear? Diabetic dermopathy appears as round or oval, brown or reddish patches, primarily on the shins. The spots are usually flat, don't cause discomfort, and can vary in size from a few millimeters to centimeters.
What causes diabetic dermopathy and why is it common in people with diabetes? Diabetic dermopathy is caused by changes in small blood vessels, minor trauma to the skin, and long-term blood sugar fluctuations. It's common in people with diabetes due to these vascular changes and the body's altered healing response.
How is diabetic dermopathy diagnosed and can it be mistaken for other skin conditions? Diagnosis is typically made through visual examination and medical history. While it can be mistaken for age spots or fungal infections, its characteristic appearance and location make it relatively easy for healthcare providers to identify.
Is there a treatment for diabetic dermopathy and how can I manage the appearance of the lesions? There's no specific treatment required for diabetic dermopathy. The best management approach is maintaining good blood sugar control and protecting the skin from injury. The lesions may fade over time but can sometimes persist.
Can diabetic dermopathy be prevented, and does it indicate other diabetes complications? While not entirely preventable, good diabetes management can reduce the risk of developing diabetic dermopathy. Its presence may indicate other diabetes-related complications, making it important to maintain regular medical check-ups and proper diabetes care.