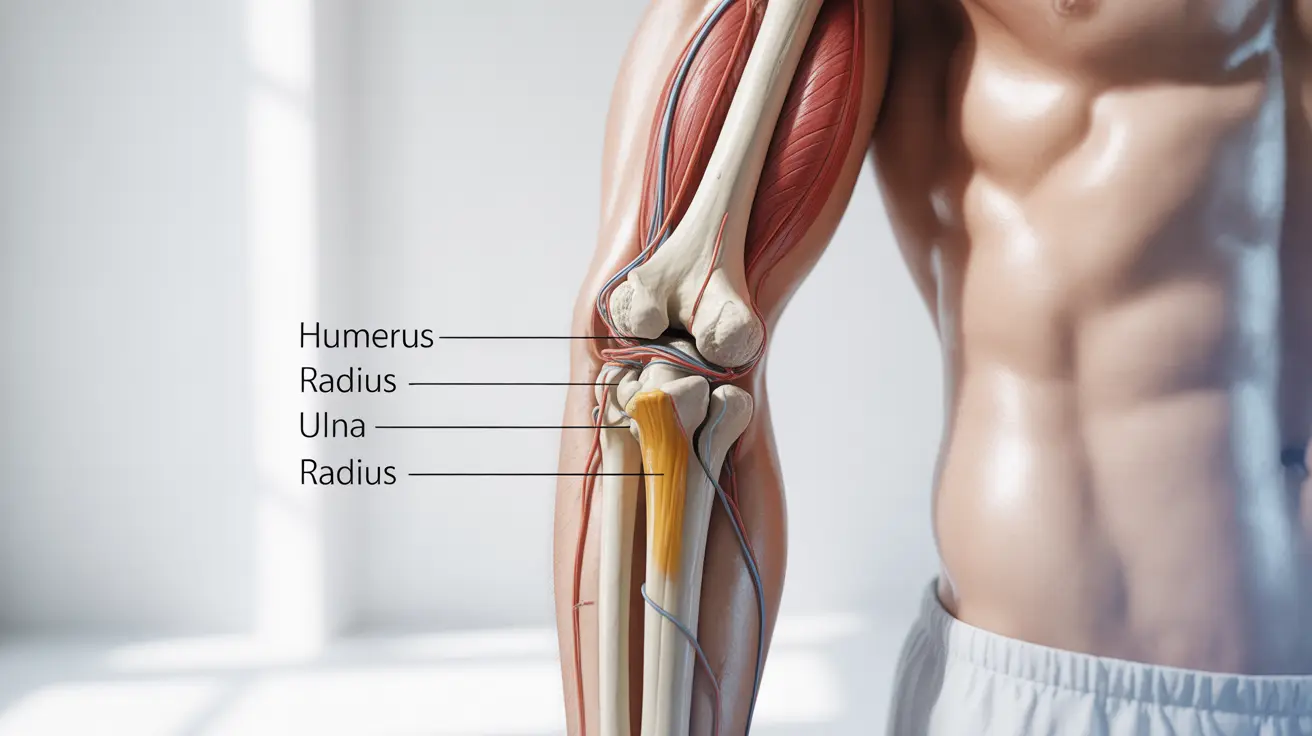
Elbow pain can significantly impact daily activities, from typing on a computer to lifting objects or playing sports. Understanding the causes, diagnosis, and treatment options for elbow pain is crucial for effective management and prevention of long-term complications. This comprehensive guide will help you navigate the complexities of elbow pain and its various manifestations.
Common Causes of Elbow Pain
Elbow pain can arise from various conditions, each requiring specific diagnostic approaches and treatment plans. Understanding these causes is the first step in proper diagnosis and management:
Overuse Injuries
The most frequent causes of elbow pain are repetitive stress injuries, including:
- Tennis elbow (lateral epicondylitis)
- Golfer's elbow (medial epicondylitis)
- Bursitis
- Tendinitis
Traumatic Injuries
Sudden injuries that can cause significant elbow pain include:
- Sprains and strains
- Fractures
- Dislocations
- Direct impact injuries
Diagnostic Process
Healthcare providers use various methods to diagnose elbow pain accurately. The diagnostic process typically includes:
Physical Examination
During the initial evaluation, your doctor will:
- Assess range of motion
- Check for swelling and tenderness
- Evaluate strength and stability
- Test for specific conditions through specialized maneuvers
Imaging Studies
Different imaging techniques may be employed:
- X-rays for bone-related issues
- MRI for soft tissue problems
- Ultrasound for dynamic evaluation
- CT scans for complex cases
Treatment Approaches
Treatment options vary depending on the specific diagnosis and severity of the condition. Common approaches include:
Conservative Treatment
Initial treatment usually focuses on non-invasive methods:
- Rest and activity modification
- Ice and heat therapy
- Physical therapy exercises
- Anti-inflammatory medications
Advanced Interventions
For persistent or severe cases, additional treatments might include:
- Corticosteroid injections
- Platelet-rich plasma therapy
- Surgery (in severe cases)
- Rehabilitation programs
Prevention Strategies
Preventing elbow pain is crucial, especially for those involved in repetitive activities or sports. Key preventive measures include:
- Proper warm-up before activities
- Using correct technique in sports and daily activities
- Regular stretching and strengthening exercises
- Ergonomic workplace modifications
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common causes of elbow pain, and how is it diagnosed?
Elbow pain commonly results from overuse injuries like tennis elbow, traumatic injuries, or inflammatory conditions. Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, detailed medical history, and possibly imaging studies like X-rays or MRI scans.
How is elbow pain typically treated, and what are the most effective home remedies?
Treatment usually begins with conservative measures like RICE (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation), over-the-counter pain medications, and gentle exercises. Effective home remedies include ice/heat therapy, gentle stretching, and activity modification.
Can sports injuries like tennis elbow be prevented, and what exercises help reduce the risk?
Yes, sports injuries can often be prevented through proper warm-up, correct technique, and specific strengthening exercises. Wrist flexor and extensor exercises, along with forearm strengthening, can help reduce the risk of tennis elbow.
What is the difference between tennis elbow and golfer's elbow, and how are they treated differently?
Tennis elbow affects the outer elbow (lateral epicondyle), while golfer's elbow affects the inner elbow (medial epicondyle). While both conditions share similar treatment approaches, the specific exercises and activity modifications differ based on the affected area.
Are there any risks associated with corticosteroid injections for treating elbow pain, and what are the alternatives?
Corticosteroid injections can have risks including tissue weakening, infection, and temporary pain increase. Alternatives include physical therapy, platelet-rich plasma injections, acupuncture, and in some cases, surgery.