Disc desiccation is a common age-related condition that occurs when the spinal discs lose moisture and begin to thin, potentially leading to back pain and reduced mobility. This natural degenerative process can affect anyone but becomes increasingly common as we age. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options is crucial for managing this condition effectively.
While disc desiccation is a normal part of aging, various factors can accelerate this process, and proper management can help maintain quality of life. This comprehensive guide will explore everything you need to know about this condition, from its early warning signs to treatment approaches.
What is Disc Desiccation?
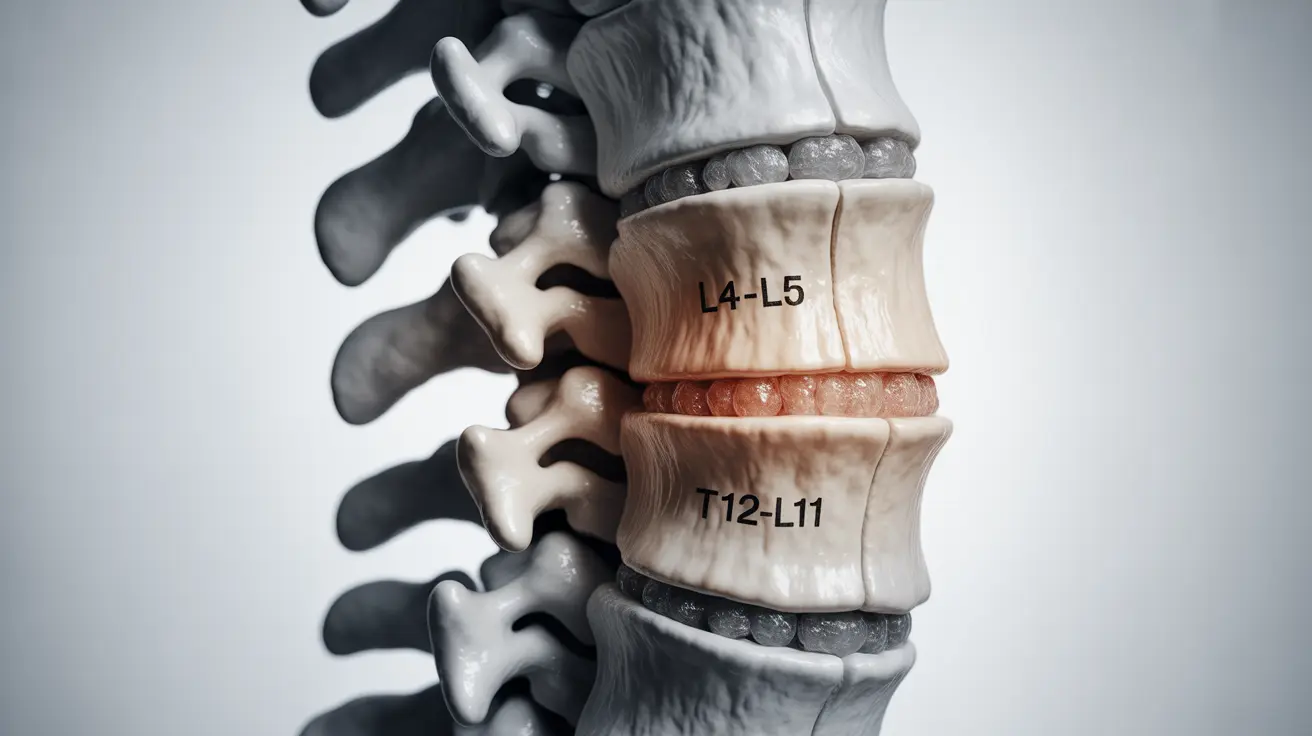
Disc desiccation refers to the loss of water content in the intervertebral discs, which act as cushions between the vertebrae in your spine. These discs naturally contain a high percentage of water, which helps them maintain their height and flexibility. When these discs begin to dry out, they become thinner and less effective at absorbing shock and supporting spinal movement.
Common Symptoms and Warning Signs
The symptoms of disc desiccation can vary from person to person, but typically include:
- Chronic lower back pain
- Stiffness in the spine
- Reduced flexibility
- Pain that worsens with certain movements
- Radiating pain into the legs or arms
- Numbness or tingling in extremities
The severity of symptoms often depends on the location and extent of the disc desiccation, as well as individual factors such as overall health and activity level.
Risk Factors and Causes
Several factors can contribute to the development or acceleration of disc desiccation:
- Natural aging process
- Genetic predisposition
- Repetitive physical stress
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Previous spine injuries
Diagnosis Process
Healthcare providers typically use a combination of methods to diagnose disc desiccation:
Physical Examination
During the initial assessment, doctors will evaluate your range of motion, muscle strength, and reflexes. They'll also discuss your medical history and specific symptoms.
Imaging Tests
Common diagnostic tools include:
- MRI scans (most effective for viewing disc condition)
- X-rays
- CT scans
- Discography (in specific cases)
Treatment Approaches
Conservative Management
Initial treatment typically focuses on non-invasive approaches:
- Physical therapy
- Targeted exercises
- Pain management techniques
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Heat and cold therapy
Advanced Treatment Options
For more severe cases, additional treatments may include:
- Epidural steroid injections
- Regenerative medicine procedures
- Minimally invasive surgical options (in severe cases)
Prevention and Lifestyle Modifications
While some degree of disc desiccation is inevitable with age, certain lifestyle changes can help slow its progression:
- Maintaining proper posture
- Regular exercise focusing on core strength
- Staying hydrated
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Avoiding smoking
- Using proper lifting techniques
- Taking regular breaks from prolonged sitting
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of disc desiccation and how can I tell if my back pain is related to it? Disc desiccation typically causes chronic lower back pain, stiffness, and reduced flexibility. The pain often worsens with certain movements and may radiate to the extremities. However, proper diagnosis requires medical evaluation and imaging tests.
What causes disc desiccation and who is most at risk for developing this condition? While aging is the primary cause, risk factors include genetic predisposition, repetitive physical stress, smoking, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle. People over 40 and those with physically demanding jobs are at higher risk.
How is disc desiccation diagnosed by doctors and what imaging tests are used? Doctors diagnose disc desiccation through physical examination and imaging tests, primarily MRI scans, which can clearly show disc water content and height. X-rays and CT scans may also be used to evaluate overall spine health.
What treatment options are available for disc desiccation, including physical therapy and medications? Treatment options range from conservative approaches like physical therapy, pain medication, and exercise to more advanced treatments such as epidural injections. Surgery is rarely needed and reserved for severe cases.
Can lifestyle changes like exercise and weight management help prevent or slow down disc desiccation? Yes, lifestyle modifications can help manage disc desiccation. Regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, proper posture, staying hydrated, and avoiding smoking can all help slow the progression of disc degeneration.