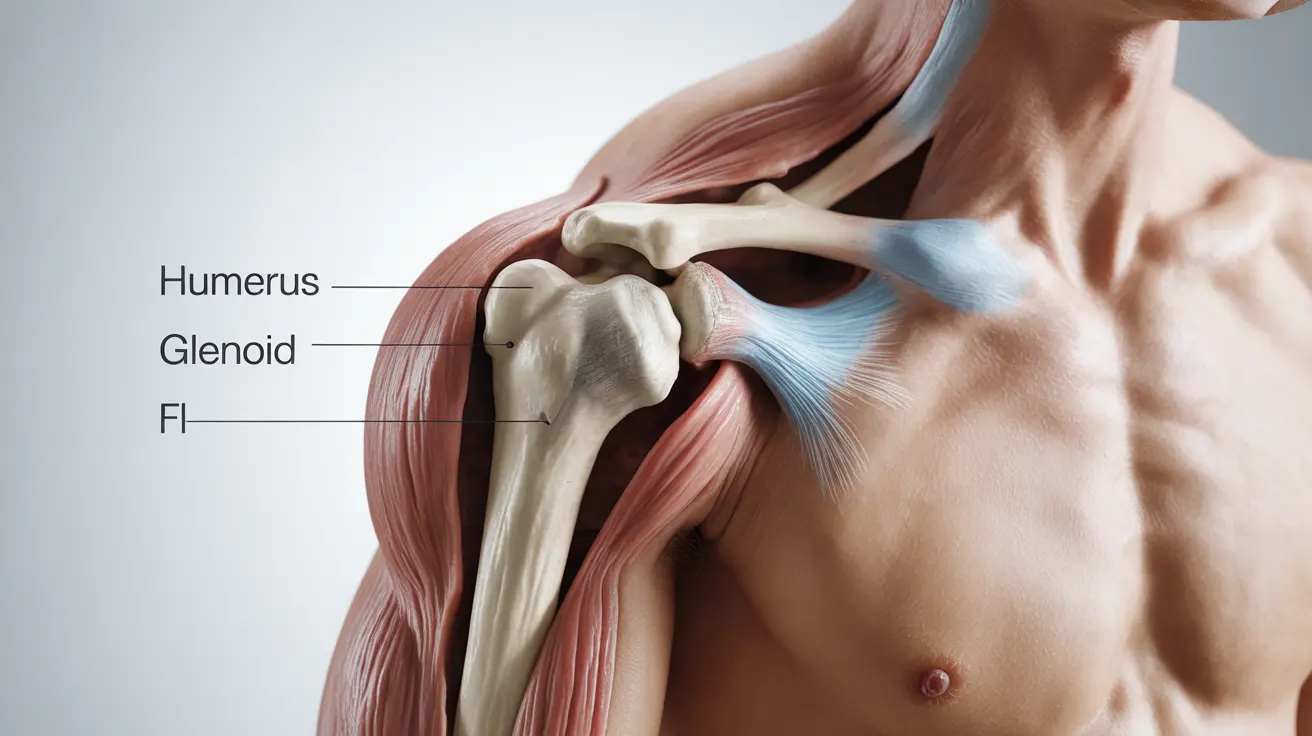
A dislocated shoulder occurs when the upper arm bone (humerus) pops out of the shoulder socket (glenoid), causing immediate pain and mobility issues. This injury commonly affects athletes and active individuals but can happen to anyone through accidents or falls. Understanding the signs, treatment options, and recovery process is crucial for proper healing and preventing future dislocations.
Understanding Shoulder Dislocation and Its Causes
The shoulder is one of the most mobile joints in the body, making it particularly vulnerable to dislocation. Common causes include:
- Sports injuries, especially in contact sports
- Falls on an outstretched arm
- Motor vehicle accidents
- Forceful twisting or pulling of the arm
- Repetitive overhead movements
Signs and Symptoms to Watch For
Recognizing a dislocated shoulder is crucial for seeking prompt medical attention. Key symptoms include:
- Visible deformity or bulge in the shoulder area
- Severe pain and inability to move the arm
- Swelling and bruising
- Muscle spasms
- Numbness or tingling in the arm or hand
Emergency Treatment and Diagnosis
When a shoulder dislocation occurs, immediate medical attention is essential. Healthcare providers will typically:
- Perform a physical examination
- Order X-rays to confirm the dislocation and check for associated injuries
- Assess nerve and blood vessel damage
- Provide pain medication as needed
The Reduction Process
The primary treatment involves a procedure called reduction, where the doctor carefully guides the arm bone back into its socket. This is usually done under sedation to minimize pain and muscle tension.
Non-Surgical Treatment and Recovery
After reduction, several non-surgical treatments may be recommended:
- Immobilization with a sling for 2-3 weeks
- Ice therapy to reduce swelling
- Gradual physical therapy exercises
- Pain management medications
- Activity modification during healing
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
A structured rehabilitation program typically includes:
- Range of motion exercises
- Strengthening of shoulder muscles
- Stability training
- Gradual return to normal activities
- Sport-specific training when appropriate
Surgical Intervention and Considerations
Surgery might be necessary in cases of:
- Repeated dislocations
- Significant damage to surrounding tissues
- Young, active patients at high risk of recurrence
- Failed conservative treatment
Types of Surgical Procedures
Common surgical approaches include:
- Arthroscopic stabilization
- Bankart repair
- Capsular shift
- Open surgery for complex cases
Prevention and Long-Term Management
Preventing future dislocations involves:
- Regular shoulder-strengthening exercises
- Proper warm-up before activities
- Avoiding high-risk positions
- Using proper technique in sports and activities
- Following protective measures during healing
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common causes and symptoms of a dislocated shoulder? A dislocated shoulder typically occurs from falls, sports injuries, or accidents. Key symptoms include severe pain, visible deformity, inability to move the arm, and possible numbness or tingling.
How is a dislocated shoulder diagnosed and treated in an emergency setting? Diagnosis involves physical examination and X-rays. Emergency treatment focuses on pain management and reduction - carefully guiding the arm bone back into its socket under medical supervision.
What are the non-surgical treatment options and recovery steps for a dislocated shoulder? Non-surgical treatment includes immobilization with a sling, ice therapy, pain management, and a structured physical therapy program to restore strength and mobility.
When is surgery recommended for a dislocated shoulder, and what does it involve? Surgery is typically recommended for repeated dislocations, significant tissue damage, or in young, active patients. Procedures may include arthroscopic stabilization or open surgery to repair damaged tissues.
How can I prevent repeated shoulder dislocations and improve long-term shoulder stability? Prevention involves regular strengthening exercises, proper warm-up, avoiding risky positions, and following rehabilitation guidelines. Working with a physical therapist can help develop an effective prevention strategy.