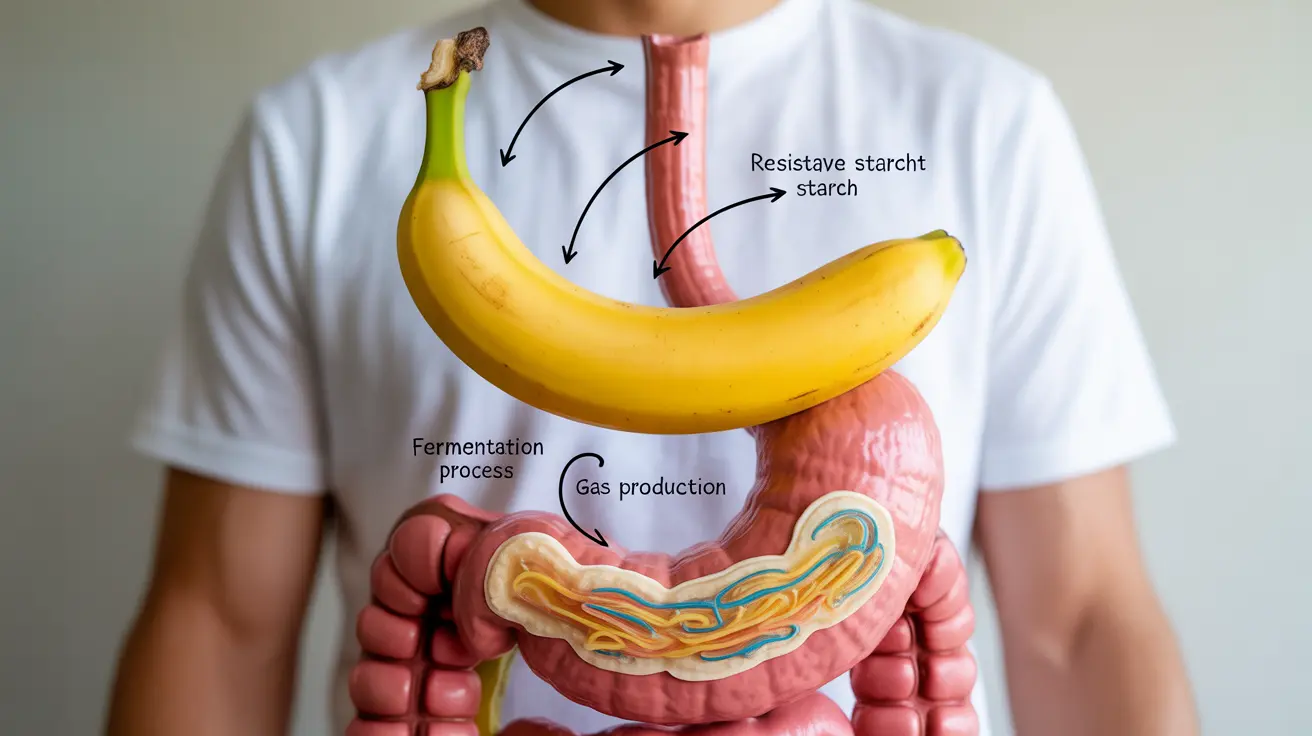
For many people, bananas are a go-to healthy snack, but some individuals report experiencing digestive issues after eating them. Understanding the relationship between bananas and gas production can help you make informed decisions about including this nutritious fruit in your diet.
This comprehensive guide explores how bananas affect your digestive system, why they might cause gas in some people, and what you can do to minimize any uncomfortable symptoms while still enjoying their health benefits.
How Bananas Affect Your Digestive System
Bananas contain several compounds that can influence digestion, including fiber, resistant starch, and natural sugars. These components are processed differently by your digestive system, potentially leading to varying degrees of gas production.
The Role of Resistant Starch
Unripe bananas contain higher levels of resistant starch, which passes through your digestive system largely unchanged until it reaches your large intestine. Here, gut bacteria ferment this starch, potentially producing gas as a byproduct. As bananas ripen, this resistant starch converts into more easily digestible sugars.
The Impact of Banana Ripeness
The ripeness of a banana significantly affects its digestive properties. Green or unripe bananas typically contain more resistant starch and less sugar, while fully ripe bananas have a different nutritional profile that may be easier for some people to digest.
Unripe Bananas
- Higher in resistant starch
- More likely to cause gas
- Contains prebiotics that feed gut bacteria
- May be harder to digest
Ripe Bananas
- Lower in resistant starch
- Higher in natural sugars
- Generally easier to digest
- Less likely to cause significant gas
Benefits vs. Potential Digestive Issues
Despite potentially causing gas in some individuals, bananas offer numerous health benefits that make them worth including in your diet. They're rich in potassium, vitamin B6, and fiber, which support overall health and digestion.
Positive Effects on Gut Health
- Provide beneficial prebiotics
- Support regular bowel movements
- Help maintain healthy gut bacteria
- Can aid in managing diarrhea
Managing Banana-Related Digestive Issues
If you experience gas after eating bananas, several strategies can help you continue enjoying this nutritious fruit while minimizing digestive discomfort:
- Start with small portions
- Choose riper bananas if you're sensitive to resistant starch
- Eat bananas as part of a balanced meal rather than alone
- Pay attention to your individual tolerance levels
Frequently Asked Questions
Do bananas cause gas and bloating, and why does this happen?
Yes, bananas can cause gas and bloating in some people due to their content of resistant starch and fiber, which are fermented by gut bacteria. This fermentation process can produce gas as a byproduct.
How does the ripeness of a banana affect its likelihood to cause gas?
Unripe bananas are more likely to cause gas because they contain higher levels of resistant starch. As bananas ripen, this starch converts to easier-to-digest sugars, potentially reducing gas production.
Can eating too many bananas lead to digestive problems like flatulence or diarrhea?
Yes, consuming excessive amounts of bananas can lead to increased gas production and, in some cases, diarrhea. This is particularly true if you're not used to eating foods high in fiber and resistant starch.
Are bananas good or bad for gut health and digestion?
Overall, bananas are good for gut health and digestion. While they may cause gas in some people, they provide important prebiotics, fiber, and nutrients that support digestive health and regular bowel movements.
What can people with sensitive digestion or IBS do to reduce gas caused by bananas?
People with sensitive digestion or IBS can choose riper bananas, start with small portions, eat them as part of a balanced meal, and monitor their individual tolerance. Some may find that eating bananas in moderation helps prevent digestive issues.