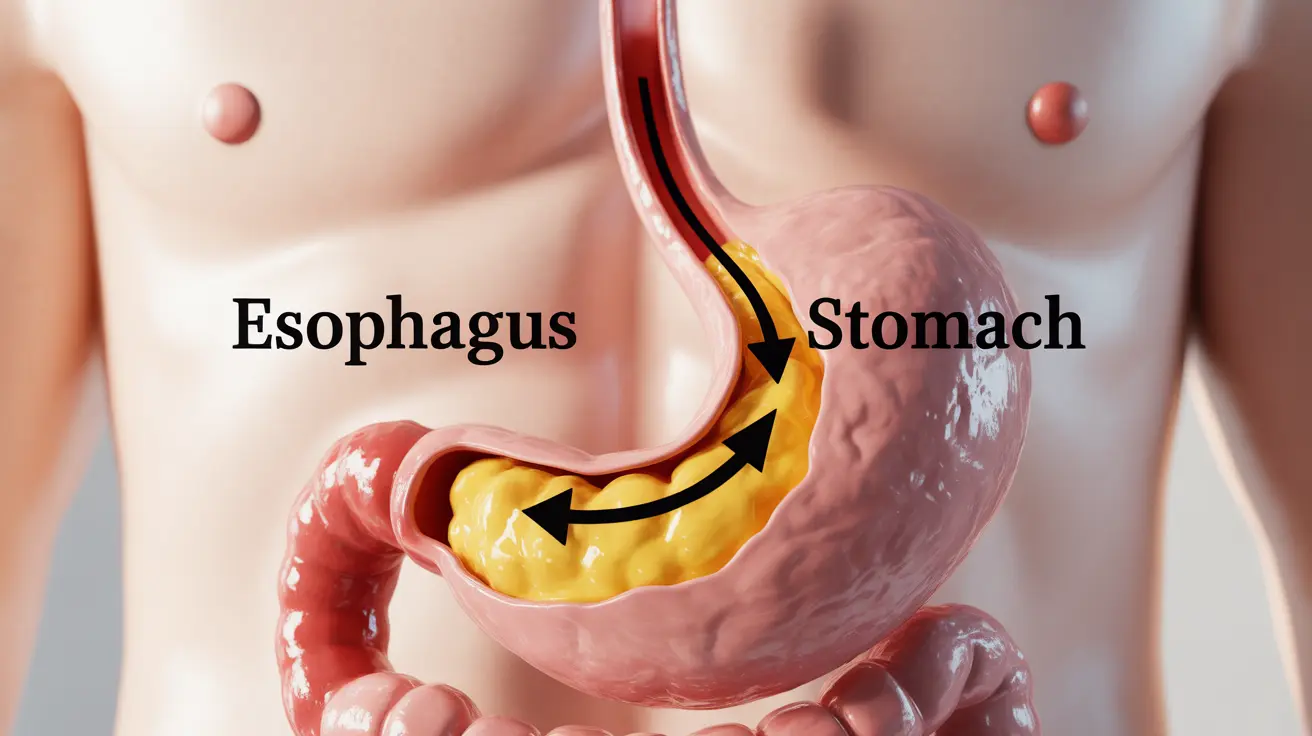
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a chronic digestive condition that affects millions of Americans, causing uncomfortable symptoms like heartburn, chest pain, and regurgitation. Many people wonder whether GERD is a temporary condition that will resolve on its own or if it requires long-term management. Understanding the nature of GERD and available treatment options is crucial for effectively managing this condition.
Understanding GERD as a Chronic Condition
GERD occurs when stomach acid frequently flows back into the esophagus, causing irritation and inflammation of the esophageal lining. While some people may experience occasional acid reflux, GERD represents a more persistent and serious form of this condition that typically requires active management and treatment.
Can GERD Resolve Without Treatment?
While mild cases of acid reflux might improve with simple lifestyle modifications, established GERD typically doesn't go away completely on its own. The condition often requires a combination of lifestyle changes, medication, and ongoing management strategies. However, with proper treatment and commitment to lifestyle modifications, many people can effectively control their symptoms and prevent complications.
Essential Lifestyle Changes for GERD Management
Implementing specific lifestyle modifications can significantly impact GERD symptoms and their frequency:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Eating smaller, more frequent meals
- Avoiding lying down for 2-3 hours after eating
- Elevating the head of the bed
- Wearing loose-fitting clothes
- Quitting smoking
- Limiting alcohol consumption
Medical Treatment Options
Over-the-Counter Medications
Several medications can help manage GERD symptoms:
- Antacids for quick relief
- H2 blockers for reduced acid production
- Over-the-counter proton pump inhibitors (PPIs)
Prescription Medications
For more severe cases, doctors may prescribe stronger versions of these medications, particularly prescription-strength PPIs, which can provide more effective and longer-lasting relief from GERD symptoms.
Surgical Interventions
In cases where lifestyle changes and medications don't provide adequate relief, surgical options may be considered. The most common surgical procedure is the Nissen fundoplication, which strengthens the lower esophageal sphincter to prevent acid reflux. While surgery can provide significant relief, it's typically reserved for severe cases that don't respond well to other treatments.
Dietary Considerations for GERD Management
Certain foods commonly trigger or worsen GERD symptoms. Identifying and avoiding these triggers can help manage the condition:
- Citrus fruits and juices
- Tomato-based products
- Spicy foods
- Fatty or fried foods
- Chocolate
- Mint
- Caffeine
- Carbonated beverages
Frequently Asked Questions
Does GERD go away on its own or is it a lifelong condition?
GERD typically doesn't go away completely on its own. While symptoms may fluctuate, most people require ongoing management through lifestyle modifications and possibly medication. However, with proper treatment, many individuals can effectively control their symptoms.
What lifestyle changes can help manage or reduce GERD symptoms?
Key lifestyle changes include maintaining a healthy weight, eating smaller meals, avoiding trigger foods, not lying down after eating, elevating the head of the bed, and quitting smoking. These modifications can significantly reduce GERD symptoms.
How effective are medications like proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) in treating GERD?
PPIs are highly effective in treating GERD symptoms by reducing stomach acid production. Most people experience significant symptom relief within a few weeks of starting PPI therapy, though the duration of treatment varies by individual.
When is surgery recommended for GERD treatment, and does it cure the condition?
Surgery is typically recommended when lifestyle changes and medications don't provide adequate relief, or when complications develop. While surgery can significantly improve symptoms, it may not completely cure GERD in all cases.
What are common foods and habits that can trigger or worsen GERD symptoms?
Common triggers include spicy foods, citrus, tomato-based products, fatty foods, chocolate, caffeine, and alcohol. Eating large meals, lying down after eating, and wearing tight clothing can also worsen symptoms.