Living with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) can present various challenges, and one concern that often worries patients is the possibility of hair loss. Understanding the relationship between RA and hair loss is crucial for managing this potential side effect and maintaining overall well-being.
If you're experiencing hair loss while managing RA, it's important to know that multiple factors could be at play. Let's explore the connection between RA and hair loss, including both direct and indirect causes, and discuss effective management strategies.
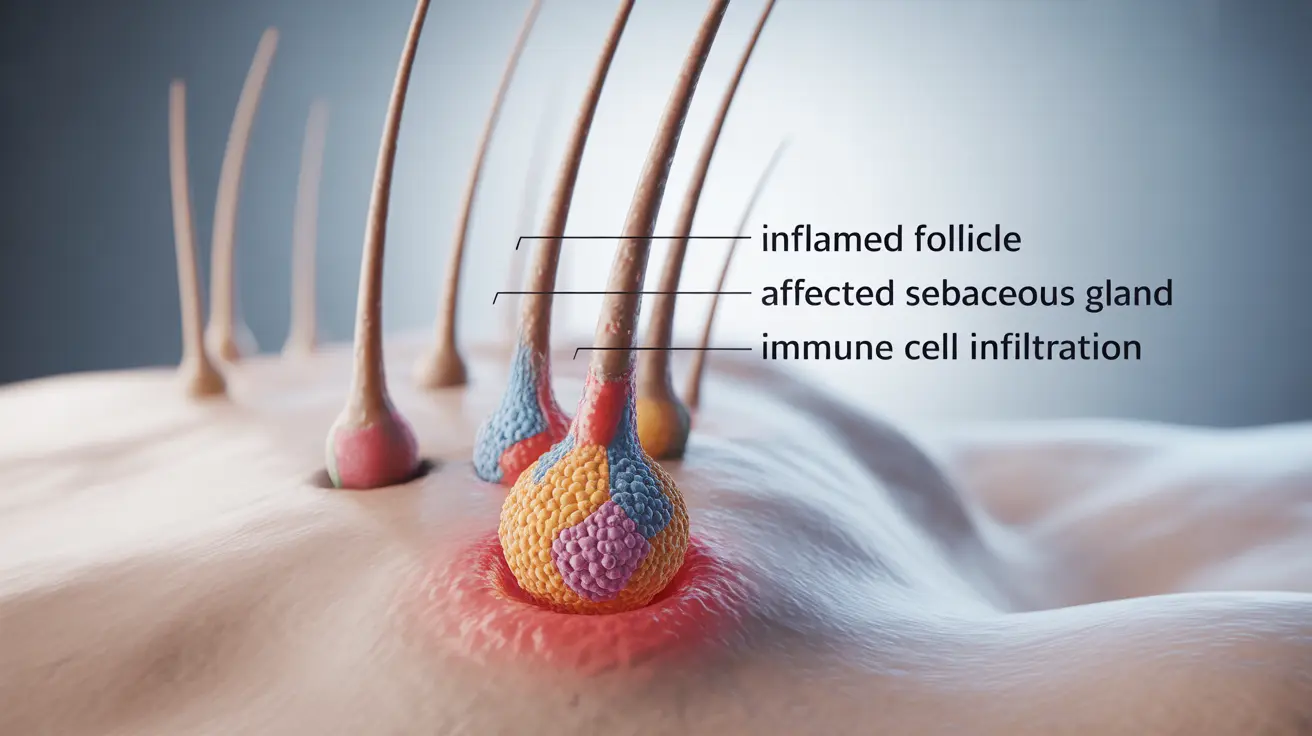
The Direct Impact of Rheumatoid Arthritis on Hair Health
Rheumatoid arthritis itself can potentially contribute to hair loss through several mechanisms:
- Inflammation affecting hair follicles
- Autoimmune responses targeting hair follicles
- Stress on the body due to chronic inflammation
- Changes in scalp blood circulation
However, it's important to note that direct hair loss from RA alone is relatively uncommon. Most cases of hair loss in RA patients are related to other factors, particularly medications used to treat the condition.
Medications and Hair Loss in RA Treatment
Several common RA medications can contribute to hair thinning or loss:
Methotrexate and Hair Loss
Methotrexate, a widely used RA medication, may cause hair loss by interfering with cell division in hair follicles. This effect is usually temporary and dose-dependent.
Biologics and Other DMARDs
Some biologic medications and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) can also affect hair growth. The impact varies among individuals and specific medications.
Managing Hair Loss During RA Treatment
There are several strategies to help minimize and manage hair loss while treating RA:
- Proper nutrition and supplementation
- Gentle hair care practices
- Regular consultation with your rheumatologist
- Stress management techniques
- Use of mild, sulfate-free hair products
Associated Autoimmune Conditions
Some autoimmune conditions that commonly occur alongside RA can also contribute to hair loss:
- Lupus
- Thyroid disorders
- Alopecia areata
Prevention and Treatment Options
Working with your healthcare team, you can explore various options to address hair loss:
- Medication adjustments when possible
- Nutritional support
- Topical treatments
- Protective styling methods
- Alternative treatment protocols
Frequently Asked Questions
Does rheumatoid arthritis itself cause hair loss or is it mainly due to medications?
While RA itself can potentially cause some hair loss due to inflammation and autoimmune responses, the majority of hair loss cases in RA patients are related to medications used for treatment, particularly drugs like methotrexate and other DMARDs.
Which rheumatoid arthritis medications are most likely to cause hair thinning?
Methotrexate is the most commonly associated medication with hair loss in RA treatment. Other medications that may cause hair thinning include certain biologics, leflunomide, and some anti-inflammatory drugs.
How can I manage or reduce hair loss if it is related to my RA treatment?
You can manage treatment-related hair loss through proper nutrition, gentle hair care practices, stress management, and working with your doctor to adjust medications if necessary. Taking supplements like biotin and using mild hair products can also help.
Can hair loss from rheumatoid arthritis reverse after stopping or changing medication?
Yes, in most cases, hair loss related to RA medications is reversible. Hair growth typically resumes within a few months after stopping or changing the medication, though the timeline can vary among individuals.
Are there other autoimmune conditions linked to RA that can also cause hair loss?
Yes, several autoimmune conditions that often co-occur with RA can cause hair loss, including lupus, thyroid disorders, and alopecia areata. Managing these conditions alongside RA may help improve hair health.