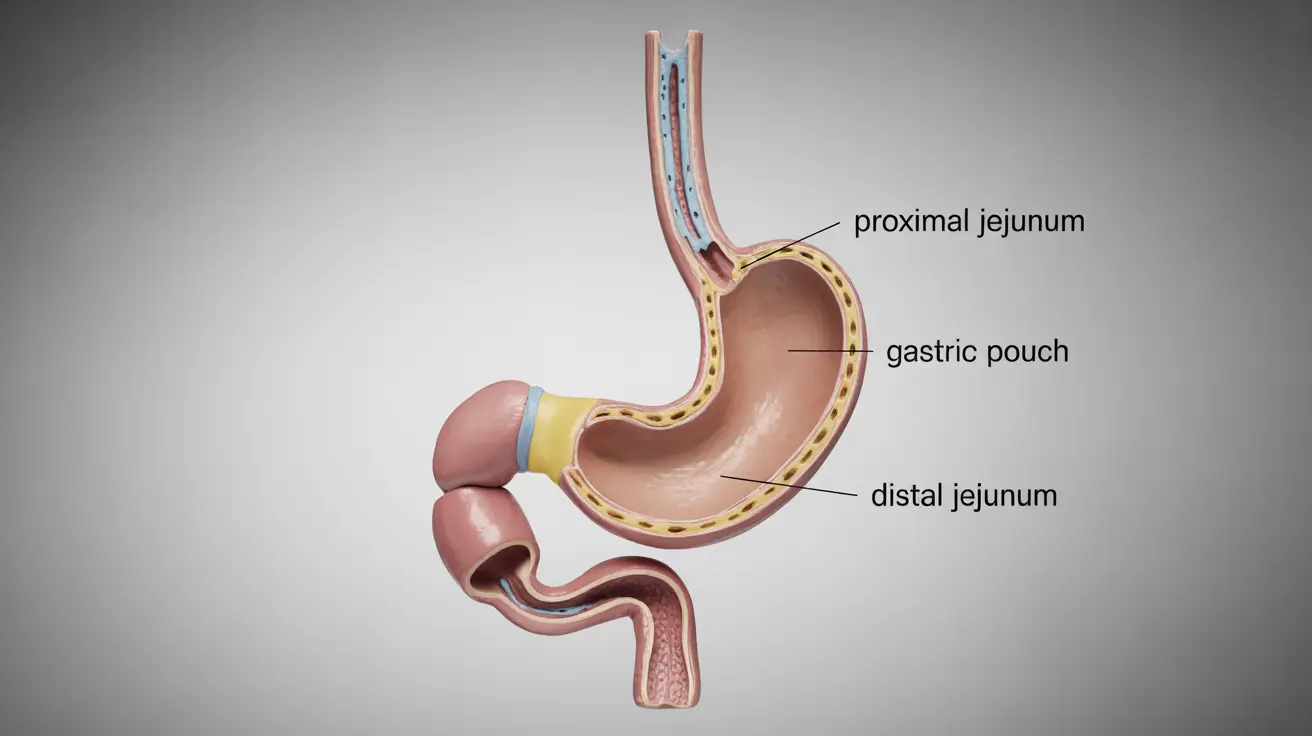
Dual switch surgery, also known as biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch (BPD/DS), is an advanced bariatric surgery procedure that helps individuals with severe obesity achieve significant and sustainable weight loss. This complex but effective procedure combines restrictive and malabsorptive elements to help patients reach their weight loss goals while improving obesity-related health conditions.
As one of the most technically sophisticated weight loss surgeries available today, dual switch surgery has demonstrated impressive long-term results for appropriate candidates. Understanding how this procedure works, its benefits, and potential considerations is crucial for anyone considering this weight loss option.
How Dual Switch Surgery Works
The dual switch procedure involves two main surgical components that work together to promote weight loss:
- Creation of a smaller, tubular stomach (sleeve gastrectomy)
- Intestinal bypass that changes how food travels through the digestive system
During the procedure, surgeons remove approximately 80% of the stomach, creating a smaller stomach pouch that restricts food intake. They then reroute the small intestine, creating two pathways - one for food and another for digestive juices - that eventually "switch" or reconnect near the end of the small intestine.
Benefits and Weight Loss Outcomes
Dual switch surgery offers several significant advantages for patients struggling with severe obesity:
- Substantial and sustained weight loss (typically 60-80% of excess body weight)
- Improved resolution of obesity-related health conditions
- Better long-term weight maintenance compared to some other procedures
- Allows patients to eat relatively normal-sized meals over time
Potential Risks and Complications
As with any major surgery, dual switch surgery carries certain risks that patients should carefully consider:
- Immediate surgical risks (bleeding, infection, blood clots)
- Nutritional deficiencies requiring lifelong supplementation
- Possible dumping syndrome
- Risk of internal hernias
- Potential for vitamin and mineral malabsorption
Recovery and Long-term Care
Recovery from dual switch surgery requires dedication and careful attention to post-operative guidelines:
- Initial hospital stay of 2-4 days
- Gradual diet progression over several weeks
- Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare team
- Lifetime commitment to vitamin and mineral supplementation
- Regular blood work to monitor nutritional status
Determining Candidacy for Surgery
Not everyone is an appropriate candidate for dual switch surgery. Key eligibility factors include:
- BMI of 40 or higher, or 35+ with obesity-related health conditions
- History of failed weight loss attempts through conventional methods
- Commitment to lifestyle changes and long-term follow-up care
- Good understanding of the procedure and its requirements
- Absence of certain medical conditions that could increase surgical risk
Frequently Asked Questions
What is dual switch surgery and how does it help with severe obesity?
Dual switch surgery is a complex bariatric procedure that combines stomach reduction with intestinal rerouting. It helps with severe obesity by both restricting food intake and reducing calorie absorption, leading to significant weight loss.
How does duodenal switch surgery compare to other bariatric procedures in terms of weight loss and health benefits?
Dual switch surgery typically results in greater weight loss compared to other bariatric procedures, with patients losing 60-80% of excess weight. It also shows superior results in resolving obesity-related health conditions, though it requires more intensive long-term care.
What are the common risks and nutritional complications after dual switch surgery?
Common risks include surgical complications, nutritional deficiencies, dumping syndrome, and potential vitamin malabsorption. Patients must commit to lifelong vitamin supplementation and regular monitoring to prevent these complications.
What does recovery and long-term care look like following duodenal switch surgery?
Recovery involves a hospital stay, careful diet progression, and regular follow-up care. Long-term success requires consistent vitamin supplementation, regular medical check-ups, and commitment to lifestyle changes.
Who is a good candidate for duodenal switch surgery and what factors determine eligibility?
Good candidates typically have a BMI of 40+ (or 35+ with obesity-related conditions), demonstrate commitment to lifestyle changes, have tried other weight loss methods, and understand the long-term requirements of the procedure.