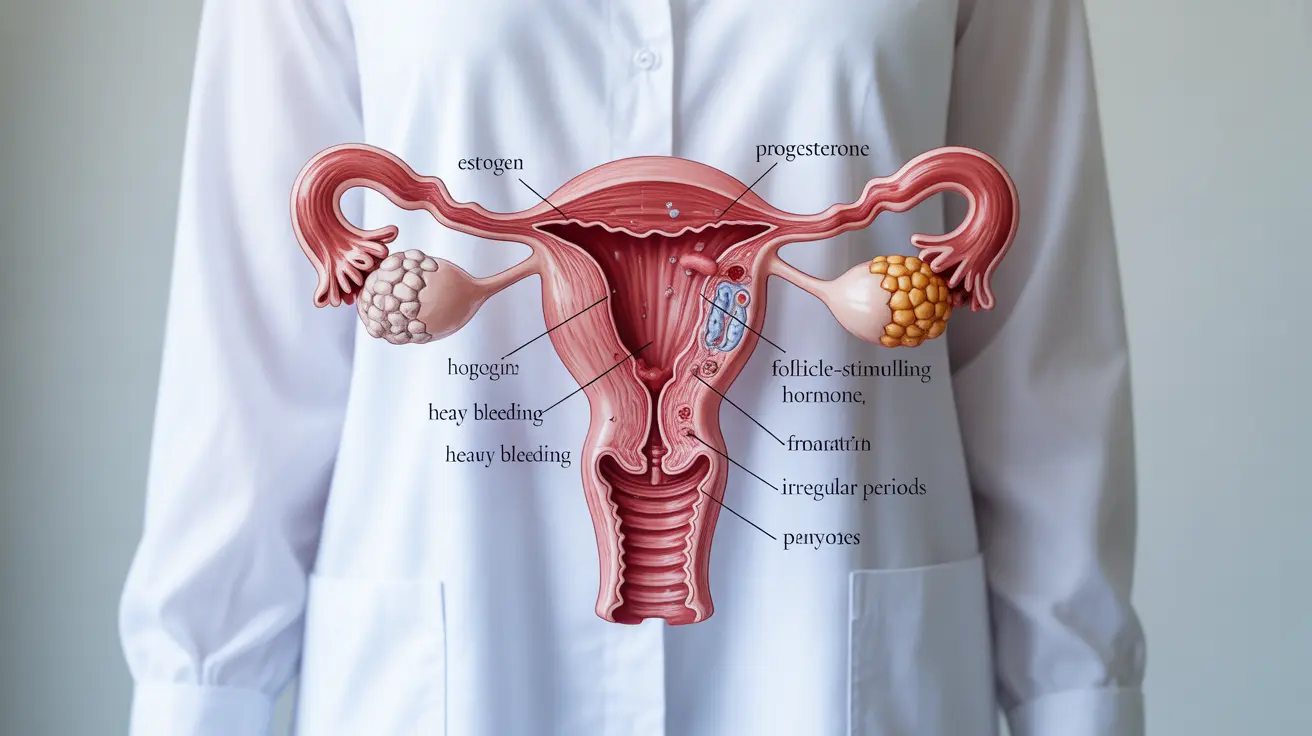
Abnormal uterine bleeding, also known as dysfunctional uterine bleeding (DUB), is a common gynecological condition that affects many women during their reproductive years. This condition occurs when the uterus bleeds outside of regular menstrual periods or when menstrual flow becomes unusually heavy or prolonged. Understanding this condition is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
While occasional changes in menstrual patterns are normal, persistent abnormal bleeding can significantly impact quality of life and may indicate underlying health issues that require medical attention. This comprehensive guide will explore the causes, symptoms, and various treatment options available for managing dysfunctional uterine bleeding.
Understanding the Condition
Dysfunctional uterine bleeding typically occurs when there's an imbalance in hormones that regulate the menstrual cycle, particularly estrogen and progesterone. This hormonal disruption can lead to irregular bleeding patterns and various associated symptoms that can affect daily activities.
Common Symptoms and Warning Signs
Recognizing the symptoms of dysfunctional uterine bleeding is crucial for early intervention. Key indicators include:
- Bleeding between menstrual periods
- Heavy menstrual flow requiring frequent pad or tampon changes
- Periods lasting longer than seven days
- Irregular menstrual cycles
- Passing blood clots larger than one inch
- Severe menstrual cramping
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can contribute to the development of dysfunctional uterine bleeding:
Hormonal Causes
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Thyroid disorders
- Hormonal imbalances
- Perimenopause
Structural Causes
- Uterine fibroids
- Polyps
- Adenomyosis
- Endometrial hyperplasia
Diagnosis Process
Healthcare providers typically use a combination of methods to diagnose dysfunctional uterine bleeding:
- Physical examination
- Medical history review
- Blood tests
- Ultrasound imaging
- Endometrial biopsy (when necessary)
Treatment Approaches
Non-Surgical Options
Several non-surgical treatments can effectively manage dysfunctional uterine bleeding:
- Hormonal birth control pills
- Progesterone therapy
- Intrauterine devices (IUDs)
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
Lifestyle Modifications
Certain lifestyle changes can help manage symptoms:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Regular exercise
- Stress management
- Balanced nutrition
- Adequate iron intake to prevent anemia
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main causes of dysfunctional uterine bleeding, and how is it diagnosed?
Dysfunctional uterine bleeding is primarily caused by hormonal imbalances, particularly involving estrogen and progesterone. Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, blood tests, ultrasound imaging, and sometimes an endometrial biopsy to rule out other conditions.
How can abnormal uterine bleeding be treated, and what are the non-surgical options?
Non-surgical treatment options include hormonal medications like birth control pills, progesterone therapy, hormonal IUDs, and anti-inflammatory medications. These treatments aim to regulate hormone levels and reduce bleeding.
Can changes in diet or lifestyle help manage symptoms of abnormal uterine bleeding?
Yes, lifestyle modifications can help manage symptoms. These include maintaining a healthy weight, regular exercise, stress reduction techniques, and ensuring adequate iron intake through diet or supplements to prevent anemia.
What are the common symptoms of dysfunctional uterine bleeding, and when should I seek medical attention?
Common symptoms include irregular bleeding, heavy periods lasting more than seven days, passing large blood clots, and bleeding between periods. Seek medical attention if you experience severe bleeding, significant pain, or if bleeding patterns change suddenly.
How does hormonal therapy, such as birth control pills, help regulate abnormal uterine bleeding?
Hormonal therapy works by stabilizing hormone levels and regulating the menstrual cycle. Birth control pills provide synthetic versions of estrogen and progesterone, which help control the growth of the uterine lining and establish regular bleeding patterns.