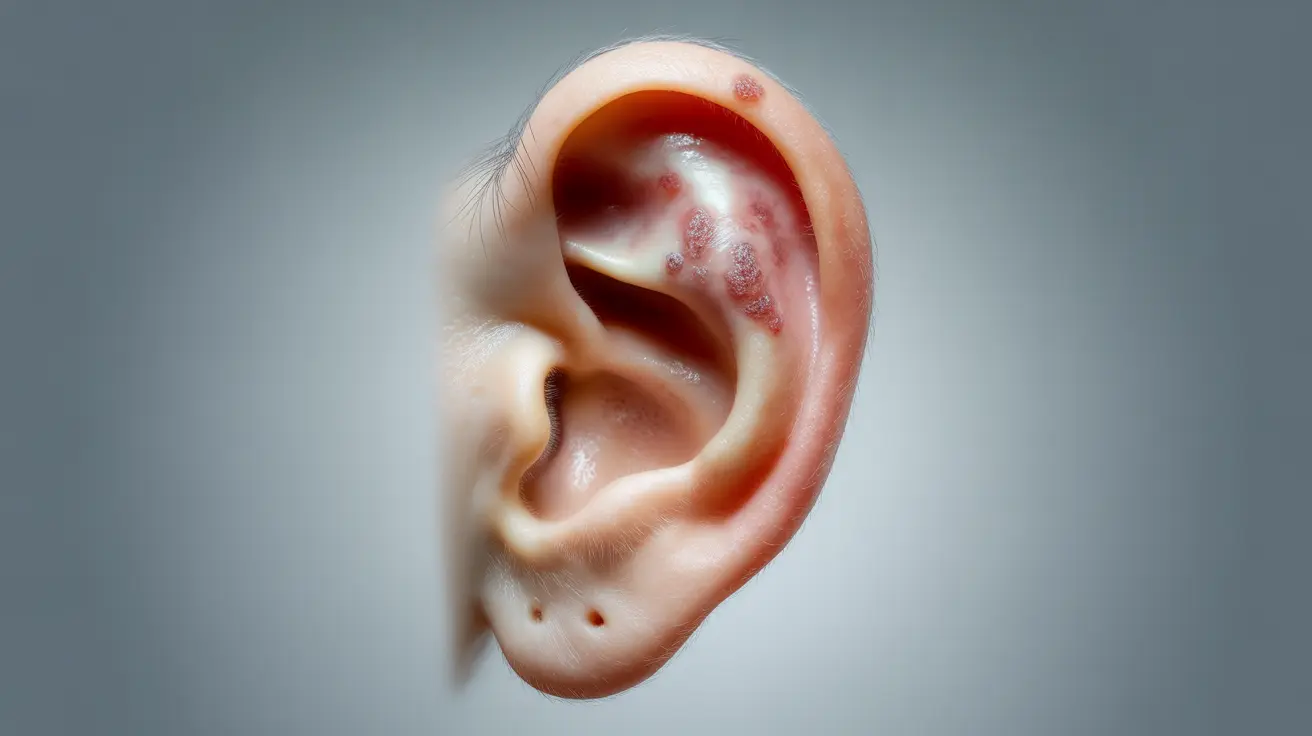
Understanding the visual signs and symptoms of ear cancer is crucial for early detection and successful treatment. This comprehensive guide will help you recognize potential warning signs, understand the progression of ear cancer, and learn about essential prevention strategies. While ear cancer is relatively rare, being informed about its appearance and symptoms can lead to earlier diagnosis and better outcomes.
Recognizing Early Signs of Ear Cancer
Ear cancer often begins as subtle changes to the skin of the outer ear or ear canal. Early visual indicators may include:
- Scaly patches or unusual skin texture
- Small, firm nodules or lumps
- Changes in skin color or pigmentation
- Persistent sores that don't heal
- Irregular growths or lesions
These changes typically appear gradually and may be easily overlooked, making regular self-examination and professional check-ups important for early detection.
Distinguishing Cancer from Common Ear Problems
It's important to understand how ear cancer symptoms differ from typical ear conditions. While both may cause discomfort, certain characteristics are more concerning:
Common Ear Infection Signs
- Temporary pain and inflammation
- Clear drainage or discharge
- Fever and general illness
- Symptoms that respond to antibiotics
Potential Cancer Warning Signs
- Persistent ulceration
- Bleeding that doesn't stop
- Progressive hearing loss
- Chronic pain without infection
- Non-healing wounds
Understanding Ear Cancer Development
Ear cancer typically develops through several stages, often beginning as skin cancer on the outer ear. The main contributing factors include:
- Prolonged sun exposure
- Chronic ear infections
- Previous radiation exposure
- Genetic predisposition
Progression Patterns
The cancer may start in different parts of the ear structure:
- Outer ear (most common)
- External ear canal
- Middle ear
- Inner ear (rare)
Treatment Approaches for Different Stages
Early-Stage Treatment
Early detection often allows for less invasive treatment options:
- Surgical removal of affected tissue
- Targeted radiation therapy
- Local chemotherapy applications
Advanced Stage Management
More extensive treatment may be necessary for progressed cases:
- Comprehensive surgery
- Combined radiation and chemotherapy
- Reconstructive procedures
- Hearing rehabilitation
Prevention and Protection Strategies
Taking proactive steps to protect your ears can significantly reduce cancer risk:
- Regular use of broad-spectrum sunscreen
- Wearing protective hats with ear coverage
- Avoiding prolonged sun exposure
- Regular skin checks and professional examinations
- Prompt treatment of chronic ear conditions
Frequently Asked Questions
What do early signs of ear cancer look like in pictures?
Early signs of ear cancer typically appear as scaly patches, unusual growths, or changes in skin color on the outer ear. These may present as small, firm nodules, persistent sores that don't heal, or irregular lesions that gradually change in size or appearance.
How can I tell the difference between ear cancer symptoms and common ear infections?
Ear cancer symptoms tend to be persistent and progressive, unlike ear infections which usually improve with treatment. Cancer-related symptoms often include non-healing sores, unexplained bleeding, and progressive hearing loss, while infections typically cause temporary pain, fever, and respond to antibiotics.
What causes skin cancer on the ear and how does it progress to ear cancer?
Skin cancer on the ear is primarily caused by cumulative sun exposure, with additional risk factors including chronic infections and genetic predisposition. It typically begins as surface-level changes and can progress deeper into ear structures if left untreated.
What treatment options are available for different stages of ear cancer?
Treatment options range from minimally invasive procedures for early-stage cancer to comprehensive approaches for advanced cases. These include surgical removal, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and reconstructive surgery, with the specific treatment plan depending on the cancer's stage and location.
How can I protect my ears from the risk factors that lead to ear cancer?
Protection strategies include consistent use of sunscreen on exposed ear areas, wearing protective headwear, avoiding prolonged sun exposure, maintaining good ear hygiene, and getting regular medical check-ups. Early intervention for persistent ear problems is also crucial for prevention.