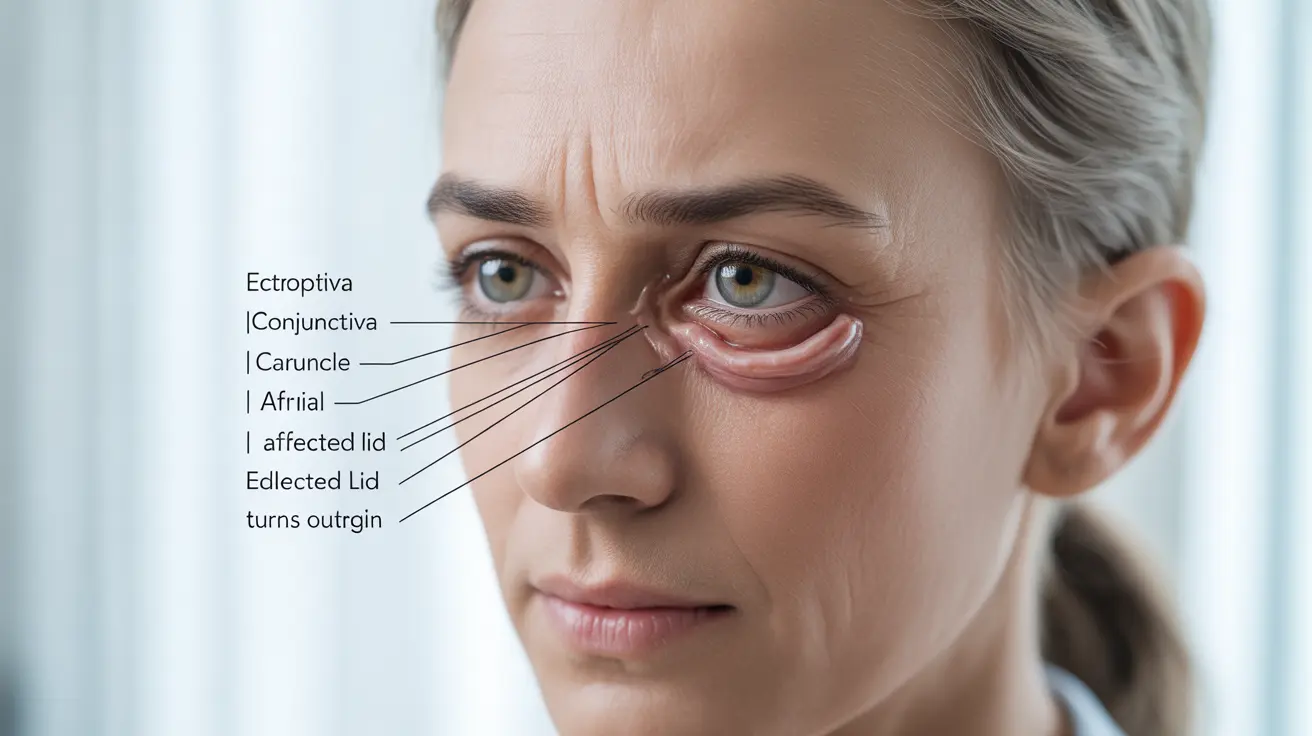
Ectropion is a medical condition affecting the eyelids where the lower eyelid turns outward or sags away from the eye. This condition can cause significant discomfort and potentially lead to eye-related complications if left untreated. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and available treatments is crucial for maintaining eye health and preventing further complications.
While ectropion can affect anyone, it's most commonly seen in older adults due to natural aging processes that affect eyelid tissue elasticity. Early recognition and proper medical intervention can help manage symptoms and prevent potential complications.
Understanding the Symptoms of Ectropion
Ectropion can cause various uncomfortable and noticeable symptoms that affect daily life and eye comfort. Common signs include:
- Chronic eye irritation and redness
- Excessive tearing (watery eyes)
- Burning sensation in the eyes
- Increased sensitivity to light and wind
- Eye dryness, particularly in the morning
- Chronic eye inflammation
These symptoms occur because the outward-turning eyelid prevents tears from properly lubricating the eye surface and interferes with normal drainage through the tear ducts.
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can contribute to the development of ectropion:
Age-Related Changes
The most common cause is age-related weakening of the muscles and tendons that hold the eyelid in its normal position. As we age, tissue elasticity naturally decreases, potentially leading to eyelid sagging.
Medical Conditions
Certain conditions can increase the risk of developing ectropion:
- Facial paralysis (Bell's palsy)
- Previous eye surgeries
- Skin conditions affecting the eyelids
- Trauma or injury to the face
- Congenital conditions (present from birth)
Diagnosis Process
An eye care specialist typically diagnoses ectropion through a comprehensive eye examination. This includes:
- Visual inspection of the eyelid position
- Assessment of tear production and drainage
- Evaluation of corneal health
- Testing for any underlying conditions
Treatment Approaches
Treatment options for ectropion vary depending on severity and underlying causes:
Conservative Management
For mild cases, conservative treatments may include:
- Artificial tears and lubricating ointments
- Regular eye cleaning and moisture maintenance
- Protection from wind and environmental irritants
Surgical Options
When conservative treatments aren't sufficient, surgical intervention may be necessary. Common procedures include:
- Horizontal lid tightening
- Canthal tendon repair
- Tissue grafting in some cases
Preventing Complications
Proper management and prevention strategies are essential to avoid serious complications:
- Regular eye examinations
- Prompt treatment of eye infections
- Protection from environmental factors
- Maintaining good eye hygiene
- Following medical advice consistently
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of ectropion and how does it affect the eyes? Ectropion causes the lower eyelid to turn outward, leading to chronic eye irritation, excessive tearing, burning sensations, and increased sensitivity to light and wind. The condition affects eye lubrication and tear drainage, potentially causing chronic discomfort.
What causes ectropion and which factors increase the risk of developing it? The primary causes include age-related tissue weakening, facial paralysis, previous eye surgeries, skin conditions, and facial trauma. Older adults are at higher risk due to natural aging processes affecting eyelid tissue elasticity.
How is ectropion diagnosed by an eye specialist? Eye specialists diagnose ectropion through a comprehensive eye examination, including visual inspection of the eyelid position, assessment of tear production and drainage, and evaluation of corneal health.
What treatment options are available for ectropion, and when is surgery necessary? Treatment options range from conservative approaches like artificial tears and lubricating ointments to surgical procedures. Surgery becomes necessary when conservative treatments fail to provide relief or when the condition is severe enough to risk complications.
How can ectropion be managed or prevented to avoid complications such as eye infections or vision loss? Management includes regular use of prescribed eye lubricants, protecting eyes from environmental irritants, maintaining good eye hygiene, and attending regular eye check-ups. Early intervention and consistent treatment adherence are crucial for preventing complications.