Egg donation is a profound way to help individuals and couples achieve their dreams of starting a family. As more women consider becoming egg donors, understanding the process, requirements, and experiences of past donors becomes increasingly important. This comprehensive guide explores what potential donors need to know, from initial screening to recovery.
Understanding the Egg Donation Process
The egg donation journey involves multiple steps, careful medical screening, and a significant time commitment. Most clinics follow strict protocols to ensure both donor and recipient safety while maximizing the chances of successful outcomes.
Initial Screening and Requirements
Becoming an egg donor requires meeting specific criteria established by fertility clinics and donor agencies:
- Age between 21-32 years
- Healthy BMI range
- No smoking or drug use
- No family history of genetic disorders
- Regular menstrual cycles
- Willingness to commit to the entire process
Medical Evaluation and Preparation
Once accepted into a donation program, donors undergo comprehensive medical screening including:
- Physical examination
- Genetic testing
- Psychological evaluation
- Infectious disease screening
- Ultrasound and blood work
The Donation Timeline
The entire egg donation process typically spans 3-4 months from initial application to egg retrieval. This includes screening, synchronization with the recipient's cycle, and the stimulation phase.
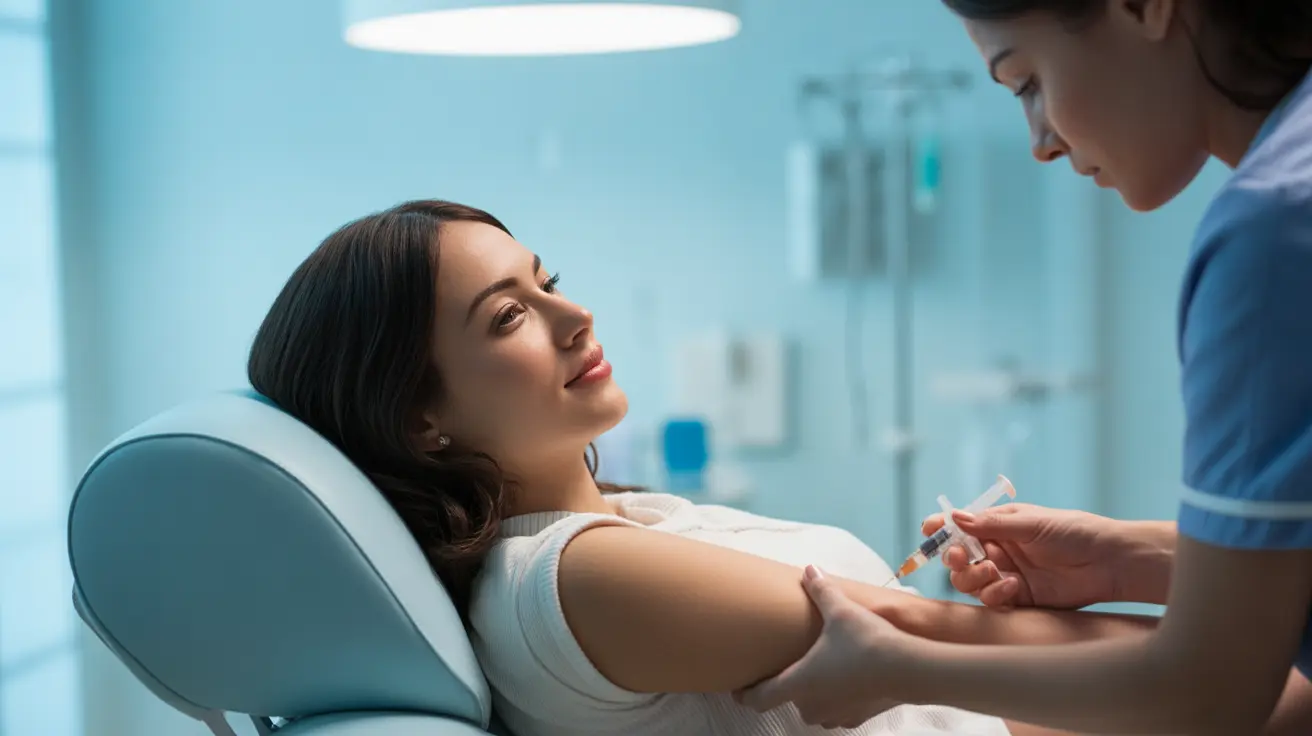
Medication and Monitoring
During the stimulation phase, donors receive hormone injections to promote egg development. Regular monitoring through blood tests and ultrasounds ensures proper response to medication and optimal timing for retrieval.
Recovery and Aftercare
Following egg retrieval, donors typically need 1-2 days of rest. Most women return to normal activities within a week, though they should avoid strenuous exercise for about two weeks post-procedure.
Compensation and Support
Egg donors receive compensation for their time, commitment, and the medical procedures involved. Many clinics also provide comprehensive support throughout the process, including access to medical professionals and counselors.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the typical motivations for women to become egg donors, and how do they help families?
Women often choose to become egg donors to help others build families while receiving compensation for their time and effort. They assist individuals and couples who cannot conceive using their own eggs, including same-sex couples, single parents, and those with fertility challenges.
What are the common medical risks and side effects associated with egg donation?
Common side effects include bloating, mood changes, and discomfort from hormone injections. More serious but rare risks include ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS), infection, or bleeding. All procedures are closely monitored to minimize these risks.
How long does the entire egg donation process take, from initial screening to retrieval?
The complete process typically takes 3-4 months, including initial screening (2-3 weeks), synchronization with the recipient's cycle (2-3 weeks), and the stimulation and retrieval phase (2-3 weeks).
Is it safe to donate eggs multiple times, and what are the potential long-term effects?
Most clinics allow women to donate up to six times, with minimum three-month intervals between donations. While short-term effects are well-documented, long-term studies are limited. Regular monitoring helps ensure donor safety throughout repeated donations.
What are the basic requirements and qualifications necessary to become an egg donor?
Basic requirements typically include being between 21-32 years old, having a healthy BMI, being a non-smoker, having no significant genetic disorders in family history, and being willing to commit to the entire process. Educational background and physical characteristics may also be considered.