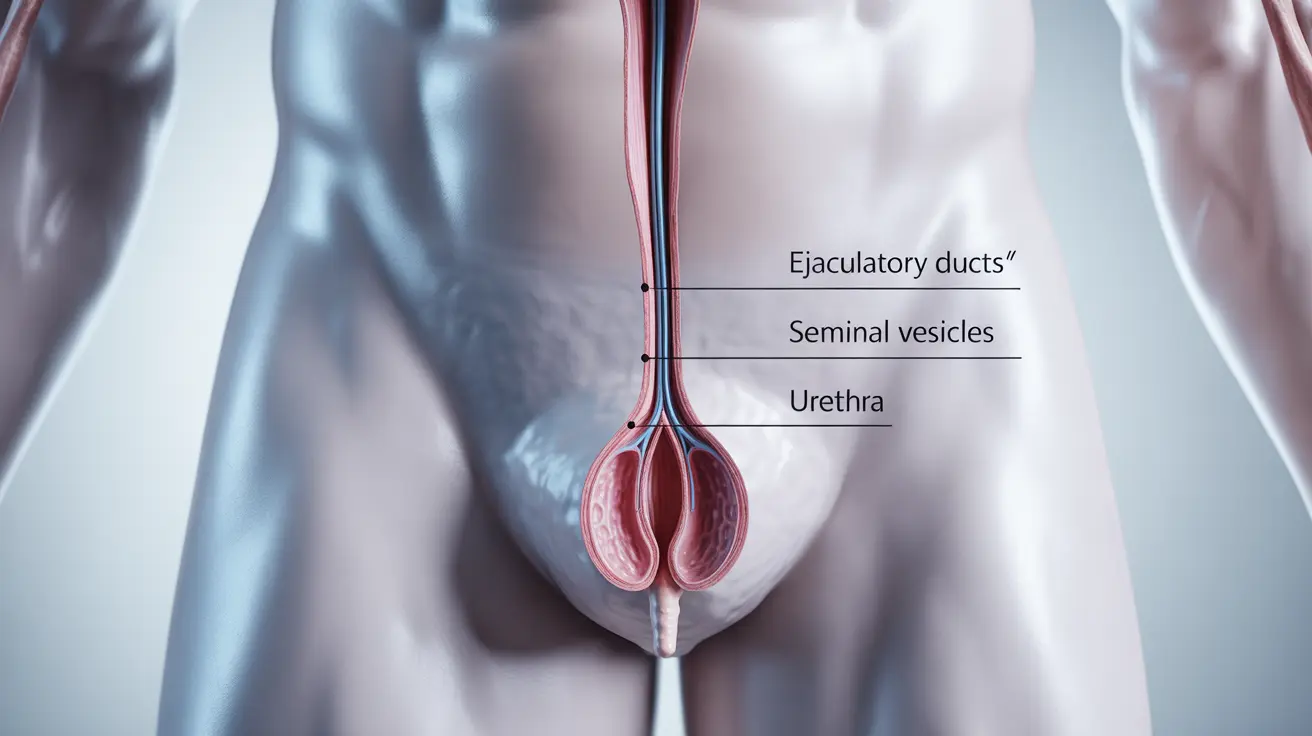
The ejaculatory ducts play a crucial role in male reproductive health and fertility. These important anatomical structures serve as the final pathway for sperm transport during ejaculation. Understanding how these ducts function, and what happens when problems arise, is essential for addressing male reproductive health concerns.
When issues affect the ejaculatory ducts, they can significantly impact fertility and sexual function. This comprehensive guide explores the various conditions that can affect these vital structures, their symptoms, and available treatment options.
The Role of Ejaculatory Ducts in Male Reproduction
Ejaculatory ducts are paired tubes that connect the seminal vesicles and vas deferens to the urethra through the prostate gland. These ducts are essential for:
- Transporting sperm from the testes
- Carrying seminal fluid from the seminal vesicles
- Ensuring proper ejaculation during sexual activity
- Contributing to male fertility
Common Ejaculatory Duct Conditions
Ejaculatory Duct Obstruction (EDO)
Ejaculatory duct obstruction is a condition where the ducts become blocked, preventing the normal flow of reproductive fluids. This condition can be:
- Congenital (present from birth)
- Acquired through infection or injury
- Partial or complete
- Unilateral (affecting one side) or bilateral (affecting both sides)
Signs and Symptoms
Common indicators of ejaculatory duct problems include:
- Decreased ejaculate volume
- Pain during ejaculation
- Infertility
- Recurring urinary tract infections
- Discomfort in the pelvic area
Diagnostic Approaches
Healthcare providers may use several methods to diagnose ejaculatory duct disorders:
- Transrectal ultrasound
- Semen analysis
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Physical examination
- Medical history review
Treatment Options
Conservative Management
Initial treatment approaches may include:
- Antibiotics for infection-related cases
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Physical therapy
- Lifestyle modifications
Surgical Interventions
When conservative treatments aren't effective, surgical options include:
- Transurethral resection of the ejaculatory ducts (TURED)
- Balloon dilation
- Direct cannulation
- Microsurgical reconstruction
Impact on Male Fertility
Ejaculatory duct disorders can significantly affect fertility through:
- Reduced sperm count in ejaculate
- Compromised sperm quality
- Incomplete emptying of the reproductive tract
- Altered composition of seminal fluid
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of ejaculatory duct obstruction and how does it affect fertility?
Common symptoms include reduced ejaculate volume, pain during ejaculation, and infertility. The condition affects fertility by preventing sperm from reaching the urethra during ejaculation, potentially leading to male infertility.How is ejaculatory duct obstruction diagnosed and what treatment options are available?
Diagnosis typically involves transrectal ultrasound, semen analysis, and sometimes MRI imaging. Treatment options range from conservative approaches like antibiotics and anti-inflammatories to surgical procedures such as TURED.What causes ejaculatory duct obstruction and can it be congenital or acquired?
Ejaculatory duct obstruction can be either congenital (present at birth) or acquired through infections, inflammation, trauma, or previous surgical procedures. Some cases may be related to cysts or calcifications in the prostate.How can benign prostatic hyperplasia impact the ejaculatory ducts and ejaculation?
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) can compress or obstruct the ejaculatory ducts as the prostate enlarges, potentially affecting ejaculation volume and causing discomfort during sexual activity.What is the role of the ejaculatory ducts in the male reproductive system and ejaculation process?
The ejaculatory ducts serve as crucial passageways for sperm and seminal fluid, connecting the seminal vesicles and vas deferens to the urethra. They are essential for normal ejaculation and fertility, allowing reproductive fluids to properly exit the body during climax.