Enteral feeding, also known as tube feeding, is a vital medical intervention that provides nutrition directly to the digestive system when a person cannot eat normally. This essential nutritional support method helps maintain proper nourishment in patients who have difficulty swallowing, eating, or maintaining adequate nutrition through regular food intake.
For many patients and their caregivers, understanding enteral feeding is crucial for ensuring proper nutrition and preventing complications. This comprehensive guide will explore the various aspects of enteral feeding, including different types of feeding tubes, administration methods, and important safety considerations.
Types of Enteral Feeding Tubes
Several types of feeding tubes are available, each designed for specific patient needs and duration of use:
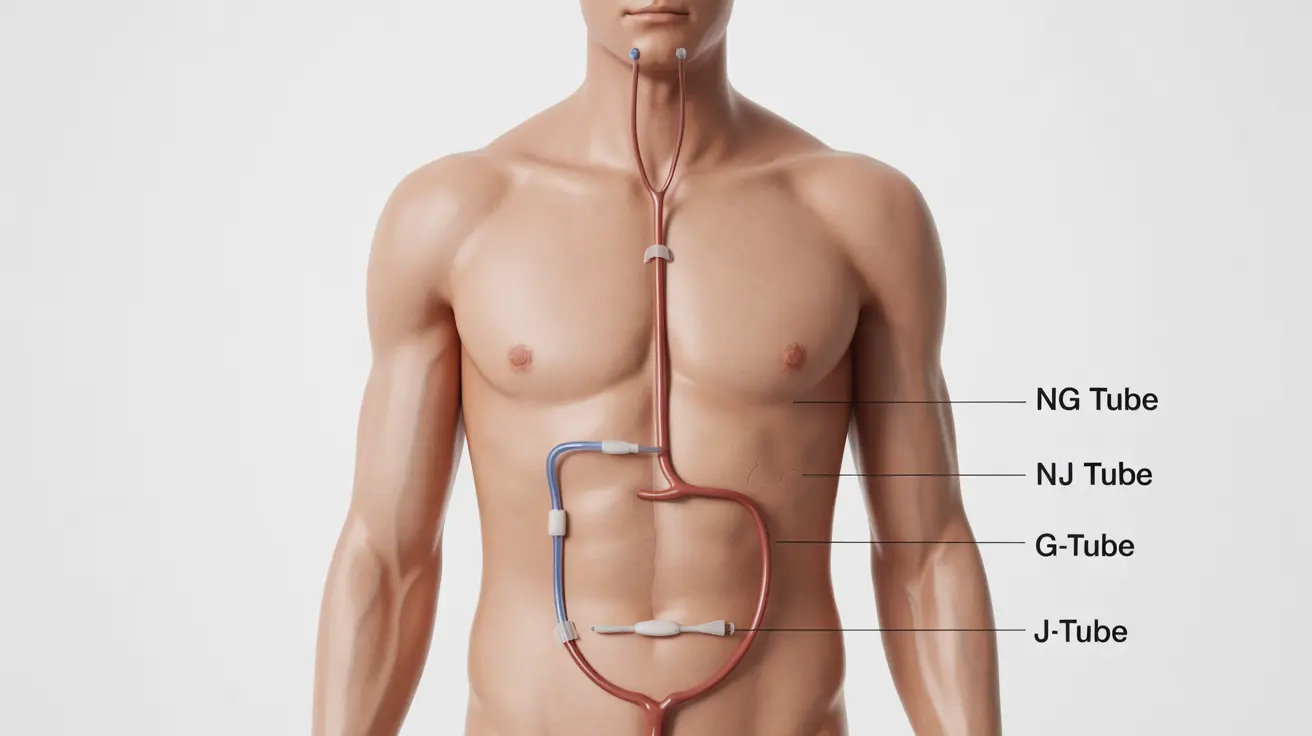
Nasogastric (NG) Tubes
These tubes are inserted through the nose and down into the stomach. They are typically used for short-term feeding support and are the most common type of feeding tube. NG tubes are often recommended for temporary nutritional support lasting a few days to several weeks.
Nasojejunal (NJ) Tubes
Similar to NG tubes, these are inserted through the nose but extend further into the small intestine (jejunum). They're particularly useful for patients who cannot tolerate gastric feeding or are at risk of aspiration.
Gastrostomy Tubes (G-tubes)
These tubes are surgically placed directly through the abdominal wall into the stomach. They're suitable for long-term feeding support and are more discrete than nasal tubes. Common types include percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) tubes.
Jejunostomy Tubes (J-tubes)
These tubes are surgically placed directly into the jejunum and are typically used when feeding into the stomach isn't possible or safe.
Administration Methods
Enteral feeding can be administered through several methods, depending on the patient's needs and medical condition:
Continuous Feeding
This method involves delivering nutrition at a steady rate over several hours or throughout the day using a feeding pump. It's often preferred for patients who need consistent nutrition or have absorption issues.
Bolus Feeding
This method delivers larger amounts of formula at scheduled times, similar to regular meals. It's typically used with gastric tubes and can offer more flexibility in daily activities.
Intermittent Feeding
A combination approach that provides nutrition at regular intervals but for longer periods than bolus feeding, typically lasting 20-60 minutes per feeding.
Managing Complications and Safety
While enteral feeding is generally safe, awareness of potential complications is essential:
- Tube displacement or blockage
- Infection at the insertion site
- Gastrointestinal issues (nausea, diarrhea, or constipation)
- Aspiration risk
- Skin irritation around stoma sites
Regular monitoring and proper care can help prevent these complications and ensure successful feeding outcomes.
Home Care Guidelines
Successful home management of enteral feeding requires careful attention to several key areas:
- Proper hand hygiene and infection control
- Regular cleaning and maintenance of feeding equipment
- Correct positioning during and after feeds
- proper storage and handling of formula
- Regular monitoring of insertion sites
- Maintaining accurate feeding schedules
Frequently Asked Questions
What is enteral feeding and when is it needed? Enteral feeding is a method of providing nutrition through a tube directly into the digestive system. It's needed when patients cannot eat normally due to conditions affecting swallowing, consciousness, or their ability to maintain adequate nutrition through regular food intake.
What types of feeding tubes are used for enteral nutrition? The main types include nasogastric (NG) tubes, nasojejunal (NJ) tubes, gastrostomy tubes (G-tubes), and jejunostomy tubes (J-tubes). The choice depends on factors like expected duration of use and patient condition.
How is enteral feeding administered and what are the common methods? Enteral feeding can be administered through continuous feeding (steady rate over hours), bolus feeding (larger amounts at scheduled times), or intermittent feeding (regular intervals but longer than bolus). The method chosen depends on patient needs and tolerance.
What are the potential complications to watch for with enteral feeding? Key complications include tube displacement or blockage, infection, gastrointestinal issues, aspiration risk, and skin irritation around insertion sites. Regular monitoring and proper care are essential for prevention.
How can enteral feeding be managed safely at home? Safe home management involves maintaining strict hygiene, proper equipment care, correct positioning during feeds, appropriate formula handling, regular site monitoring, and adherence to feeding schedules. Training from healthcare providers is essential for successful home care.