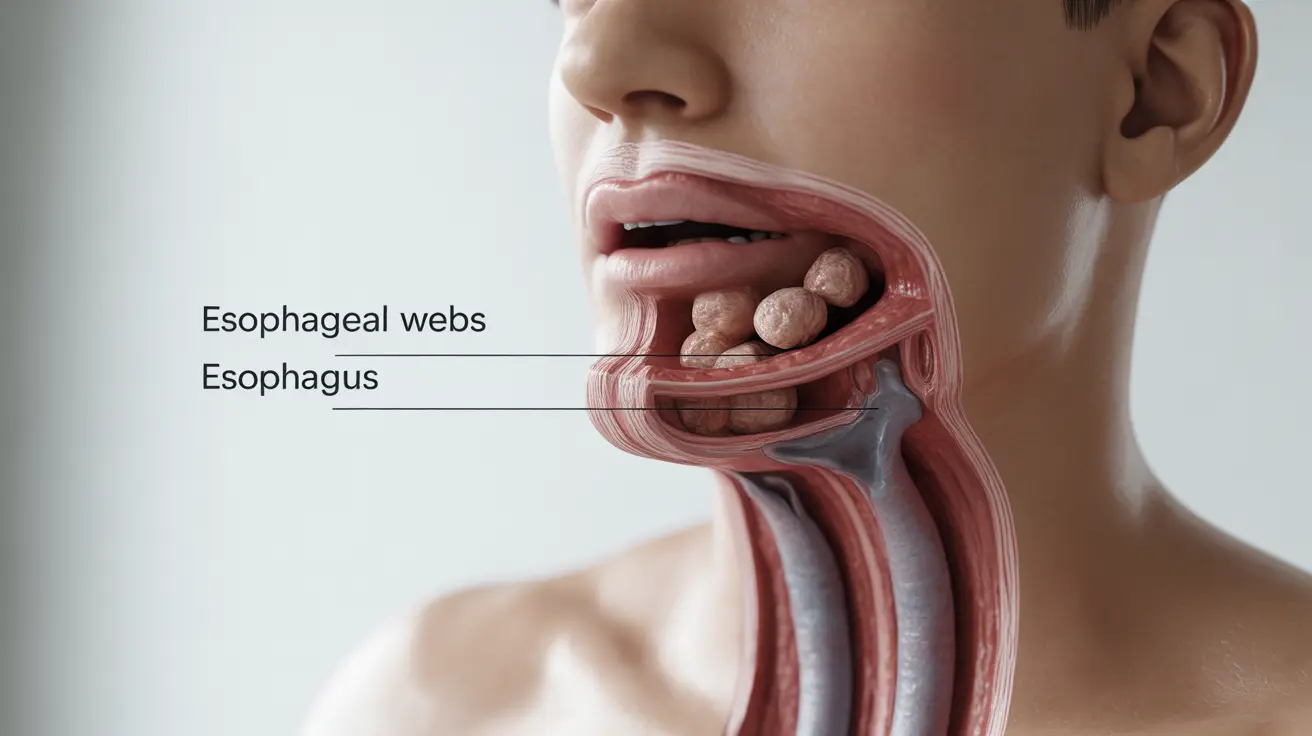
Esophageal webs are thin, membranous tissue growths that can develop in the upper part of the esophagus, potentially causing difficulties with swallowing and other related symptoms. These unusual tissue formations can significantly impact a person's ability to eat and drink comfortably, making understanding their nature and treatment options essential for those affected.
While relatively uncommon, esophageal webs deserve attention due to their potential impact on quality of life and their association with certain underlying health conditions. This comprehensive guide explores the key aspects of esophageal webs, from recognition to treatment options.
Understanding Esophageal Webs and Their Impact
Esophageal webs are thin layers of tissue that partially block the esophagus, typically forming in the upper portion of this vital digestive tract structure. These tissue formations can vary in size and thickness, directly affecting how significantly they impact swallowing function. Understanding their structure and location helps explain the symptoms they cause and guides treatment approaches.
Common Symptoms to Watch For
The presence of esophageal webs often manifests through several distinctive symptoms:
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia), particularly with solid foods
- Sensation of food getting stuck in the throat
- Chest pain while eating
- Unintentional weight loss
- Regurgitation of food
- Persistent cough during meals
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can contribute to the development of esophageal webs:
Primary Causes
- Iron deficiency anemia
- Plummer-Vinson syndrome
- Genetic predisposition
- Autoimmune conditions
Associated Risk Factors
- Female gender (more commonly affected)
- Advanced age
- Chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
- Certain inflammatory conditions
Diagnostic Approaches
Healthcare providers use various methods to diagnose esophageal webs accurately:
Primary Diagnostic Tools
- Barium swallow studies (most common)
- Upper endoscopy
- Videofluoroscopy
- CT scans in specific cases
These diagnostic procedures help determine the web's exact location, size, and impact on swallowing function, enabling healthcare providers to develop appropriate treatment plans.
Treatment Options and Management
Treatment for esophageal webs typically follows a structured approach based on severity and underlying causes:
Conservative Management
- Dietary modifications
- Proper eating techniques
- Treatment of underlying conditions (especially iron deficiency)
Medical Interventions
- Esophageal dilation (primary treatment)
- Endoscopic procedures
- Surgical intervention in rare cases
The success rate for treating esophageal webs is generally high, particularly with dilation procedures. Many patients experience significant improvement in their symptoms after appropriate treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of esophageal webs and how do they affect swallowing? The most common symptoms include difficulty swallowing (especially solid foods), feeling food stuck in the throat, and chest pain while eating. These webs can significantly impact the swallowing process by creating a partial obstruction in the esophagus.
What causes esophageal webs and which conditions are they most commonly associated with? Esophageal webs are most commonly associated with iron deficiency anemia and Plummer-Vinson syndrome. They can also develop due to genetic factors, autoimmune conditions, and chronic inflammation of the esophagus.
How are esophageal webs diagnosed and what tests are used to detect them? Diagnosis typically involves barium swallow studies, which are the gold standard. Other diagnostic tools include upper endoscopy, videofluoroscopy, and occasionally CT scans. These tests help visualize the web and assess its impact on swallowing.
What treatment options are available for esophageal webs, and how effective is esophageal dilation? Esophageal dilation is the primary treatment option and is highly effective. Other approaches include treating underlying conditions and, in rare cases, surgical intervention. Success rates for dilation procedures are generally very high.
Can iron deficiency anemia or Plummer-Vinson syndrome increase the risk of developing esophageal webs? Yes, both conditions significantly increase the risk of developing esophageal webs. Iron deficiency anemia is one of the most common associated conditions, and Plummer-Vinson syndrome, which includes iron deficiency anemia, is strongly linked to the development of esophageal webs.