Eustachian tube dysfunction (ETD) is a common condition that affects the small passages connecting your middle ear to the back of your throat. When these tubes aren't functioning properly, you may experience uncomfortable pressure changes, hearing difficulties, and other troublesome symptoms. Understanding this condition is crucial for recognizing when to seek treatment and managing its effects on your daily life.
This comprehensive guide will explore the key aspects of eustachian tube dysfunction, including its symptoms, causes, treatment options, and prevention strategies. Whether you're dealing with temporary discomfort or chronic issues, we'll help you understand when to try home remedies and when to seek professional medical care.
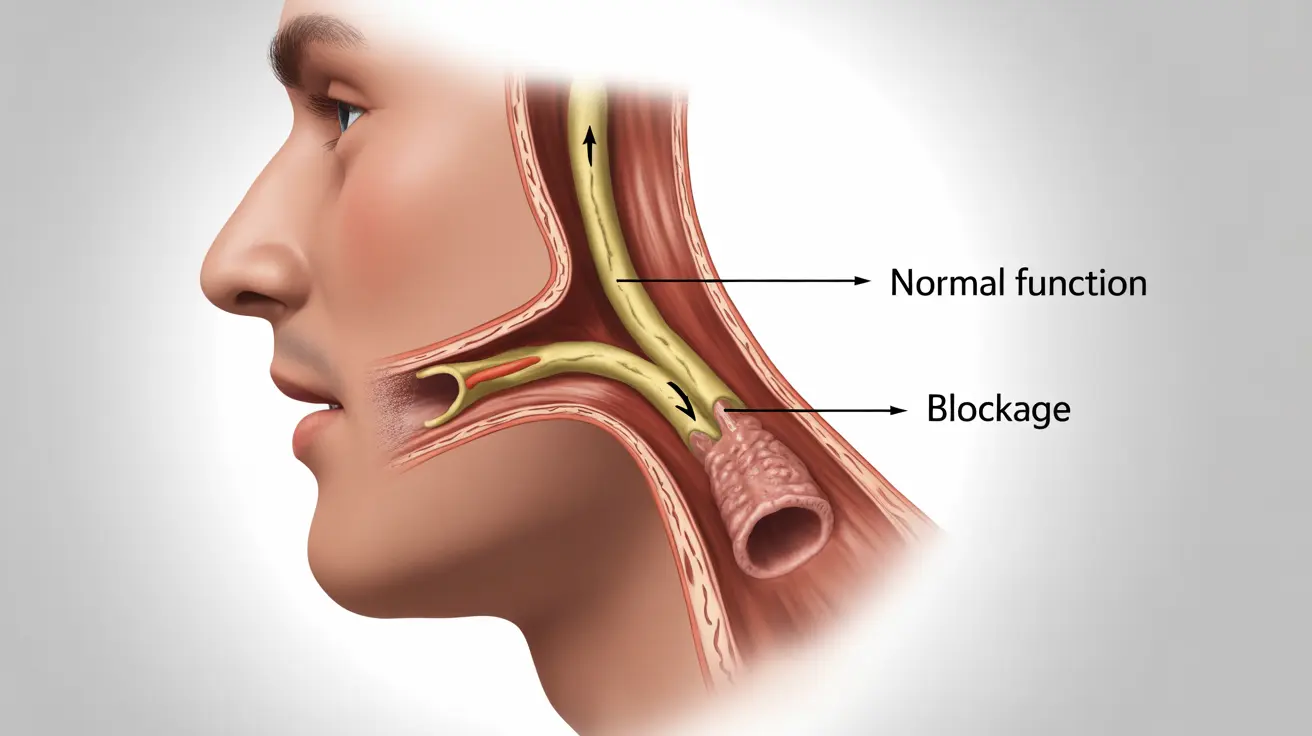
Understanding Eustachian Tube Function and Dysfunction
The eustachian tubes play a vital role in maintaining proper ear health by equalizing air pressure between your middle ear and the outside environment. When functioning normally, these tubes open briefly when you yawn, swallow, or chew, allowing air to flow and pressure to equalize. However, when dysfunction occurs, this natural process is disrupted, leading to various uncomfortable symptoms.
Common Symptoms of Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
Recognizing the symptoms of ETD is the first step toward getting appropriate treatment. Common signs include:
- Feeling of fullness or pressure in your ears
- Muffled hearing or hearing loss
- Popping or clicking sounds in your ears
- Pain or discomfort in one or both ears
- Ringing in the ears (tinnitus)
- Balance problems or dizziness
Risk Factors and Causes
Several factors can contribute to the development of eustachian tube dysfunction:
Medical Conditions
- Allergies
- Upper respiratory infections
- Sinus infections
- Common cold
- Chronic sinusitis
Environmental Factors
- Altitude changes during air travel
- Scuba diving
- Rapid changes in atmospheric pressure
- Exposure to smoke or other irritants
Home Management and Treatment Options
Many cases of eustachian tube dysfunction can be managed with simple home remedies and over-the-counter solutions:
Self-Help Techniques
- Yawning or swallowing deliberately
- Performing the Valsalva maneuver (gently blowing out while pinching your nostrils closed)
- Chewing gum during pressure changes
- Using saline nasal sprays
Medical Treatments
- Decongestant nasal sprays (short-term use only)
- Antihistamines for allergy-related cases
- Over-the-counter pain relievers for discomfort
When to Seek Medical Attention
While many cases resolve on their own, certain situations warrant professional medical evaluation:
- Symptoms lasting longer than two weeks
- Severe ear pain
- Persistent hearing loss
- Fever accompanying ear symptoms
- Dizziness affecting daily activities
Prevention Strategies
Taking proactive steps can help prevent or minimize episodes of ETD:
- Managing allergies effectively
- Avoiding exposure to secondhand smoke
- Staying hydrated during air travel
- Using proper equalization techniques while diving
- Treating upper respiratory infections promptly
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the most common symptoms of eustachian tube dysfunction? The most common symptoms include ear pressure or fullness, muffled hearing, popping or clicking sounds in the ears, and occasional ear pain or discomfort.
2. What causes eustachian tube dysfunction, and who is most at risk? ETD is commonly caused by allergies, upper respiratory infections, and rapid pressure changes. People with chronic allergies, frequent sinus infections, or those who regularly experience altitude changes are at higher risk.
3. How can I treat or manage eustachian tube dysfunction at home? Home management includes performing the Valsalva maneuver, using saline nasal sprays, chewing gum during pressure changes, and trying over-the-counter decongestants when appropriate.
4. When should I see a doctor for eustachian tube dysfunction, and what medical treatments are available? Seek medical attention if symptoms persist beyond two weeks, cause severe pain, or include persistent hearing loss. Medical treatments may include prescription medications, nasal steroids, or in some cases, surgical intervention.
5. Can eustachian tube dysfunction be prevented, especially during flying or diving? Yes, prevention strategies include managing allergies, staying hydrated, using proper pressure equalization techniques during altitude changes, and treating upper respiratory infections promptly. For flying or diving, techniques like the Valsalva maneuver can help prevent issues.