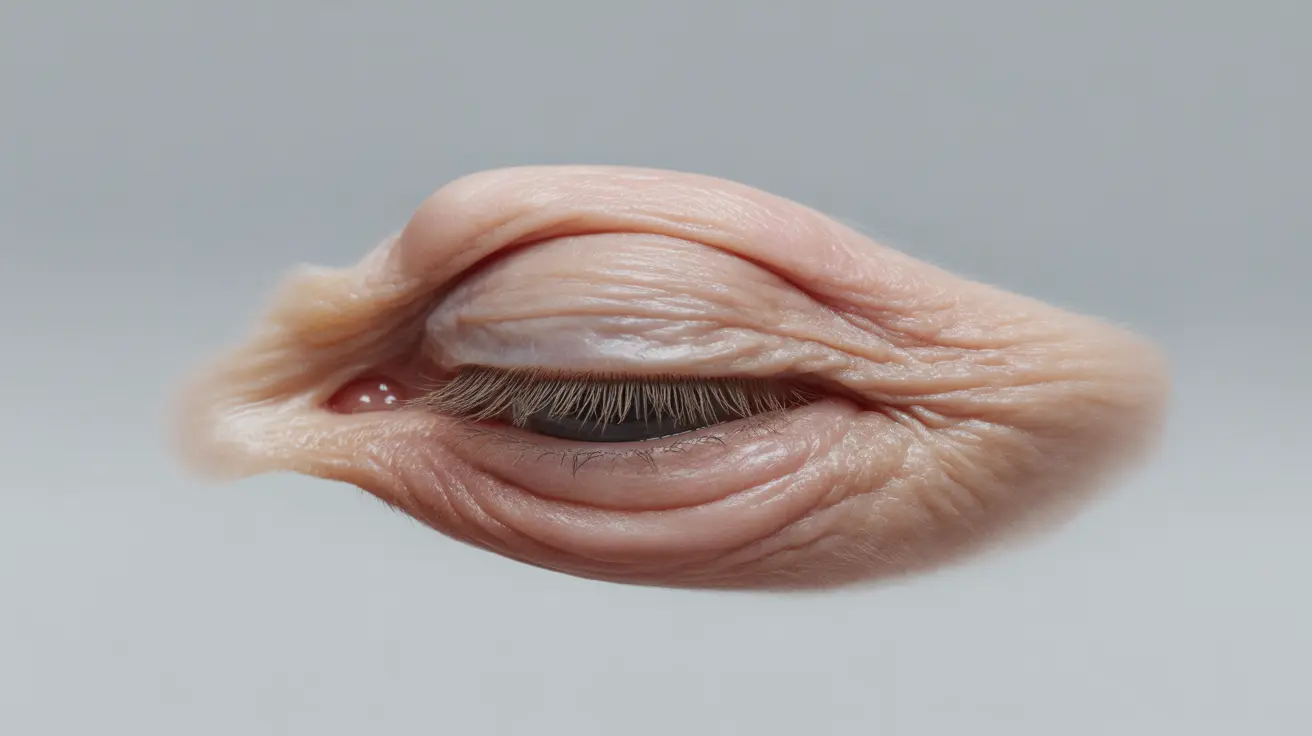
As we age, many people notice changes in their eyelids, including the development of extra skin that can create a heavy or drooping appearance. This condition, medically known as dermatochalasis, is a common concern that can affect both appearance and, in some cases, vision. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for extra skin on eyelids is crucial for making informed decisions about your eye health.
Understanding Extra Skin on Eyelids
Extra skin on the eyelids occurs when the elastic tissue in the upper or lower eyelids becomes stretched and loses its ability to retract. This natural aging process, combined with factors like genetics and environmental conditions, can lead to excess skin that creates folds or drooping in the eyelid area.
Common Causes of Excess Eyelid Skin
Several factors contribute to the development of extra skin on the eyelids:
- Age-related loss of skin elasticity
- Genetic predisposition
- Sun exposure and UV damage
- Smoking
- Chronic eye rubbing
- Weight fluctuations
Signs and Symptoms
Identifying the presence of excess eyelid skin involves recognizing several key indicators:
Physical Changes
- Visible folds of skin on upper or lower eyelids
- Drooping or heavy-looking eyelids
- Creases above the natural eyelid fold
Functional Impact
In some cases, extra skin on the eyelids can cause:
- Reduced peripheral vision
- Eye fatigue
- Difficulty applying makeup
- Persistent tired appearance
Treatment Options
Non-Surgical Approaches
While non-surgical treatments cannot remove excess skin, they may help improve the appearance and prevent further deterioration:
- Regular use of sunscreen
- Proper skincare routine
- Eye exercises
- Cold compresses
- Lifestyle modifications
Surgical Solutions
For significant cases of excess eyelid skin, surgical intervention may be recommended:
Blepharoplasty
This surgical procedure removes excess skin and sometimes fat from the eyelids. It can be performed on upper eyelids, lower eyelids, or both, depending on individual needs. The surgery typically takes 1-2 hours and is often performed under local anesthesia with sedation.
Prevention Strategies
While some factors contributing to extra eyelid skin are unavoidable, certain preventive measures can help minimize its development:
- Protection from sun exposure
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Avoiding smoking
- Regular skincare routine
- Adequate sleep and hydration
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes extra skin on the eyelids and how can I tell if I have dermatochalasis? Extra skin on the eyelids (dermatochalasis) is primarily caused by aging, genetics, and environmental factors. You may have this condition if you notice visible folds of excess skin on your eyelids, particularly if they feel heavy or interfere with your field of vision.
Can extra skin on the eyelid affect my vision or cause eye discomfort? Yes, significant excess eyelid skin can obstruct peripheral vision and cause eye fatigue, especially when reading or performing detailed tasks. Some people may also experience irritation or discomfort from the skin rubbing against itself.
What treatment options are available for sagging eyelids caused by extra skin? Treatment options range from conservative measures like skincare and sun protection to surgical procedures such as blepharoplasty. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the condition and its impact on vision and quality of life.
Are there non-surgical ways to reduce or prevent excess eyelid skin from developing? While non-surgical methods cannot remove existing excess skin, preventive measures include sun protection, maintaining good skin health, avoiding smoking, and proper hydration. Regular skincare routines may help slow the progression of skin laxity.
How is eyelid surgery (blepharoplasty) performed to remove extra skin on the eyelids? Blepharoplasty is typically performed under local anesthesia with sedation. The surgeon makes precise incisions along natural eyelid creases, removes excess skin and sometimes fat, and closes the incisions with fine sutures. Recovery usually takes 1-2 weeks, with final results visible after several months.