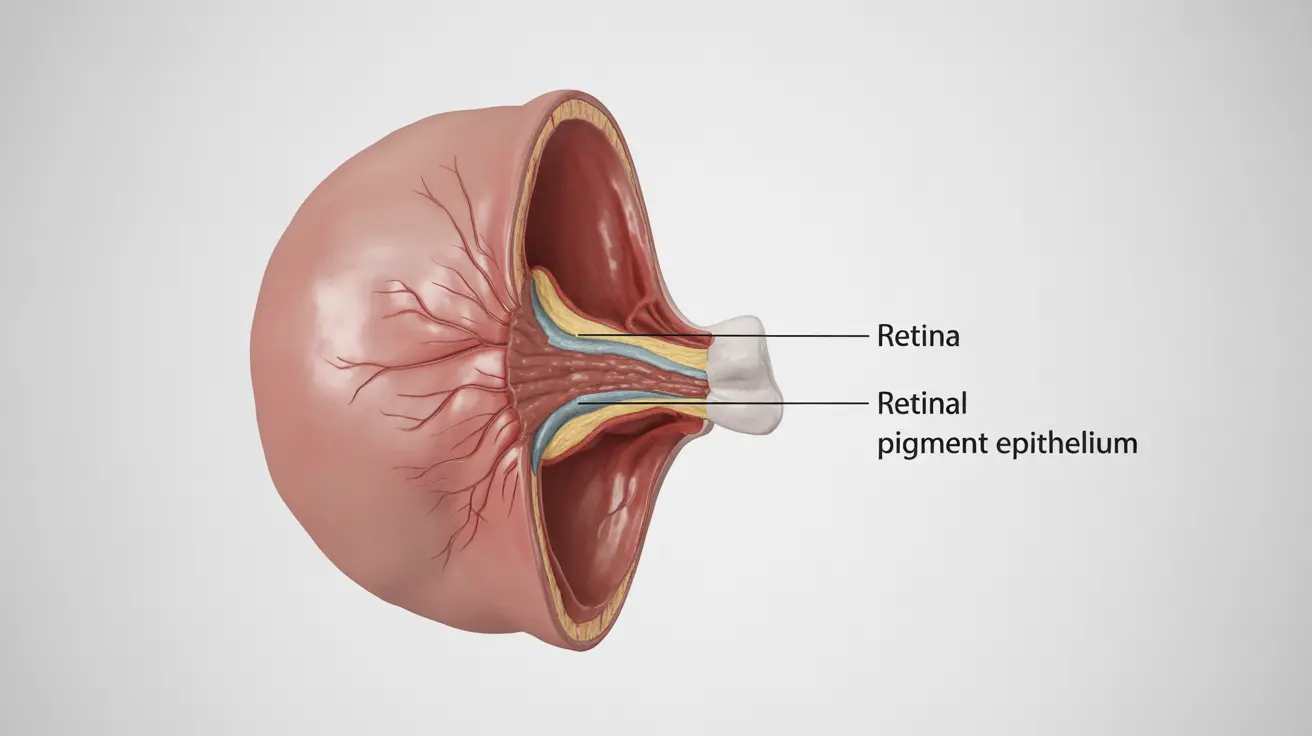
Exudative retinal detachment is a serious eye condition where fluid accumulates beneath the retina, causing it to separate from the underlying tissue. Unlike other forms of retinal detachment, this type occurs without any tears or holes in the retina itself. Understanding this condition is crucial for early detection and proper treatment.
This condition often develops as a secondary complication of other underlying health issues, making it particularly important to recognize its unique characteristics and seek prompt medical attention when symptoms arise.
What Is Exudative Retinal Detachment?
Exudative retinal detachment, also known as serous retinal detachment, occurs when fluid builds up between the retina and the underlying retinal pigment epithelium (RPE). This accumulation causes the retina to lift away from its normal position, potentially leading to vision problems if not addressed promptly.
Common Signs and Symptoms
Recognizing the early warning signs of exudative retinal detachment is crucial for timely intervention. Common symptoms include:
- Blurred or distorted vision
- A curtain-like shadow in your field of vision
- Sudden decrease in peripheral vision
- Visual disturbances that don't go away
- Floating spots or flashes of light
Unlike other types of retinal detachment, symptoms in exudative cases may develop more gradually, making it essential to pay attention to any persistent changes in vision.
Understanding the Causes
Exudative retinal detachment typically occurs due to underlying medical conditions that affect the blood vessels in the eye. Common causes include:
- Inflammatory conditions like uveitis
- Severe hypertension
- Cancer-related conditions such as choroidal melanoma
- Age-related macular degeneration
- Certain medications or treatments
- Central serous chorioretinopathy
Diagnosis Process
Eye care professionals use several diagnostic tools and procedures to identify and assess exudative retinal detachment:
- Comprehensive dilated eye examination
- Optical coherence tomography (OCT)
- Fluorescein angiography
- Ultrasound imaging
- Blood tests to identify underlying conditions
Treatment Approaches
Treatment for exudative retinal detachment focuses primarily on addressing the underlying condition causing the fluid accumulation. Common treatment strategies include:
- Medications to reduce inflammation
- Blood pressure management
- Laser therapy in specific cases
- Photodynamic therapy
- Regular monitoring and follow-up care
Prevention and Risk Reduction
While not all cases of exudative retinal detachment can be prevented, certain measures can help reduce risk:
- Regular eye examinations
- Proper management of existing health conditions
- Blood pressure control
- Healthy lifestyle choices
- Prompt attention to vision changes
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms and early signs of exudative retinal detachment?
Early signs include blurred vision, visual distortion, and the appearance of a shadow or curtain in your field of vision. Unlike other forms of retinal detachment, symptoms often develop gradually rather than suddenly.
What causes exudative retinal detachment if there are no retinal tears or holes?
This condition is caused by fluid accumulation beneath the retina due to underlying conditions such as inflammatory diseases, severe hypertension, or certain cancers affecting the eye. The fluid buildup occurs without any physical breaks in the retinal tissue.
How is exudative retinal detachment diagnosed and differentiated from other types of retinal detachment?
Diagnosis involves comprehensive eye examinations, imaging tests like OCT and fluorescein angiography, and sometimes ultrasound. The absence of retinal tears and the presence of fluid accumulation help differentiate it from other types of retinal detachment.
What treatment options are available for exudative retinal detachment and how do they depend on the underlying cause?
Treatment primarily focuses on addressing the underlying condition causing the fluid buildup. Options may include anti-inflammatory medications, blood pressure management, laser therapy, or photodynamic therapy, depending on the specific cause.
Can exudative retinal detachment be prevented, and what lifestyle or health measures reduce the risk?
While not entirely preventable, risk can be reduced through regular eye check-ups, proper management of existing health conditions (especially hypertension), maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and seeking prompt medical attention for any vision changes.