Factor II blood disorder, also known as prothrombin deficiency, is a rare bleeding disorder that affects the body's ability to form blood clots properly. This condition occurs when there isn't enough factor II, a crucial protein involved in the blood clotting process, or when the protein doesn't function correctly. Understanding this disorder is essential for proper management and prevention of bleeding complications.
What is Factor II Blood Disorder?
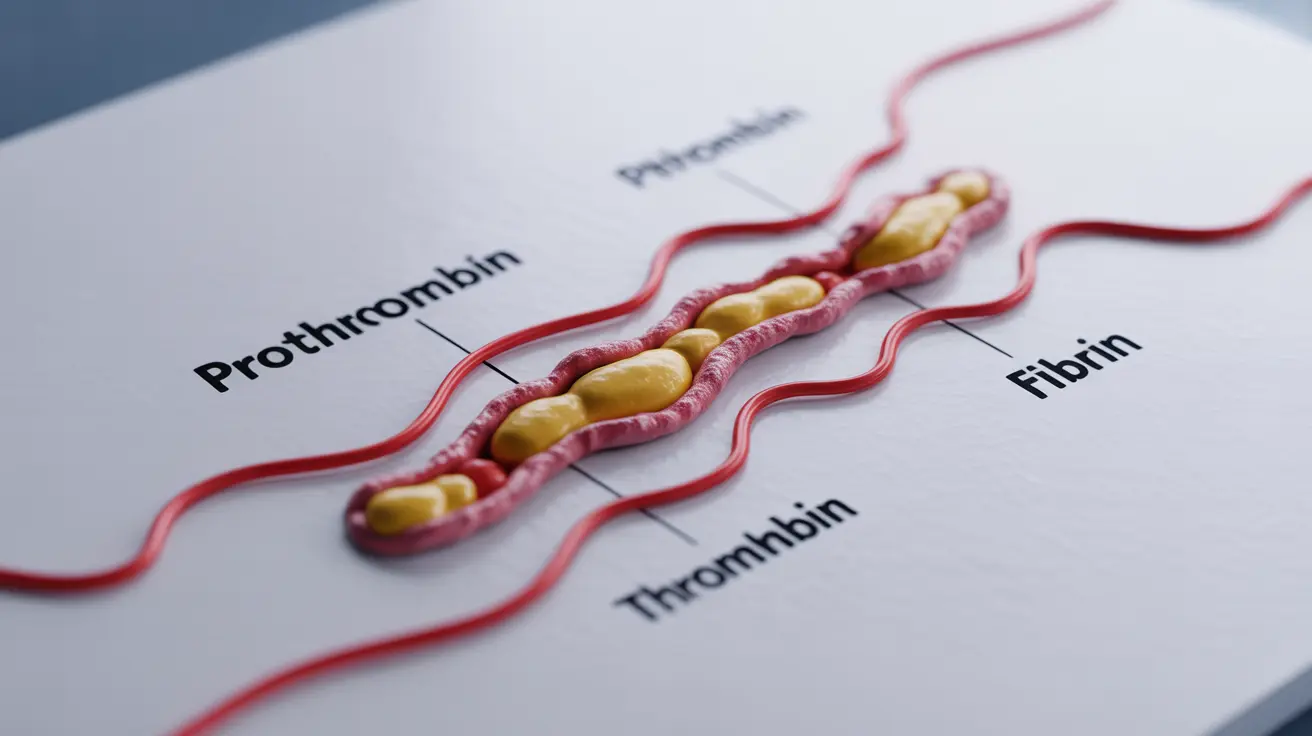
Factor II blood disorder is characterized by a deficiency in prothrombin, a vital protein that helps blood to clot effectively. When blood vessels are damaged, prothrombin is converted to thrombin, which then helps convert fibrinogen to fibrin, forming a stable blood clot. In people with this disorder, this process is impaired, leading to prolonged or excessive bleeding.
Signs and Symptoms
The severity of symptoms can vary significantly among individuals with factor II blood disorder. Common manifestations include:
- Easy bruising
- Prolonged bleeding from minor cuts
- Frequent nosebleeds
- Heavy menstrual periods
- Bleeding after dental procedures
- Joint bleeding
- Muscle hemorrhages
Diagnosis Process
Diagnosing factor II blood disorder involves several specific blood tests that measure clotting function and factor II levels. Healthcare providers typically perform:
- Prothrombin time (PT) test
- Partial thromboplastin time (PTT) test
- Factor II activity assay
- Genetic testing when hereditary cases are suspected
Treatment Approaches
Treatment for factor II blood disorder is tailored to each patient's specific needs and may include:
Immediate Bleeding Management
For active bleeding episodes, treatment often involves:
- Fresh frozen plasma administration
- Prothrombin complex concentrates
- Vitamin K supplementation in some cases
Preventive Care
Preventive measures may include:
- Regular prophylactic treatment
- Vitamin K supplementation when appropriate
- Close monitoring during surgical procedures
- Regular medical check-ups
Living with Factor II Blood Disorder
Managing factor II blood disorder requires careful attention to lifestyle choices and preventive measures. This includes avoiding activities with high injury risk, maintaining good oral hygiene to prevent gum bleeding, and working closely with healthcare providers to develop appropriate treatment plans.
Genetic Considerations
Factor II blood disorder can be inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern. Understanding the genetic component is crucial for family planning and determining the risk of passing the condition to children. Genetic counseling can provide valuable guidance for affected individuals and their families.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of factor II (prothrombin) deficiency to watch for? Common symptoms include easy bruising, prolonged bleeding from cuts, frequent nosebleeds, heavy menstrual periods, and spontaneous bleeding into joints or muscles.
How is factor II deficiency diagnosed through blood tests? Diagnosis involves specific blood tests including prothrombin time (PT), partial thromboplastin time (PTT), and factor II activity assay. These tests measure blood clotting function and factor II levels.
What treatment options are available to manage bleeding in factor II deficiency? Treatment options include fresh frozen plasma, prothrombin complex concentrates, and vitamin K supplementation. The specific treatment plan depends on the severity of symptoms and individual patient needs.
Can factor II deficiency be inherited, and how does genetic counseling help? Yes, factor II deficiency can be inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern. Genetic counseling helps families understand inheritance patterns, assess risks for future pregnancies, and make informed family planning decisions.
What lifestyle precautions should people with factor II deficiency take to prevent bleeding episodes? People with factor II deficiency should avoid high-impact activities, maintain good oral hygiene, wear protective gear during physical activities, and inform healthcare providers about their condition before any medical procedures.