Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) is a serious genetic condition that affects how the body processes cholesterol, leading to dangerously high levels of LDL (bad) cholesterol from birth. This inherited disorder can significantly increase the risk of early heart disease if left untreated, making early detection and proper management crucial for those affected.
While FH affects approximately 1 in 250 people worldwide, many individuals remain undiagnosed until they experience cardiovascular complications. Understanding the signs, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for better outcomes and prevention of serious health complications.
Understanding the Genetics Behind Familial Hypercholesterolemia
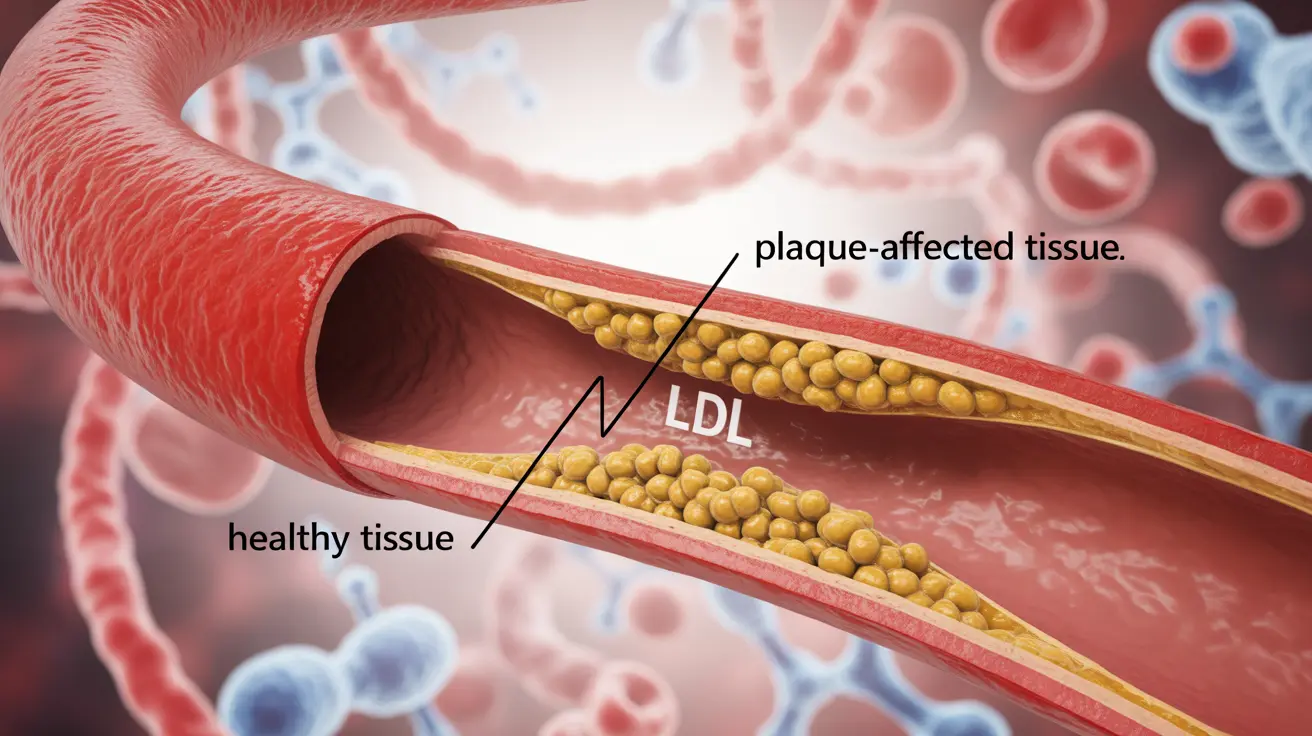
Familial hypercholesterolemia occurs due to genetic mutations that affect the body's ability to remove LDL cholesterol from the blood. These mutations primarily affect the LDL receptor gene, which is responsible for clearing cholesterol from the bloodstream. When this process is impaired, cholesterol accumulates in the arteries from an early age.
The condition can be inherited in two forms:
- Heterozygous FH (inherited from one parent)
- Homozygous FH (inherited from both parents, more severe)
Early Warning Signs and Symptoms
Recognizing the signs of familial hypercholesterolemia is crucial for early intervention. Common physical indicators include:
- Xanthomas (cholesterol deposits) on tendons
- Corneal arcus (white ring around the cornea) in people under 45
- Xanthelasmas (cholesterol deposits around the eyes)
- Severely elevated LDL cholesterol levels, often above 190 mg/dL
Diagnosis and Testing Procedures
Diagnosing familial hypercholesterolemia involves several steps, including:
- Comprehensive lipid panel tests
- Physical examination for characteristic signs
- Detailed family history assessment
- Genetic testing when appropriate
Early diagnosis is particularly important for children with a family history of FH, as treatment can begin before cardiovascular damage occurs.
Treatment Approaches and Management
Managing familial hypercholesterolemia requires a comprehensive approach combining medication and lifestyle modifications. Treatment typically includes:
Medication Options
- Statins as first-line therapy
- PCSK9 inhibitors for additional cholesterol lowering
- Bile acid sequestrants
- Ezetimibe for enhanced cholesterol absorption blocking
Lifestyle Modifications
Important lifestyle changes that support treatment include:
- Following a heart-healthy diet low in saturated fats
- Regular physical activity
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Avoiding tobacco use
- Regular medical monitoring
Preventing Cardiovascular Complications
Early intervention and consistent treatment are crucial for preventing heart disease in individuals with FH. Regular cardiovascular assessments, including stress tests and imaging studies, help monitor heart health and adjust treatment plans as needed.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms and signs of familial hypercholesterolemia that I should look out for?
Common signs include extremely high LDL cholesterol levels (above 190 mg/dL), xanthomas on tendons, corneal arcus in young people, and xanthelasmas around the eyes. A strong family history of early heart disease is also a significant indicator.
How is familial hypercholesterolemia diagnosed, and when should I consider genetic testing?
Diagnosis involves blood tests to check cholesterol levels, physical examination, and family history evaluation. Genetic testing is recommended when there's a strong family history of high cholesterol or early heart disease, especially in young people with very high LDL levels.
What treatment options are available for managing familial hypercholesterolemia, especially for children?
Treatment options include statins (usually started in childhood for severe cases), other cholesterol-lowering medications, and lifestyle modifications. Children typically begin with dietary changes and may start medication between ages 8-10 if necessary, under careful medical supervision.
How does familial hypercholesterolemia increase the risk of heart disease, and can early treatment reduce this risk?
FH increases heart disease risk by causing cholesterol buildup in arteries from birth. Early treatment can significantly reduce this risk by lowering LDL cholesterol levels and preventing arterial damage. Studies show that early intervention can lead to near-normal life expectancy.
What lifestyle changes and medications are recommended to control high LDL cholesterol in familial hypercholesterolemia?
Recommended lifestyle changes include a low-saturated fat diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking. Medications typically include statins as primary treatment, often combined with other drugs like PCSK9 inhibitors or ezetimibe for optimal cholesterol control.