Understanding the difference between kidney pain and back pain can be crucial for women's health. While both types of pain occur in the back area, they have distinct characteristics, causes, and implications for treatment. This comprehensive guide will help you identify whether you're experiencing kidney-related pain or typical back pain, and when to seek medical attention.
Understanding Kidney Pain Location in Women
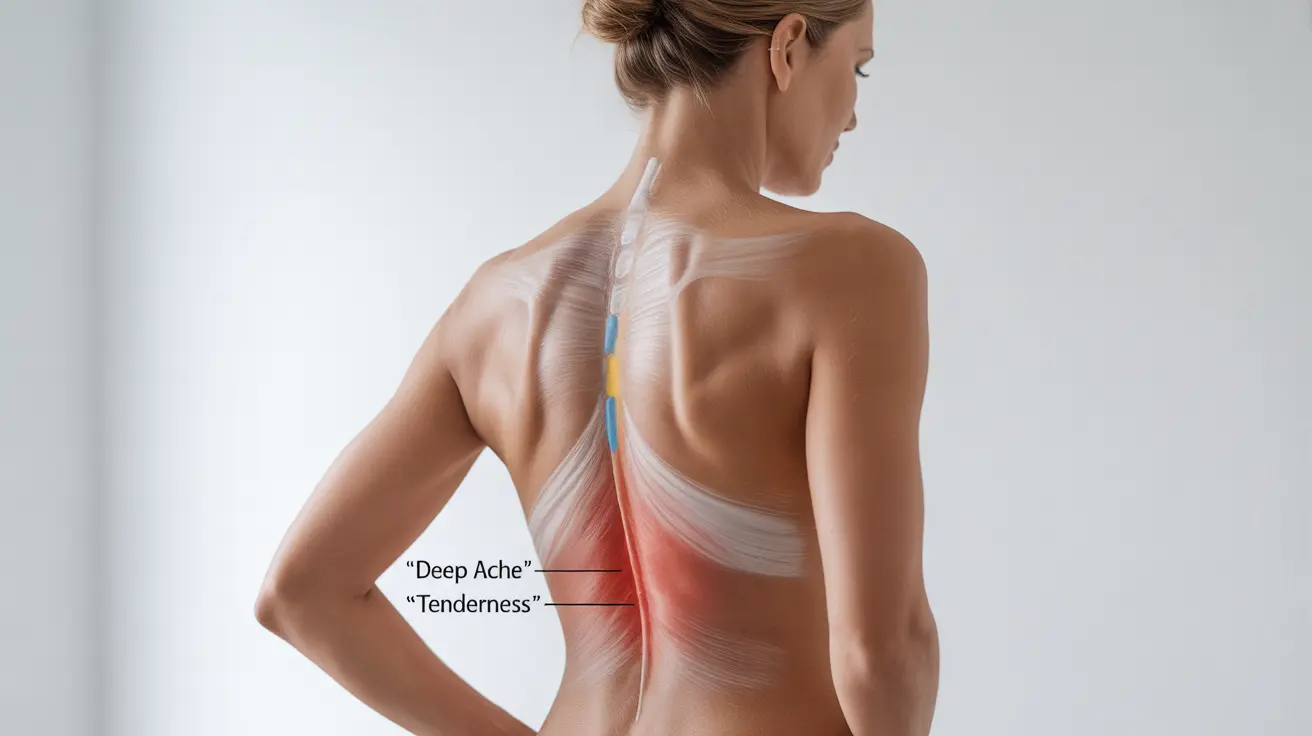
Kidney pain in women typically occurs in the flank area, located on either side of the spine between the bottom of the ribcage and the hips. This pain is usually deeper and higher up on the back compared to typical back pain. The pain may be felt on one side (unilateral) or both sides (bilateral) depending on whether one or both kidneys are affected.
Distinctive Features of Kidney Pain
Women experiencing kidney pain often describe it as:
- A deep, constant ache beneath the rib cage
- Pain that doesn't change with movement or position
- Tenderness when pressing on the affected area
- Pain that may radiate to the lower abdomen or groin
Common Causes of Kidney Pain in Women
Several conditions can trigger kidney pain in women, and these differ significantly from typical back pain causes:
Kidney-Specific Causes
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs)
- Kidney stones
- Kidney infections (pyelonephritis)
- Polycystic kidney disease
- Kidney trauma or injury
Back Pain Causes for Comparison
- Muscle strain or sprain
- Poor posture
- Herniated discs
- Spinal stenosis
- Arthritis
Key Symptoms That Indicate Kidney Issues
When kidney problems are the source of back pain, women often experience additional symptoms such as:
- Fever and chills
- Frequent or painful urination
- Changes in urine color or smell
- Nausea and vomiting
- Swelling in the face, hands, or feet
When to Seek Medical Attention
Women should seek immediate medical care if they experience:
- Severe, persistent pain in the kidney area
- High fever accompanied by back pain
- Blood in the urine
- Difficulty urinating
- Unexplained weight loss
- Severe nausea or vomiting
Frequently Asked Questions
Where exactly is female kidney pain located on the back compared to typical back pain?
Female kidney pain is typically located in the flank area, between the bottom of the ribcage and the hips, on either side of the spine. Unlike typical back pain, kidney pain is usually deeper and higher up, and doesn't change with movement or position.
How can I tell if my pain under the ribs on my back is kidney pain or just regular back pain?
Kidney pain typically feels deeper and more constant, doesn't change with movement, and may be accompanied by urinary symptoms, fever, or nausea. Regular back pain usually worsens with movement and improves with rest or position changes.
What are the common causes of kidney pain in women and how do they differ from back pain causes?
Kidney pain is usually caused by conditions like UTIs, kidney stones, or kidney infections. Back pain typically results from musculoskeletal issues like muscle strain, poor posture, or spinal problems. Kidney pain often comes with additional symptoms like fever and urinary changes.
What symptoms along with back pain suggest a kidney infection or kidney stones in females?
Additional symptoms suggesting kidney issues include fever, chills, frequent or painful urination, changes in urine color or odor, nausea, vomiting, and pain that radiates to the lower abdomen or groin.
When should a woman see a doctor for pain near the kidneys on her back?
Women should seek medical attention if they experience severe or persistent kidney area pain, high fever, blood in urine, difficulty urinating, or if the pain is accompanied by severe nausea or vomiting.