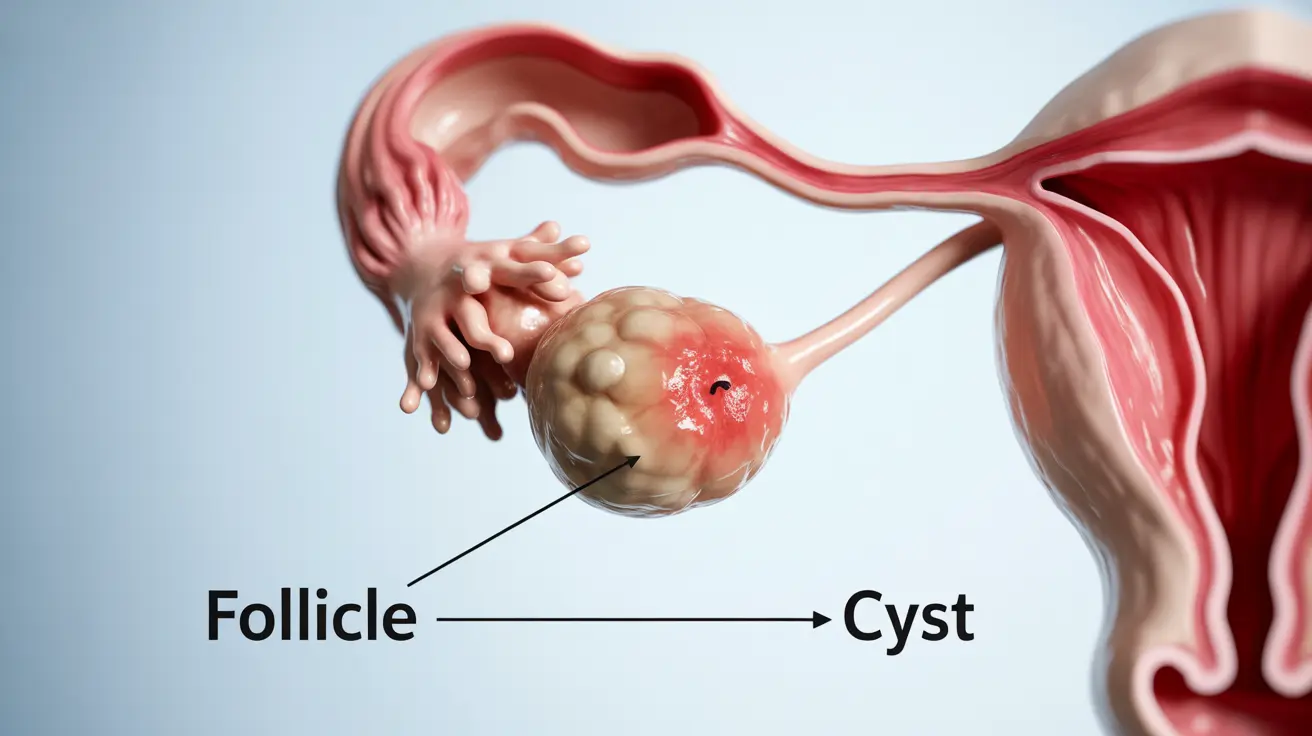
A follicular cyst is a common type of functional ovarian cyst that develops during a woman's menstrual cycle. These fluid-filled sacs form when a follicle containing an egg doesn't release the egg as it should during ovulation, instead continuing to grow and fill with fluid. While these cysts are generally harmless and often resolve on their own, understanding their nature, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for women's reproductive health.
This comprehensive guide will explore everything you need to know about follicular cysts, from their formation to management strategies, helping you make informed decisions about your health.
The Formation of Follicular Cysts
During a normal menstrual cycle, an egg develops within a follicle on the ovary. This follicle typically ruptures during ovulation, releasing the egg. However, when the follicle fails to break open and release the egg, it can continue to grow and fill with fluid, forming a follicular cyst.
Several factors can contribute to follicular cyst formation, including hormonal imbalances, certain medications, or underlying medical conditions affecting the menstrual cycle. Understanding these causes is essential for proper management and prevention.
Common Symptoms and Warning Signs
Many women with follicular cysts experience no symptoms at all. However, when symptoms do occur, they may include:
- Pelvic pain or discomfort
- Irregular menstrual cycles
- Bloating or swelling in the lower abdomen
- Pain during intercourse
- Breast tenderness
- Lower back pain
More severe symptoms that require immediate medical attention include:
- Sudden, severe abdominal pain
- Fever and vomiting
- Dizziness or weakness
- Heavy vaginal bleeding
Diagnosis and Medical Evaluation
Healthcare providers typically diagnose follicular cysts through a combination of methods:
- Physical examination
- Pelvic ultrasound
- Blood tests to check hormone levels
- Medical history review
These diagnostic tools help differentiate follicular cysts from other types of ovarian cysts and ensure appropriate treatment planning.
Treatment Approaches
Most follicular cysts resolve naturally within two to three menstrual cycles without requiring specific treatment. However, when treatment is necessary, options may include:
Conservative Management
This involves regular monitoring through ultrasound to track the cyst's size and ensure it resolves on its own. Pain management may include over-the-counter medications.
Hormonal Therapy
Birth control pills might be prescribed to prevent new cyst formation and regulate the menstrual cycle.
Surgical Intervention
Surgery is rarely needed but may be recommended if the cyst:
- Is particularly large
- Doesn't resolve on its own
- Causes severe symptoms
- Shows suspicious characteristics
Impact on Fertility and Pregnancy
Generally, follicular cysts don't affect fertility or pregnancy outcomes. In fact, their presence indicates that ovulation is occurring, though not completing normally. However, large or persistent cysts may require medical attention to ensure optimal reproductive health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes a follicular cyst to form on the ovary?
A follicular cyst forms when an ovarian follicle fails to rupture and release its egg during ovulation. Instead, the follicle continues to grow and fill with fluid, creating a cyst. This can be due to hormonal imbalances or other factors affecting the normal ovulation process.
What are the common symptoms of a follicular cyst and when should I see a doctor?
Common symptoms include pelvic pain, bloating, and irregular periods. You should see a doctor if you experience sudden severe pain, fever, vomiting, or dizziness, as these may indicate complications requiring immediate medical attention.
How is a follicular cyst diagnosed and differentiated from other ovarian cyst types?
Follicular cysts are typically diagnosed through pelvic ultrasound, which can show the cyst's size, location, and characteristics. Blood tests and physical examination help differentiate them from other types of ovarian cysts based on their appearance and hormone levels.
What treatment options are available if a follicular cyst does not resolve on its own?
Treatment options include hormonal birth control to prevent new cysts, pain medication for symptom management, and in rare cases, surgical removal. The choice of treatment depends on the cyst's size, symptoms, and other individual factors.
Can follicular cysts affect fertility or pregnancy chances?
Generally, follicular cysts don't negatively impact fertility or pregnancy chances. Most resolve naturally within a few menstrual cycles. However, persistent or large cysts should be monitored by a healthcare provider to ensure they don't interfere with reproductive function.