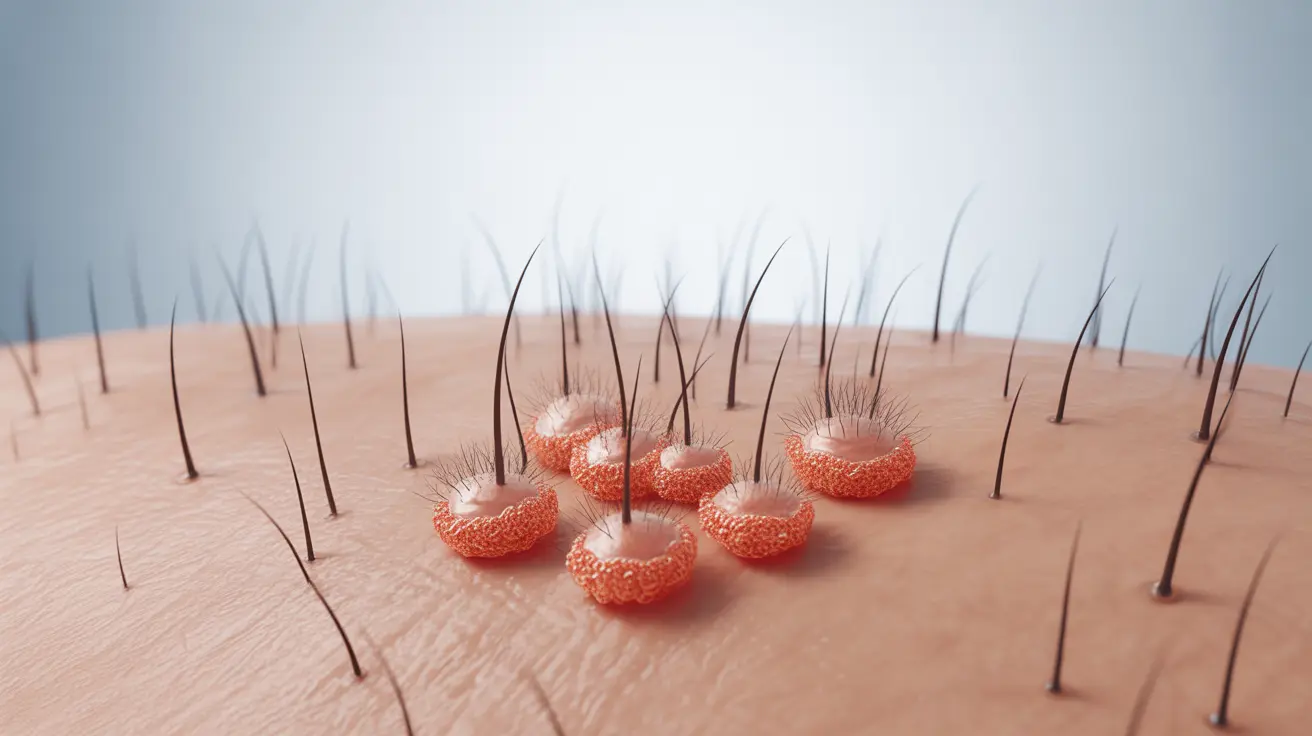
Follicular eczema is a distinct type of eczema that specifically affects the hair follicles, causing inflammation, itching, and distinctive bump-like lesions on the skin. This condition can significantly impact quality of life, but with proper understanding and management, many people can find relief from its symptoms.
If you're dealing with follicular eczema, it's essential to understand its triggers, symptoms, and available treatment options. This comprehensive guide will help you navigate the condition and develop an effective management strategy.
Understanding Follicular Eczema and Its Triggers
Follicular eczema primarily affects the hair follicles, causing small, itchy bumps to form around them. The condition commonly appears on areas with abundant hair follicles, such as the upper arms, thighs, and back. Several factors can trigger or worsen the condition:
- Hot and humid weather
- Excessive sweating
- Tight clothing that irritates the skin
- Certain fabrics, especially synthetic materials
- Stress and anxiety
- Environmental allergens
- Harsh soaps and skin care products
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms
Understanding the distinctive characteristics of follicular eczema can help you identify the condition and seek appropriate treatment:
Primary Symptoms
- Small, itchy bumps around hair follicles
- Redness and inflammation
- Dry, rough skin texture
- Persistent itching
- Possible darkening of affected skin areas
Secondary Complications
Without proper management, follicular eczema can lead to additional issues such as skin infections, scarring, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. Early intervention is crucial for preventing these complications.
Treatment Approaches for Follicular Eczema
Topical Treatments
The first line of defense typically includes topical treatments prescribed by healthcare providers:
- Corticosteroid creams or ointments
- Topical calcineurin inhibitors
- Moisturizing emollients
- Anti-itch medications
Systemic Treatments
For more severe cases, systemic treatments might be necessary:
- Oral antihistamines
- Systemic corticosteroids
- Immunosuppressant medications
- Phototherapy treatments
Lifestyle Management Strategies
Effective management of follicular eczema often requires lifestyle modifications:
- Wearing loose-fitting, breathable clothing
- Using gentle, fragrance-free skincare products
- Maintaining proper skin hydration
- Managing stress through relaxation techniques
- Avoiding known triggers
- Regular gentle exercise with appropriate post-workout skincare
Dietary Considerations
While diet's role in follicular eczema isn't fully understood, some dietary modifications may help:
- Increasing intake of anti-inflammatory foods
- Consuming omega-3 rich foods
- Staying well-hydrated
- Identifying and avoiding potential food triggers
- Maintaining a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common triggers of follicular eczema, and how can I avoid them?
The most common triggers include heat, humidity, tight clothing, synthetic fabrics, and harsh skincare products. Avoid these triggers by wearing loose-fitting, breathable clothing, using gentle skincare products, and maintaining cool, comfortable environments when possible.
How can I manage symptoms of follicular eczema, especially when it comes to reducing itching and inflammation?
Manage symptoms by applying prescribed topical medications, using regular moisturizers, taking lukewarm showers, avoiding scratching, and using cold compresses when needed. Over-the-counter antihistamines can also help control itching.
What are the best topical treatments for follicular eczema, and how often should I apply them?
The best topical treatments typically include corticosteroid creams and moisturizing emollients. Apply prescribed medications as directed by your healthcare provider, usually once or twice daily. Moisturizers should be applied multiple times throughout the day, especially after bathing.
Can dietary changes help reduce the severity of follicular eczema, or are there specific foods I should avoid?
While individual responses vary, some people benefit from an anti-inflammatory diet rich in omega-3s and antioxidants. Common trigger foods to consider avoiding include dairy, eggs, and processed foods. Keep a food diary to identify potential triggers.
How does phototherapy work for treating severe follicular eczema, and is it safe for all skin types?
Phototherapy uses controlled UV light exposure to reduce inflammation and improve symptoms. While generally safe, it must be administered by healthcare professionals and may not be suitable for all skin types or those with certain medical conditions. Treatment protocols are customized based on individual factors.