Foot infections can be a serious health concern that affects people of all ages. These infections can range from mild superficial cases to severe conditions that require immediate medical attention. Understanding the signs, symptoms, and proper treatment approaches is crucial for maintaining foot health and preventing complications.
Whether caused by bacteria, fungi, or other microorganisms, foot infections can significantly impact daily activities and overall well-being. This comprehensive guide will help you identify, treat, and prevent various types of foot infections effectively.
Common Types of Foot Infections
Foot infections typically fall into several distinct categories:
- Bacterial infections (cellulitis, abscess)
- Fungal infections (athlete's foot)
- Nail infections (onychomycosis)
- Diabetic foot infections
- Wound infections
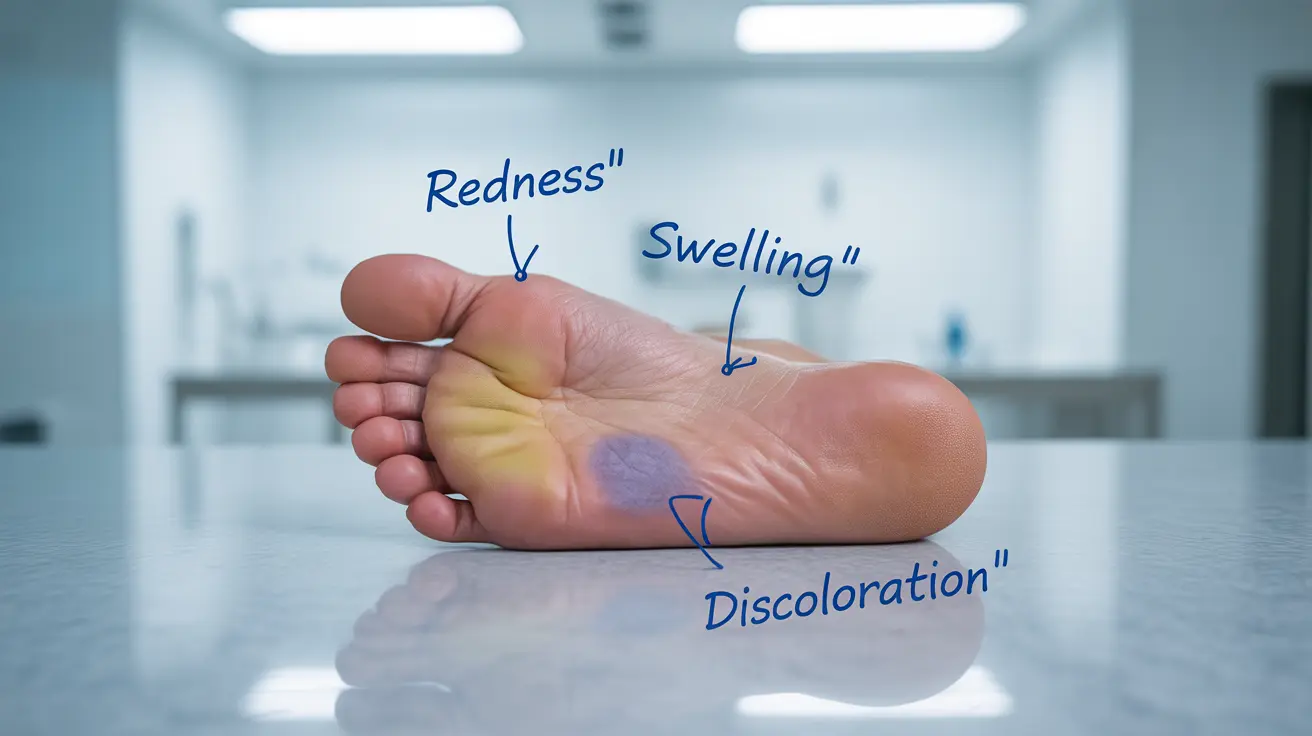
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms
Early detection of foot infections is crucial for successful treatment. Common indicators include:
- Redness and swelling
- Warmth in the affected area
- Pain or tenderness
- Unusual discharge or odor
- Skin changes or discoloration
- Fever (in severe cases)
Treatment Approaches for Different Types of Infections
Bacterial Infections
Bacterial foot infections often require targeted treatment approaches:
- Oral or topical antibiotics
- Proper wound cleaning and care
- Regular dressing changes
- Elevation to reduce swelling
- Rest and limited weight-bearing
Fungal Infections
Fungal infections typically respond well to specific treatments:
- Antifungal creams or powders
- Oral antifungal medications for severe cases
- Keeping feet dry and well-ventilated
- Regular sock changes
Risk Factors and Prevention
Understanding risk factors helps in preventing foot infections:
- Diabetes
- Poor circulation
- Compromised immune system
- Frequent exposure to moisture
- Walking barefoot in public areas
- Improper foot hygiene
Preventive Measures
Taking proactive steps can significantly reduce infection risk:
- Regular foot washing and thorough drying
- Wearing breathable footwear
- Using moisture-wicking socks
- Avoiding walking barefoot in public areas
- Regular inspection of feet for cuts or injuries
- Proper nail care and maintenance
When to Seek Medical Care
Certain symptoms warrant immediate medical attention:
- Severe pain or swelling
- Spreading redness or warmth
- Fever or chills
- Deep wounds or punctures
- Diabetes-related foot problems
- Infections that don't improve with home treatment
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms that indicate a foot infection?
Common symptoms include redness, swelling, warmth in the affected area, pain or tenderness, unusual discharge or odor, and skin changes. In severe cases, you may experience fever or chills.
How can bacterial and fungal foot infections be treated effectively?
Bacterial infections typically require antibiotics (oral or topical), while fungal infections are treated with antifungal medications. Both types require proper hygiene, regular cleaning, and keeping the affected area dry. Professional medical guidance is often necessary for proper treatment selection.
What are the risk factors that increase the chance of developing a foot infection?
Major risk factors include diabetes, poor circulation, weakened immune system, excessive moisture exposure, walking barefoot in public areas, and poor foot hygiene. Having cuts, wounds, or other foot injuries also increases infection risk.
When should I see a doctor for a foot infection instead of trying home remedies?
Seek medical attention if you experience severe pain or swelling, spreading redness, fever, deep wounds, or if you have diabetes. Also consult a healthcare provider if the infection shows no improvement after several days of home treatment.
How can I prevent foot infections, especially athlete's foot, in daily life?
Prevent foot infections by maintaining good foot hygiene, wearing breathable shoes and moisture-wicking socks, avoiding walking barefoot in public areas, regularly inspecting your feet for injuries, and keeping feet dry. Change socks daily and after exercise, and use antifungal powder if prone to athlete's foot.