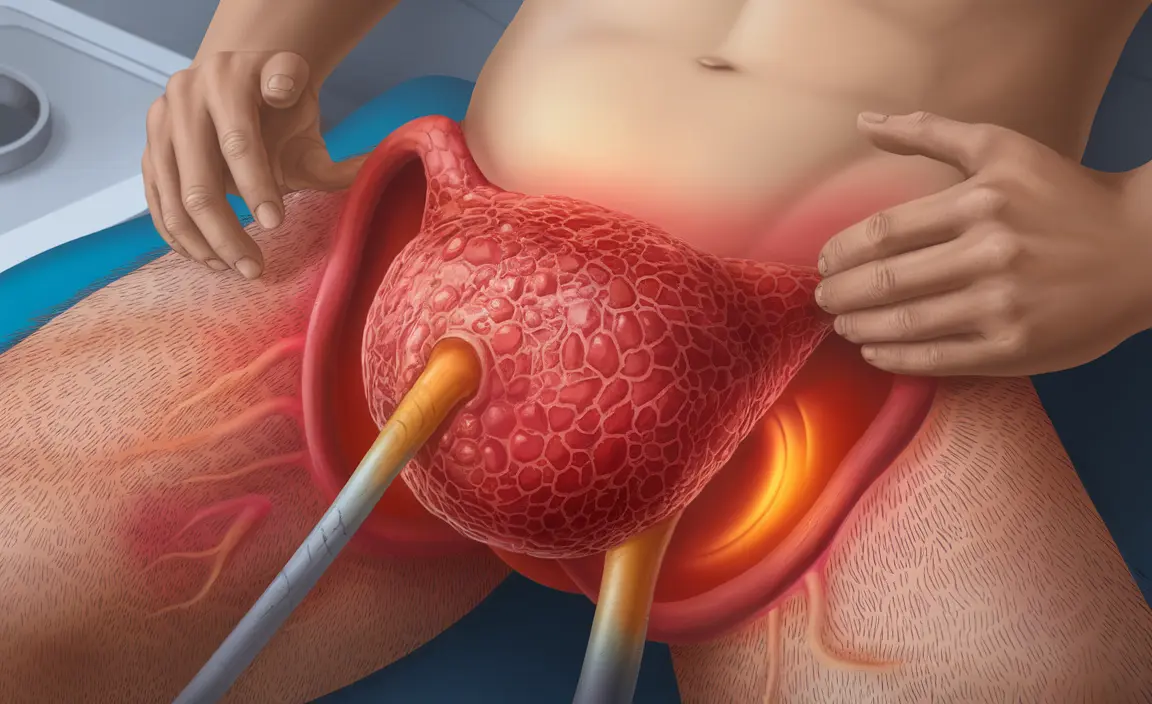
Fournier's gangrene is a rare but severe bacterial infection that primarily affects the genital, perineal, and perianal regions. This potentially life-threatening condition requires immediate medical attention and understanding its signs and symptoms is crucial for early intervention.
While uncommon, this condition can progress rapidly and demands urgent medical care. Knowledge about risk factors, symptoms, and treatment options can make a significant difference in patient outcomes.
Understanding Fournier's Gangrene
Fournier's gangrene is a type of necrotizing fasciitis that specifically targets the soft tissues in the genital and surrounding areas. The infection typically begins in the genital or anal region and can spread rapidly through the tissue planes, causing extensive damage if left untreated.
Early Warning Signs and Symptoms
Recognizing the early signs of Fournier's gangrene is crucial for prompt treatment. Initial symptoms may include:
- Severe pain and tenderness in the affected area
- Swelling of the genitals or perianal region
- Skin discoloration or darkening
- Fever and general malaise
- Foul-smelling discharge
- Crackling sensation under the skin
Risk Factors and Causes
Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing Fournier's gangrene:
- Diabetes mellitus
- Compromised immune system
- Recent surgery or trauma to the area
- Poor personal hygiene
- Obesity
- Alcohol abuse
- Chronic medical conditions
Diagnostic Process
Healthcare providers use various methods to diagnose Fournier's gangrene:
- Physical examination
- Blood tests to check for infection markers
- Imaging studies (CT scans, MRI)
- Tissue cultures to identify specific bacteria
- Assessment of organ function
Treatment Approaches
Treatment for Fournier's gangrene typically involves a multi-faceted approach:
Immediate Interventions
Emergency surgical debridement is the primary treatment, removing all infected and dead tissue. This procedure may need to be repeated multiple times to ensure complete removal of affected tissue.
Additional Treatments
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics
- Wound care and dressing changes
- Hyperbaric oxygen therapy in some cases
- Pain management
- Nutritional support
Prevention and Risk Reduction
While not all cases can be prevented, certain measures can help reduce risk:
- Maintaining good personal hygiene
- Proper management of underlying conditions like diabetes
- Prompt treatment of any cuts or injuries in the affected area
- Regular medical check-ups
- Healthy lifestyle choices
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the early symptoms and signs of Fournier's gangrene that I should watch for?
Early signs include severe pain and tenderness in the genital or anal area, swelling, skin discoloration, fever, and a foul-smelling discharge. Any combination of these symptoms requires immediate medical attention.
What causes Fournier's gangrene and who is most at risk of developing it?
Fournier's gangrene is caused by bacterial infection, often involving multiple types of bacteria. Those at highest risk include individuals with diabetes, compromised immune systems, obesity, or recent trauma to the affected area.
How is Fournier's gangrene diagnosed and what tests are commonly used?
Diagnosis involves physical examination, blood tests, imaging studies (CT scans or MRI), and tissue cultures. Doctors look for characteristic signs of infection and tissue death in the affected areas.
What are the treatment options for Fournier's gangrene and how urgent is the surgery?
Surgery (debridement) is extremely urgent and should be performed as soon as possible after diagnosis. Treatment also includes broad-spectrum antibiotics, wound care, and possibly hyperbaric oxygen therapy.
Can Fournier's gangrene be prevented and what lifestyle factors increase the risk?
While not entirely preventable, risk can be reduced through good hygiene, proper management of underlying conditions, and prompt treatment of wounds. Poor hygiene, obesity, diabetes, and alcohol abuse increase risk.