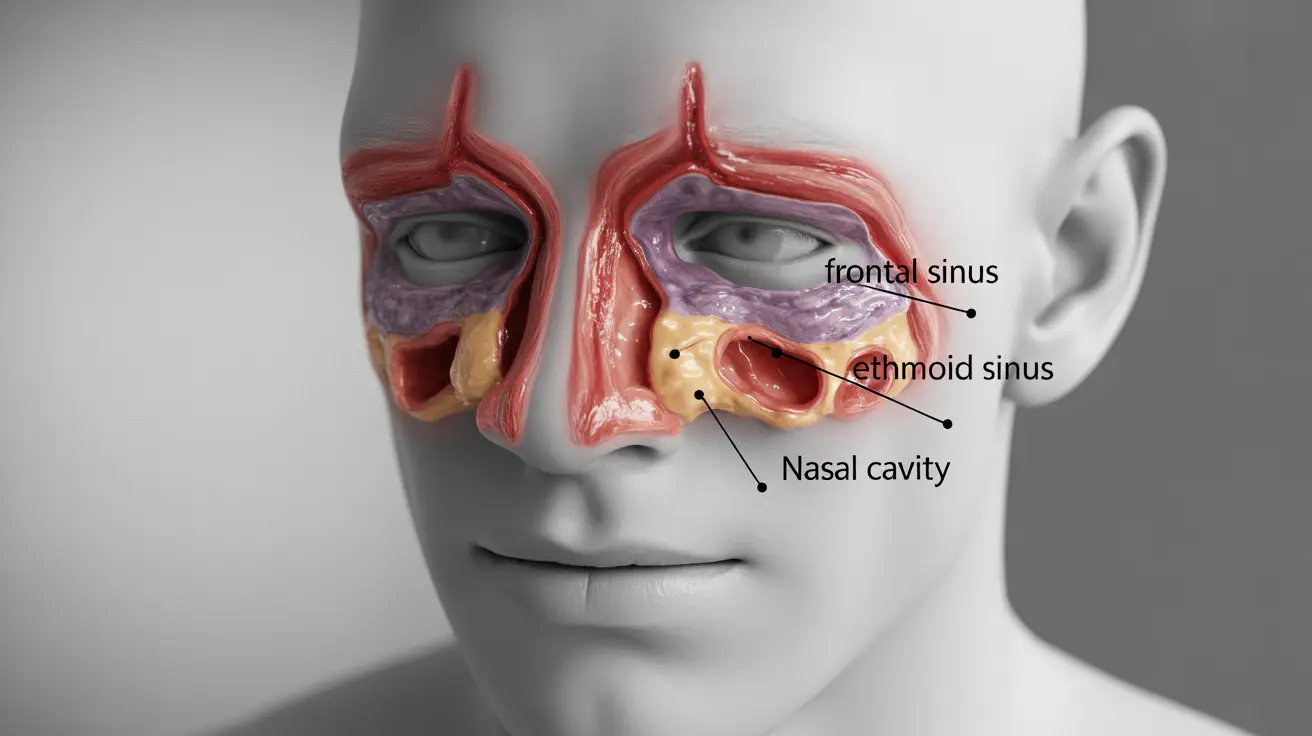
Frontal sinusitis occurs when the sinuses located behind your forehead become inflamed and infected, leading to uncomfortable pressure, pain, and various other symptoms. This condition can significantly impact your daily life, making it essential to understand its causes, recognize its symptoms, and know when to seek medical attention.
Whether caused by viral infections, bacterial growth, or allergic reactions, frontal sinusitis requires proper diagnosis and targeted treatment to achieve relief and prevent chronic complications.
Understanding Frontal Sinusitis and Its Causes
Frontal sinusitis develops when the frontal sinus cavities become inflamed and blocked, preventing proper drainage of mucus. This blockage creates an environment where bacteria can thrive, leading to infection and inflammation.
Common triggers include:
- Viral respiratory infections
- Bacterial infections
- Seasonal allergies
- Environmental irritants
- Structural abnormalities in the nasal passages
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms
The symptoms of frontal sinusitis are distinct and often centered around the forehead area. Common indicators include:
Primary Symptoms
- Intense pressure and pain above the eyes and in the forehead
- Throbbing headaches that worsen when bending forward
- Nasal congestion and discharge
- Reduced sense of smell
- Fatigue and general discomfort
Additional Signs
- Fever (particularly in bacterial cases)
- Post-nasal drip
- Cough that worsens at night
- Bad breath
- Facial tenderness
Diagnostic Process and Medical Evaluation
Healthcare providers diagnose frontal sinusitis through a combination of physical examination and patient history. They may also utilize:
- Nasal endoscopy to examine the sinus passages
- CT scans or MRI in severe or chronic cases
- Cultures of nasal discharge when bacterial infection is suspected
- Allergy testing if allergies are a potential cause
Treatment Approaches and Management Strategies
Immediate Relief Methods
- Saline nasal irrigation
- Over-the-counter decongestants
- Steam inhalation
- Warm compresses on the forehead
- Adequate hydration
Medical Treatments
- Antibiotic therapy for confirmed bacterial infections
- Antihistamines for allergy-related cases
- Nasal corticosteroid sprays
- Oral decongestants when appropriate
Prevention and Long-term Management
Preventing recurrence of frontal sinusitis involves several key strategies:
- Regular hand washing and good hygiene practices
- Using air purifiers to reduce allergens
- Maintaining optimal humidity levels
- Avoiding known triggers and irritants
- Getting annual flu vaccinations
- Managing underlying allergies effectively
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms and signs of frontal sinusitis?
Common symptoms include forehead pain and pressure, nasal congestion, thick nasal discharge, headaches that worsen when bending forward, and reduced sense of smell. Some people may also experience fever, fatigue, and post-nasal drip.
How is frontal sinusitis diagnosed and when should I see a doctor?
Diagnosis typically involves physical examination, review of symptoms, and possibly imaging tests like CT scans. See a doctor if symptoms persist beyond 10 days, are severe, or include high fever and severe headaches.
What are the most effective treatment options for frontal sinusitis caused by viruses, bacteria, and allergies?
Treatment varies by cause: viral cases typically resolve with supportive care, bacterial infections require antibiotics, and allergic cases respond to antihistamines and nasal corticosteroids. Saline irrigation and decongestants can provide relief in all cases.
Can nasal polyps or a deviated septum contribute to chronic frontal sinusitis?
Yes, both conditions can obstruct normal sinus drainage and contribute to chronic frontal sinusitis. These structural issues may require surgical correction if they consistently cause problems.
How can I prevent frontal sinusitis and reduce the risk of recurrence?
Prevention strategies include maintaining good hygiene, managing allergies, using humidifiers, avoiding irritants, staying hydrated, and treating upper respiratory infections promptly. Regular nasal irrigation can also help prevent recurrence.