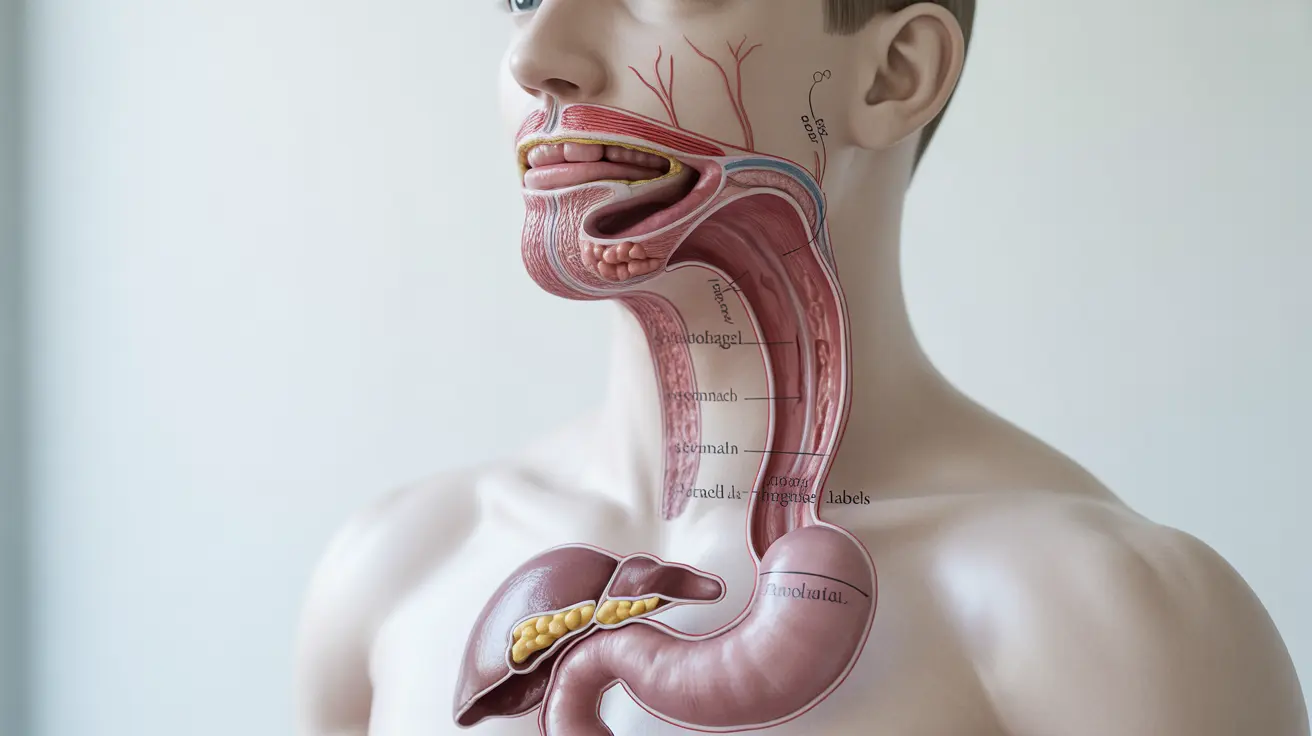
Your digestive system is a remarkable feat of biological engineering that does far more than just process food. This intricate network of organs works tirelessly to keep you healthy, extract nutrients, and even influence your mood. Let's explore some fascinating aspects of this incredible system that might surprise you.
The Remarkable Journey of Food Through Your Body
The digestive process is an extraordinary adventure that begins the moment food enters your mouth. Your digestive system is essentially a 30-foot-long tube that transforms everything you eat into energy and nutrients your body can use. From the first bite to the final stages of digestion, your body orchestrates a complex series of chemical and mechanical processes that break down food into its basic building blocks.
The Power of Saliva: Where Digestion Begins
Your digestive journey starts before you even swallow. Your mouth produces about 1.5 liters of saliva daily, containing powerful enzymes that begin breaking down food immediately. This seemingly simple fluid contains antimicrobial compounds that help protect your body from harmful bacteria.
Your Stomach: Nature's Chemical Laboratory
The stomach is a fascinating organ that produces a new protective lining every two weeks to prevent it from digesting itself. It can expand to hold up to 4 liters of food and liquid, and produces strong acid that's powerful enough to dissolve metal – yet is perfectly contained by your stomach's specialized cells.
The Mighty Small Intestine
If you were to spread out your small intestine's surface area, it would cover a tennis court! This incredible organ contains millions of tiny finger-like projections called villi that maximize nutrient absorption. Every day, your small intestine absorbs up to 90% of the nutrients you consume.
The Second Brain in Your Gut
Your digestive system contains over 100 million neurons – more than in your spinal cord. This extensive network of neural tissue is often called the "second brain" and can operate independently of your central nervous system. It plays a crucial role in not just digestion, but also your emotional well-being and immune response.
The Crucial Role of Gut Bacteria
Your digestive system hosts trillions of beneficial bacteria that collectively weigh about 4 pounds. These microscopic allies help digest food, produce vitamins, and protect you from harmful organisms. They're so numerous that bacterial cells in your gut outnumber your body's own cells!
Maintaining Digestive Health
Supporting your digestive system's health is crucial for overall wellbeing. Regular exercise, staying hydrated, eating a fiber-rich diet, and managing stress can all contribute to optimal digestive function. Even small changes in your daily routine can have significant impacts on your digestive health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some surprising facts about how the digestive system works?
The digestive system produces about 2 liters of saliva daily, contains more neurons than the spinal cord, and has enough bacteria to weigh about 4 pounds. Your stomach acid is strong enough to dissolve metal, and your small intestine, if spread out, would cover a tennis court.
How long does it take food to travel through the entire digestive tract?
Food typically takes between 24-72 hours to complete its journey through the digestive tract. The exact time varies depending on the type of food consumed and individual factors like activity level and overall health.
What role do enzymes and bacteria play in digestion?
Enzymes break down food into smaller, absorbable nutrients, while beneficial bacteria help further break down food, produce vitamins, and protect against harmful organisms. Together, they're essential for proper nutrient absorption and digestive health.
Why is the digestive system called the "second brain"?
The digestive system contains over 100 million neurons and can operate independently of the central nervous system. This extensive neural network influences mood, immune response, and overall wellbeing, earning it the nickname "second brain."
What are simple ways to keep the digestive system healthy and working well?
Maintain digestive health by eating a balanced, fiber-rich diet, staying hydrated, exercising regularly, managing stress, and establishing regular eating patterns. Limiting processed foods and getting adequate sleep also support optimal digestive function.