The human muscular system is a fascinating network of tissues that powers everything from your heartbeat to your smile. These remarkable structures work tirelessly throughout your life, enabling movement, maintaining posture, and performing countless vital functions that keep you alive and active.
Let's explore some incredible facts about muscles that showcase just how remarkable these essential body tissues truly are, from their diverse types to their crucial roles in your daily life.
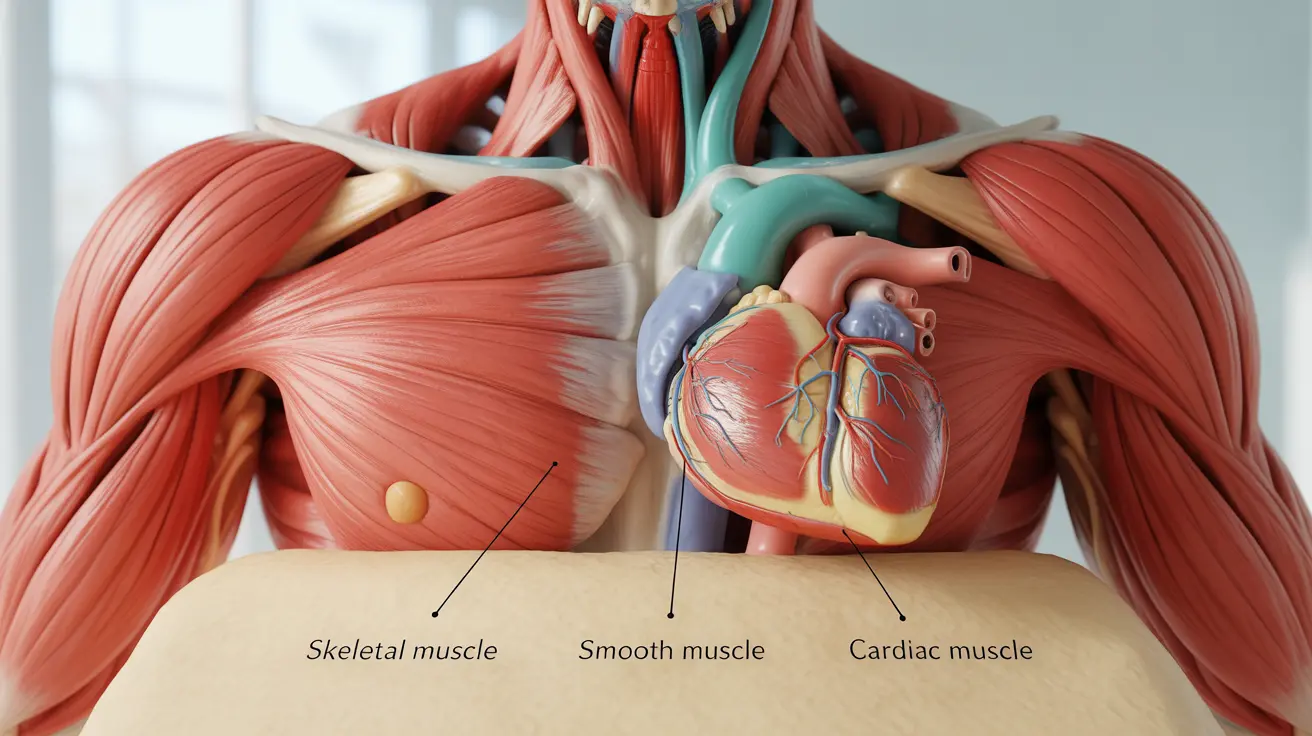
Types of Muscles: The Three Mighty Forces
Your body contains three distinct types of muscle tissue, each specialized for specific functions:
- Skeletal muscles: Attached to bones, enabling voluntary movement
- Smooth muscles: Found in internal organs, working automatically
- Cardiac muscle: The specialized heart muscle that never stops working
Each type has unique characteristics and plays vital roles in maintaining your health and bodily functions. Skeletal muscles are the ones you can consciously control, while smooth and cardiac muscles work autonomously to keep your body functioning.
The Power of Movement and Stability
Muscles are incredible powerhouses that do much more than just help you move. They work in pairs, with one contracting while the other relaxes, creating smooth, controlled movements. This coordinated effort allows you to perform everything from delicate tasks like threading a needle to powerful movements like lifting weights.
Posture and Balance
Your muscles play a crucial role in maintaining proper posture and balance. Core muscles, including those in your abdomen and back, work constantly to keep your spine aligned and your body upright. Even when you're standing still, multiple muscle groups are actively working to maintain your position.
Impressive Muscle Statistics
The human body contains approximately 650 skeletal muscles, but this represents only one type of muscle tissue. When including smooth and cardiac muscles, the numbers are even more impressive. Muscles make up about 30-40% of your total body weight, highlighting their significance in your body's composition.
The Largest and Smallest Muscles
The gluteus maximus, located in your buttocks, holds the title of largest muscle in the body. This powerful muscle is essential for maintaining an upright posture and enabling movements like climbing stairs. In contrast, the stapedius in your middle ear is the smallest, helping to dampen loud sounds to protect your hearing.
Automatic vs. Voluntary Control
While you can consciously control your skeletal muscles, many muscles in your body work automatically. Your heart muscle beats about 100,000 times per day without any conscious effort. Similarly, smooth muscles in your digestive system, blood vessels, and other organs work continuously without your awareness.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the different types of muscles in the human body and their main functions?
The human body has three types of muscles: skeletal muscles for voluntary movement and posture, smooth muscles for internal organ function, and cardiac muscle specifically for heart contractions. Each type is specialized for its specific role.
- How do muscles help maintain posture and body position?
Muscles maintain posture through constant, coordinated contractions of various muscle groups, particularly in the core, back, and legs. These muscles work together to keep your spine aligned and body balanced against gravity.
- What is the largest muscle in the human body and what is its role?
The gluteus maximus is the largest muscle in the body. It plays a crucial role in hip extension, maintaining an upright posture, and powering movements like climbing stairs, running, and jumping.
- Are all muscles under voluntary control, or are there some that work automatically?
Not all muscles are under voluntary control. Skeletal muscles are voluntary, while smooth muscles (in organs) and cardiac muscle (heart) work automatically through the autonomic nervous system.
- What percentage of the body's total weight is made up of muscles?
Muscles typically make up between 30-40% of total body weight in adults. This percentage can vary based on factors such as age, gender, and physical fitness level.
Understanding these fascinating aspects of the muscular system helps us appreciate the complexity and importance of maintaining muscle health through proper nutrition and regular exercise.