When experiencing severe abdominal or back pain, determining whether you're dealing with gallstones or kidney stones is crucial for proper treatment. While both conditions involve solid deposits forming within the body, they differ significantly in their location, causes, symptoms, and treatment approaches. This comprehensive guide will help you understand the key distinctions between these common health conditions.
Location and Formation
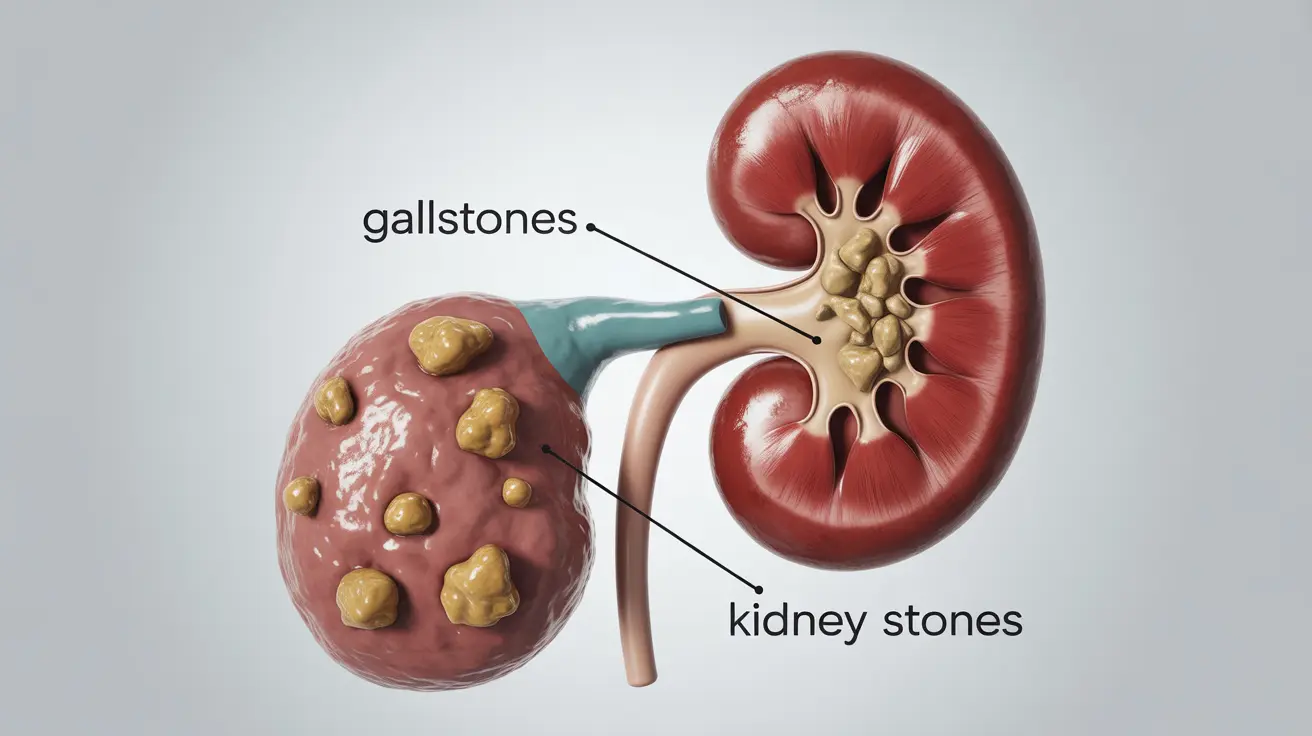
Gallstones and kidney stones develop in entirely different organ systems. Gallstones form in the gallbladder, a small organ beneath the liver that stores bile, while kidney stones develop in the kidneys, which filter waste from blood. Understanding these distinct locations helps explain why symptoms and treatments vary significantly between the two conditions.
Composition and Causes
The chemical makeup of these stones differs considerably, reflecting their unique origins within the body. Gallstones typically form from cholesterol or bilirubin, components of bile that crystallize when the bile becomes imbalanced. In contrast, kidney stones usually consist of calcium oxalate, uric acid, or struvite, resulting from concentrated minerals in urine.
Common Causes of Gallstones
- High cholesterol levels
- Inefficient gallbladder emptying
- Increased bilirubin production
- Rapid weight loss or frequent fasting
Common Causes of Kidney Stones
- Dehydration
- High-sodium diet
- Excessive animal protein consumption
- Certain medical conditions
- Family history
Distinctive Symptoms and Pain Patterns
The location and nature of pain can help distinguish between these conditions. Gallstone pain typically occurs in the upper right abdomen and may intensify after meals, particularly fatty foods. This pain, known as biliary colic, can last several hours.
Kidney stone pain, often called renal colic, typically begins in the back or side and may radiate to the lower abdomen and groin. The pain can be severe and comes in waves as the stone moves through the urinary tract. Unlike gallstone pain, kidney stone discomfort isn't typically related to eating.
Diagnosis Methods
Healthcare providers use different diagnostic approaches for each condition. Gallstones are typically diagnosed through ultrasound imaging or CT scans, while kidney stones may require a combination of CT scans, ultrasound, and urinalysis. Blood tests can help identify complications associated with either condition.
Treatment Approaches
Treatment options vary significantly between the two conditions. Gallstones often require surgical removal through cholecystectomy if they cause symptoms. Some patients may be candidates for nonsurgical treatments, though these are less common.
Kidney stones, depending on their size, may pass naturally with increased fluid intake and pain management. Larger stones might require procedures such as shock wave lithotripsy or surgical removal. The choice of treatment depends on stone size, location, and severity of symptoms.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing these conditions requires different lifestyle modifications. For gallstones, maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding rapid weight loss, and eating regular meals can help. Kidney stone prevention typically focuses on proper hydration, reducing sodium intake, and moderating animal protein consumption.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main differences between gallstones and kidney stones in terms of causes and composition? Gallstones primarily form from cholesterol or bilirubin in the gallbladder, while kidney stones develop from minerals like calcium oxalate or uric acid in the kidneys. Gallstones result from bile imbalances, whereas kidney stones form when urine becomes too concentrated with crystal-forming substances.
How can I tell if the pain I'm experiencing is from gallstones or kidney stones based on location and symptoms? Gallstone pain typically occurs in the upper right abdomen and may worsen after meals. Kidney stone pain usually starts in the back or side, radiating to the lower abdomen and groin, and isn't related to eating.
What are the common risk factors that increase the likelihood of developing gallstones versus kidney stones? Gallstone risk factors include obesity, rapid weight loss, high cholesterol, and certain medications. Kidney stone risk factors include dehydration, high-sodium diets, family history, and certain medical conditions.
How are gallstones and kidney stones diagnosed and what tests are used to confirm each condition? Gallstones are typically diagnosed through ultrasound or CT scans. Kidney stones require CT scans, ultrasound, and urinalysis for diagnosis. Blood tests may be used to check for complications in both conditions.
What treatment options and lifestyle changes help prevent and manage gallstones compared to kidney stones? Gallstones often require surgical removal through cholecystectomy, while kidney stones may pass naturally or require procedures like lithotripsy. Prevention for gallstones focuses on maintaining healthy weight and regular meals, while kidney stone prevention emphasizes hydration and dietary modifications.