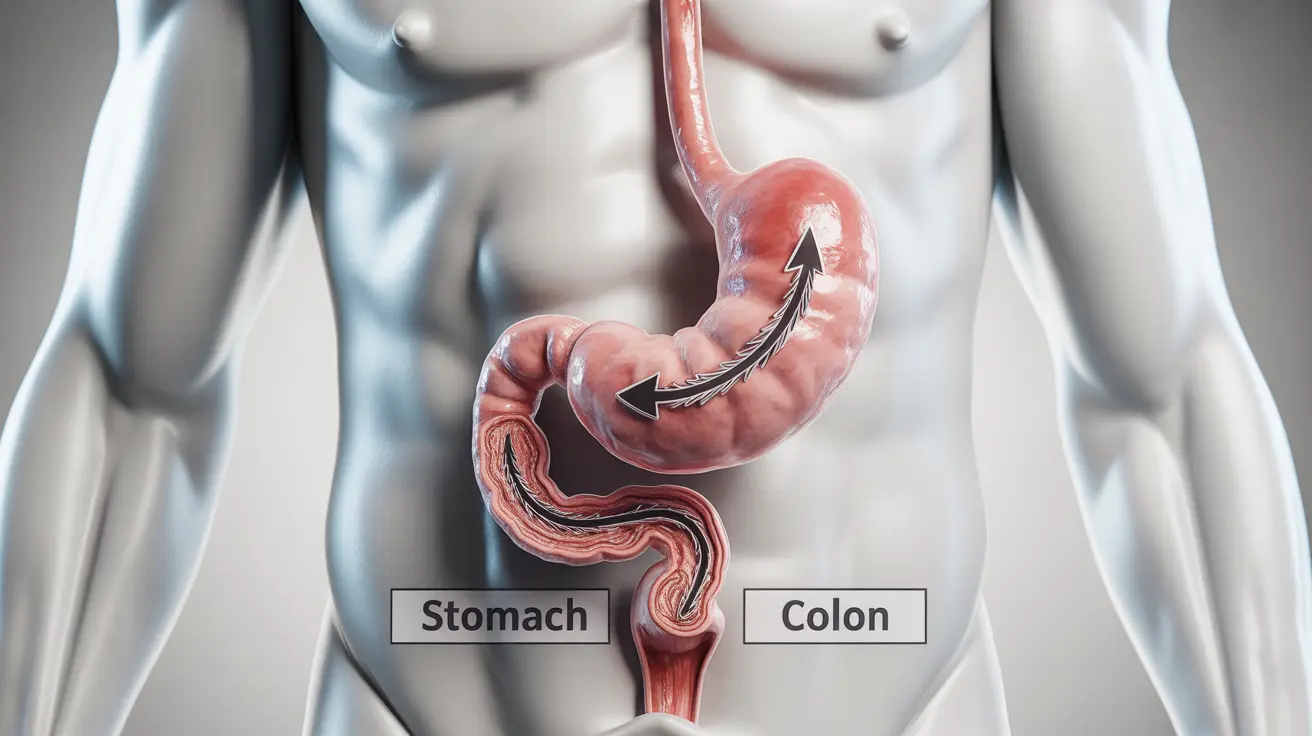
The gastrocolic reflex is a natural bodily response that triggers bowel movements shortly after eating. While this reflex is normal, some people experience an overactive response that can disrupt daily life. Understanding effective treatment options and management strategies is crucial for those dealing with pronounced gastrocolic reflex symptoms.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore various treatment approaches, from dietary modifications to medications, and discuss lifestyle changes that can help manage this condition effectively.
Understanding the Gastrocolic Reflex
The gastrocolic reflex is part of your body's natural digestive process, occurring when food enters your stomach and triggers contractions in your colon. For most people, this process happens smoothly, but some individuals experience a more intense response that requires medical attention and lifestyle adjustments.
Dietary Management Strategies
Meal Timing and Portion Control
Managing your eating schedule and portion sizes can significantly impact the intensity of the gastrocolic reflex. Consider eating smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day rather than large meals. This approach can help reduce the strength of the reflex and make symptoms more manageable.
Foods to Choose and Avoid
Certain dietary choices can help regulate your gastrocolic reflex:
- Low-fat foods
- High-fiber foods (introduced gradually)
- Lean proteins
- Well-cooked vegetables
- Complex carbohydrates
Foods that may trigger stronger reactions include:
- Fatty or fried foods
- Caffeine
- Spicy dishes
- Artificial sweeteners
- High-sugar foods
Medical Treatment Options
Prescription Medications
Several medications can help manage an overactive gastrocolic reflex:
- Antispasmodics to reduce intestinal contractions
- Anti-diarrheal medications for symptom relief
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) in some cases
- Anticholinergic medications to slow digestive processes
Over-the-Counter Solutions
Various OTC options may provide relief from symptoms:
- Fiber supplements
- Probiotics
- Digestive enzymes
- Mild antacids
Lifestyle Modifications
Stress Management
Stress can significantly impact digestive functions and worsen gastrocolic reflex symptoms. Incorporating stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga can help manage symptoms effectively.
Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular physical activity can help regulate bowel movements and reduce symptom severity. However, it's important to time your workouts appropriately, avoiding intense exercise immediately after meals.
Frequently Asked Questions
What dietary changes can help manage an overactive gastrocolic reflex? Eating smaller, more frequent meals, focusing on low-fat foods, and gradually increasing fiber intake can help manage symptoms. Avoid trigger foods like caffeine, spicy dishes, and fatty meals. Stay well-hydrated and maintain regular meal times.
How do medications like antispasmodics or laxatives treat gastrocolic reflex symptoms? Antispasmodics work by reducing intestinal muscle contractions, while laxatives can help regulate bowel movements. These medications should be used under medical supervision as part of a comprehensive treatment plan that may include other medications depending on symptom severity.
Can stress or certain foods trigger a stronger gastrocolic reflex and worsen symptoms? Yes, both stress and certain foods can intensify the gastrocolic reflex. High-fat meals, caffeine, and spicy foods are common triggers. Stress can increase gut sensitivity and strengthen the reflex response, making symptom management more challenging.
What lifestyle habits can reduce discomfort caused by the gastrocolic reflex after eating? Regular exercise, stress management techniques, maintaining consistent meal times, and proper posture while eating can help reduce discomfort. Avoiding lying down immediately after meals and practicing mindful eating can also be beneficial.
When should I see a doctor about urgent bowel movements or diarrhea related to the gastrocolic reflex? Seek medical attention if you experience persistent diarrhea, severe abdominal pain, significant weight loss, or if symptoms interfere with daily activities. Also consult a healthcare provider if you notice blood in stools or develop new or worsening symptoms.