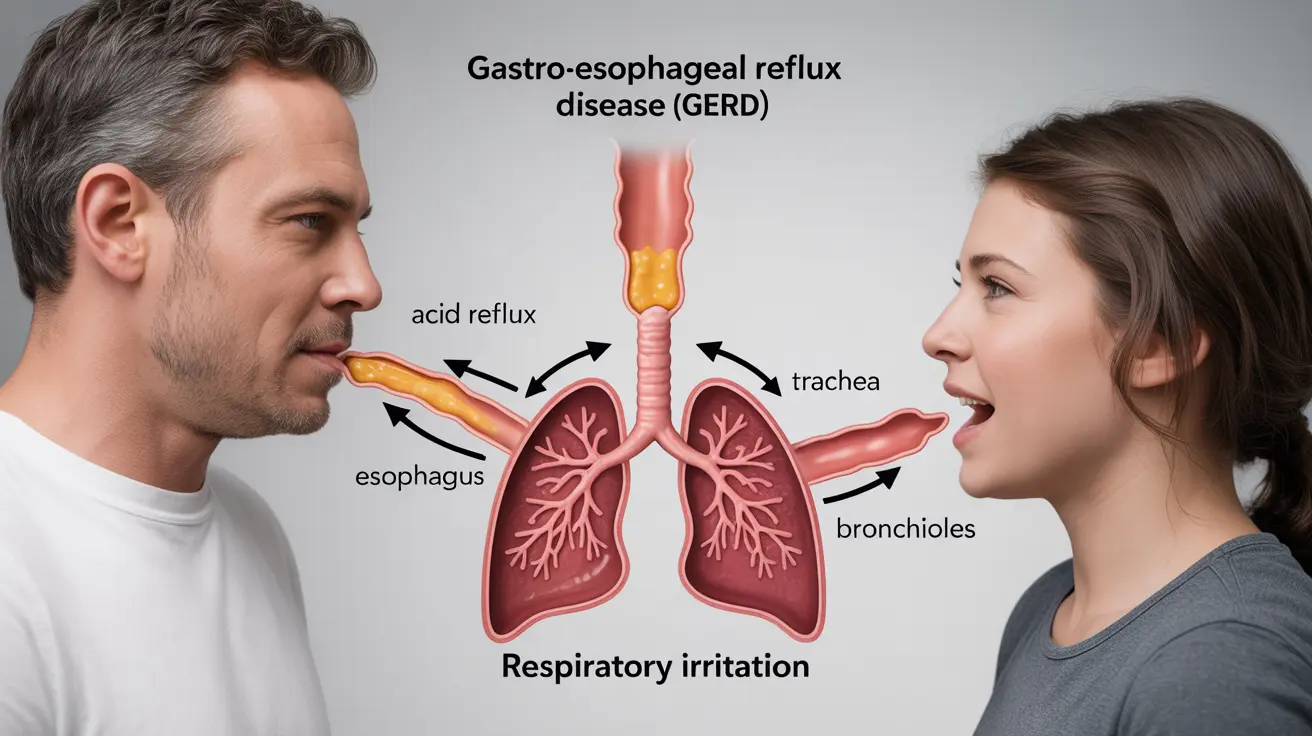
The relationship between gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and asthma represents a complex medical interaction that affects millions of people worldwide. These two conditions often coexist and can create a challenging cycle where each condition potentially worsens the other. Understanding this connection is crucial for effective management of both conditions.
Recent research suggests that up to 80% of people with asthma also experience GERD symptoms, highlighting the significant overlap between these two conditions. This article explores the intricate relationship between GERD and asthma, their mutual effects, and effective management strategies.
The GERD-Asthma Connection Explained
GERD and asthma share a bidirectional relationship, meaning they can influence and trigger each other in various ways. When stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, it can irritate nerve endings that connect to the lungs, potentially triggering asthma symptoms. Similarly, the pressure changes during asthma episodes can affect the lower esophageal sphincter, increasing the likelihood of acid reflux.
How GERD Triggers Asthma Symptoms
Several mechanisms explain how GERD can worsen asthma symptoms:
- Microaspiration of stomach acid into the airways
- Vagal nerve stimulation causing bronchial constriction
- Increased inflammation in the airways
- Enhanced bronchial sensitivity to other triggers
Impact of Asthma Medications on GERD
Certain asthma medications can affect GERD symptoms due to their impact on the lower esophageal sphincter. Common medications that may influence GERD include:
- Beta-agonists (bronchodilators)
- Theophylline
- Oral corticosteroids
However, this doesn't mean patients should stop taking their asthma medications. Instead, proper management of both conditions requires careful coordination with healthcare providers.
Identifying GERD-Related Asthma Symptoms
Several signs may indicate that GERD is contributing to asthma symptoms:
- Increased asthma symptoms after meals
- Worsening asthma symptoms while lying down
- Chronic cough, particularly at night
- Frequent throat clearing
- Hoarseness or voice changes
Treatment Approaches for Combined GERD and Asthma
Managing both conditions effectively often requires a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses both GERD and asthma simultaneously. Treatment options may include:
Medications
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs)
- H2 blockers
- Asthma controllers and rescue medications
Lifestyle Modifications
- Elevating the head of the bed
- Avoiding trigger foods
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Eating smaller, more frequent meals
- Not lying down for 2-3 hours after eating
Frequently Asked Questions
How does gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) worsen asthma symptoms?
GERD can worsen asthma symptoms through acid reflux irritating the airways, causing inflammation, and triggering bronchial spasms. The acid can also be microaspirated into the lungs, leading to increased airway reactivity and inflammation.
Can asthma medications cause or increase acid reflux and GERD symptoms?
Yes, certain asthma medications, particularly beta-agonists and theophylline, can relax the lower esophageal sphincter, potentially increasing acid reflux. However, patients should not discontinue these medications without consulting their healthcare provider.
What are the common signs that GERD may be triggering asthma attacks?
Common signs include worsening asthma symptoms after meals or while lying down, increased nighttime asthma symptoms, chronic cough, and difficulty controlling asthma despite proper medication use.
How is GERD treated to help improve asthma control?
GERD treatment typically involves acid-suppressing medications like PPIs or H2 blockers, combined with lifestyle modifications. Effectively controlling GERD often leads to better asthma control.
What lifestyle changes can reduce acid reflux and help manage both GERD and asthma?
Key lifestyle changes include maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding trigger foods, eating smaller meals, not lying down after eating, elevating the head of the bed, and quitting smoking. These modifications can help manage both conditions effectively.