The human body contains an intricate network of glands that play crucial roles in maintaining health, regulating bodily functions, and ensuring proper growth and development. These specialized organs produce and release substances that help coordinate various biological processes, from metabolism and growth to emotional responses and sexual function.
Whether you're dealing with hormonal issues or simply want to better understand your body's complex systems, learning about the different types of glands and their functions is essential for maintaining optimal health. Let's explore the fascinating world of glands and how they impact your daily life.
Types of Glands and Their Primary Functions
The human body features two main categories of glands: endocrine and exocrine. Each type serves distinct purposes in maintaining bodily functions and overall health.
Endocrine Glands
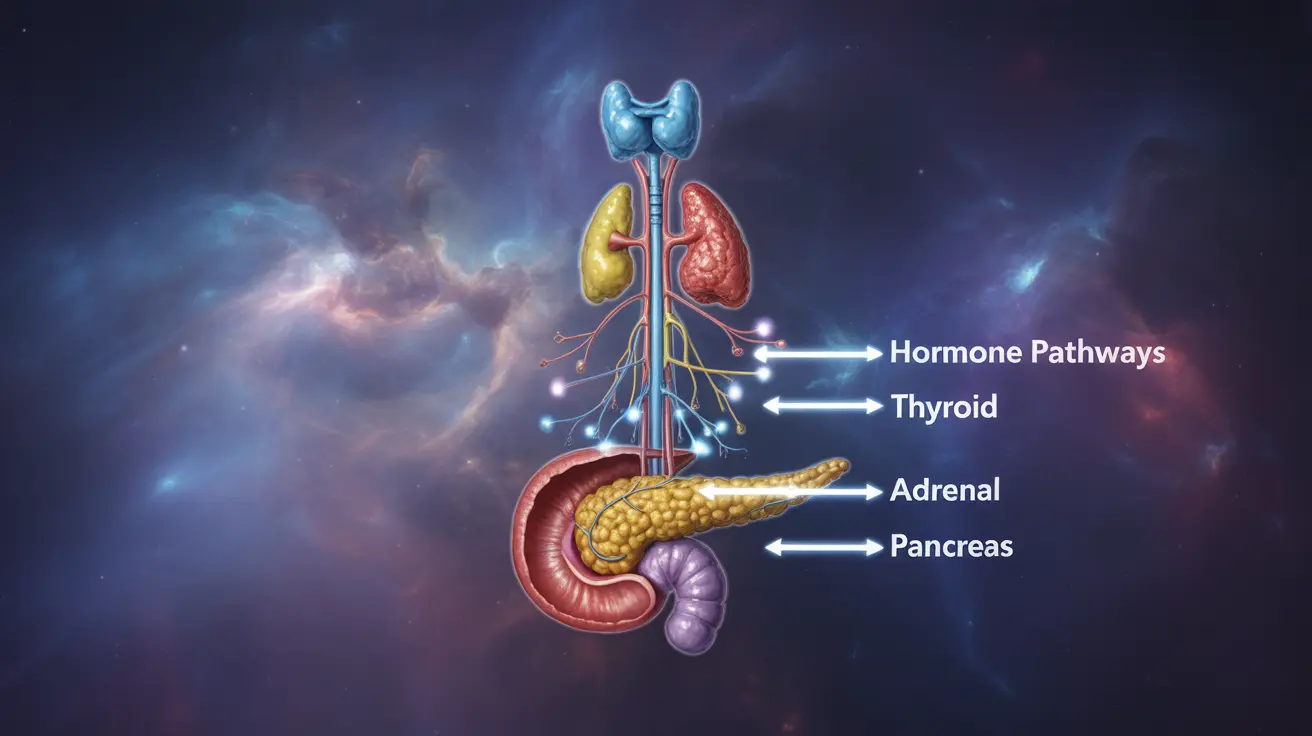
Endocrine glands secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream. Key endocrine glands include:
- Pituitary gland (the "master gland")
- Thyroid gland
- Parathyroid glands
- Adrenal glands
- Pancreas
- Ovaries (in females)
- Testes (in males)
Exocrine Glands
Exocrine glands release their products through ducts to specific areas. Common examples include:
- Sweat glands
- Salivary glands
- Mammary glands
- Sebaceous glands
- Digestive glands
The Endocrine System: Hormones and Their Impact
The endocrine system works through complex hormone signaling pathways that influence nearly every aspect of human health. These chemical messengers regulate:
- Metabolism and energy levels
- Growth and development
- Mood and emotional well-being
- Reproductive functions
- Sleep patterns
- Blood sugar levels
Common Gland Disorders and Warning Signs
Glandular dysfunction can manifest through various symptoms. Key warning signs include:
- Unexplained weight changes
- Unusual fatigue or energy fluctuations
- Mood swings or depression
- Sleep disturbances
- Changes in appetite
- Irregular heart rate
- Temperature sensitivity
Supporting Healthy Gland Function
Maintaining healthy gland function requires a comprehensive approach to wellness, including:
- Regular exercise
- Balanced nutrition
- Stress management
- Adequate sleep
- Regular medical check-ups
- Limiting exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main types of glands in the body and how do they differ in function?
The body has two main types of glands: endocrine glands, which release hormones directly into the bloodstream, and exocrine glands, which secrete substances through ducts. Endocrine glands regulate body processes internally, while exocrine glands produce substances like sweat, saliva, and digestive enzymes.
How do endocrine glands affect things like mood, growth, and metabolism through hormones?
Endocrine glands release hormones that act as chemical messengers, traveling through the bloodstream to target specific organs and tissues. These hormones regulate metabolism, influence emotional states, control growth and development, and maintain various bodily functions like blood sugar levels and reproductive processes.
What are some common signs that my thyroid or adrenal glands might not be working properly?
Common signs of thyroid dysfunction include unexplained weight changes, fatigue, depression, and sensitivity to temperature. Adrenal gland issues may present with symptoms like extreme fatigue, weakness, salt cravings, and blood pressure changes. Any persistent symptoms should be evaluated by a healthcare provider.
Can glands in the body heal or repair themselves, and what happens when they stop working as they should?
Glands have some capacity for self-repair, but severe damage may require medical intervention. When glands stop functioning properly, the body's hormone balance is disrupted, leading to various health issues. Treatment options depend on the specific condition and may include hormone replacement therapy or other medical interventions.
Are there foods, supplements, or lifestyle changes that support healthy gland function?
Yes, several lifestyle factors can support gland health. A balanced diet rich in nutrients like iodine, selenium, and zinc; regular exercise; stress management; and adequate sleep all contribute to healthy gland function. Some people may benefit from specific supplements, but these should be taken only under medical supervision.