GLP-1 receptor agonists have emerged as a groundbreaking treatment option for individuals struggling with obesity and weight management. These medications mimic natural hormones in your body to help control appetite and promote weight loss through multiple mechanisms. Understanding how these drugs work and what to expect from treatment can help you make informed decisions about your weight loss journey.
As more healthcare providers prescribe GLP-1 medications for weight management, it's crucial to understand their benefits, limitations, and proper usage. This comprehensive guide will explore everything you need to know about GLP-1 medications for weight loss.
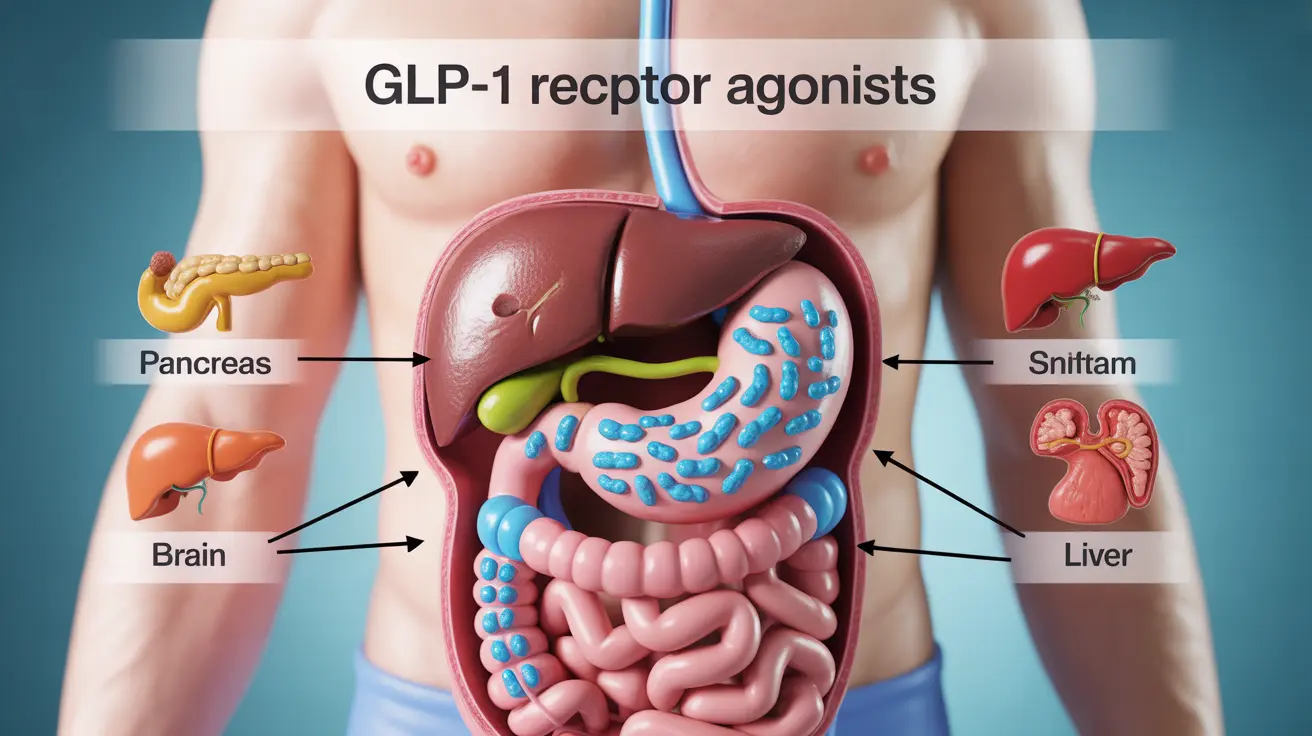
How GLP-1 Medications Work for Weight Loss
GLP-1 receptor agonists work by mimicking a natural hormone called glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1). This hormone plays several important roles in weight management:
- Slows down stomach emptying
- Reduces appetite signals in the brain
- Increases feelings of fullness after meals
- Helps regulate blood sugar levels
By targeting these multiple pathways, GLP-1 medications help create sustainable weight loss through both reduced caloric intake and improved metabolic function.
Expected Weight Loss Results
Clinical studies have shown significant weight loss results with GLP-1 medications when combined with lifestyle modifications. Most patients can expect to lose between 10-15% of their initial body weight within the first year of treatment, though individual results may vary.
Factors Affecting Weight Loss Success
Several factors can influence your weight loss results with GLP-1 medications:
- Adherence to medication schedule
- Dietary choices and portion control
- Physical activity levels
- Starting BMI and overall health status
- Consistent follow-up with healthcare providers
Administration and Usage Guidelines
GLP-1 medications are typically administered through subcutaneous injection. Most formulations require weekly dosing, though some versions may have different schedules. Your healthcare provider will start you on a lower dose and gradually increase it to minimize side effects.
Important Usage Tips
To maximize the benefits of GLP-1 medications:
- Follow your prescribed dosing schedule exactly
- Store medication properly according to instructions
- Learn proper injection technique from your healthcare provider
- Monitor and record your weight loss progress
- Maintain regular medical check-ups
Safety and Side Effects
While GLP-1 medications are generally considered safe for long-term use, they can cause various side effects, particularly during the initial weeks of treatment. Understanding these potential effects is crucial for proper management.
Common Side Effects
The most frequently reported side effects include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Decreased appetite
- Injection site reactions
- Fatigue
Frequently Asked Questions
How do GLP-1 receptor agonists help with weight loss and appetite control?
GLP-1 receptor agonists work by mimicking natural hormones that regulate appetite and digestion. They slow stomach emptying, reduce hunger signals in the brain, and increase feelings of fullness, leading to reduced caloric intake and sustainable weight loss.
What are the common side effects of GLP-1 weight loss medications like semaglutide?
Common side effects include gastrointestinal issues such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Most side effects are mild to moderate and tend to decrease over time as your body adjusts to the medication.
How much weight can I expect to lose using GLP-1 drugs for obesity treatment?
Most patients can expect to lose 10-15% of their initial body weight within the first year of treatment when combined with lifestyle modifications. Individual results may vary based on factors such as adherence to treatment, diet, and exercise habits.
Are GLP-1 medications safe for long-term use in weight management?
Clinical studies have shown that GLP-1 medications are generally safe for long-term use under medical supervision. Regular monitoring by your healthcare provider helps ensure ongoing safety and effectiveness of the treatment.
How are GLP-1 receptor agonists administered and what should I know about their usage?
GLP-1 medications are typically administered through weekly subcutaneous injections. Proper storage, correct injection technique, and adherence to the prescribed dosing schedule are essential for optimal results. Your healthcare provider will provide detailed instructions and gradually increase your dose to minimize side effects.