The relationship between gout and diabetes represents a significant health concern that affects millions of people worldwide. These two metabolic conditions share several risk factors and often occur together, making it crucial to understand their connection and how they influence each other.
Recent research has revealed important insights into how these conditions are interrelated, particularly through mechanisms involving insulin resistance and uric acid metabolism. Understanding these connections can help healthcare providers and patients better manage both conditions.
The Biological Connection Between Gout and Diabetes
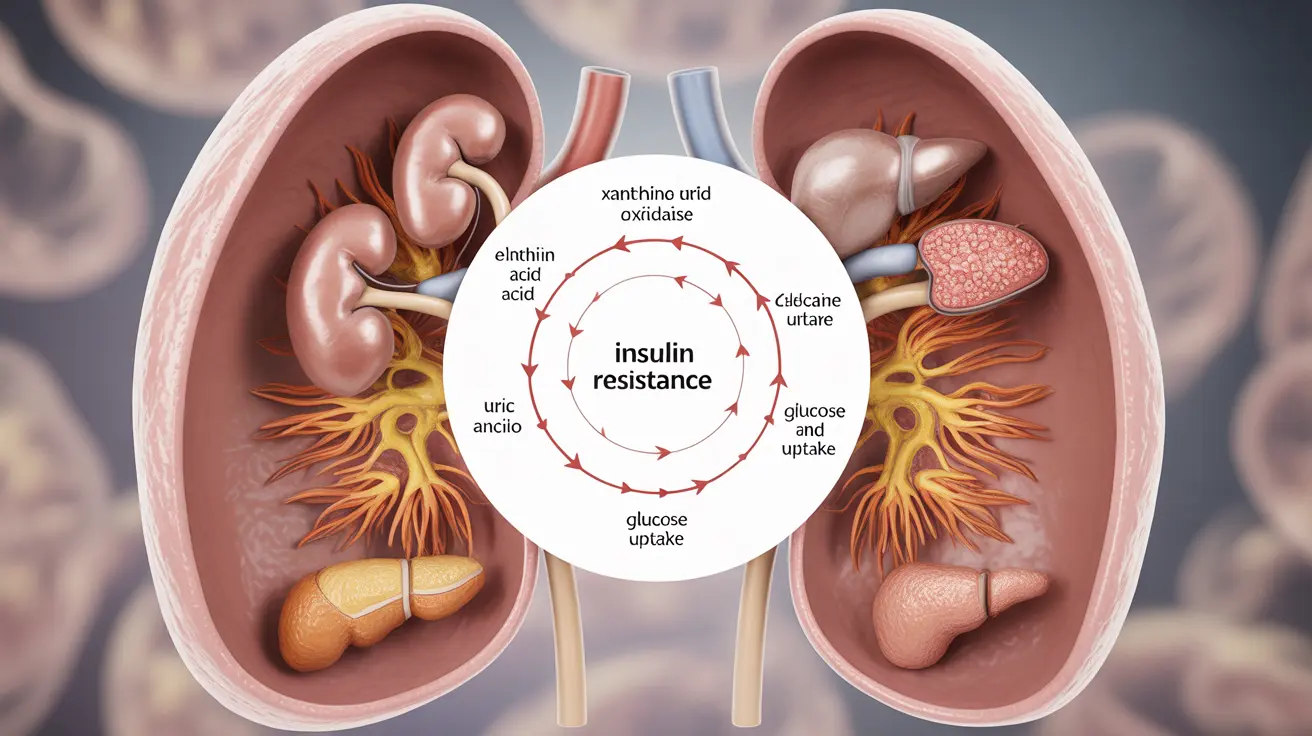
Gout and diabetes share common physiological pathways that can influence each other's development and progression. When the body struggles to process insulin effectively, it can lead to elevated uric acid levels, the primary cause of gout. Similarly, high uric acid levels may contribute to insulin resistance, creating a potential cycle of metabolic dysfunction.
The Role of Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance plays a central role in both conditions. When cells become resistant to insulin, it affects how the body processes both glucose and uric acid. This metabolic disruption can lead to:
- Increased uric acid production
- Reduced uric acid excretion
- Elevated blood sugar levels
- Inflammation throughout the body
Risk Factors and Prevention Strategies
Several shared risk factors contribute to both gout and diabetes:
- Obesity
- Poor dietary choices
- Sedentary lifestyle
- High blood pressure
- Family history
Managing Uric Acid Levels
Controlling uric acid levels is crucial for gout management and may help reduce diabetes risk. Regular monitoring of uric acid levels, along with appropriate medication when necessary, can help prevent gout attacks and potentially improve insulin sensitivity.
Lifestyle Modifications for Both Conditions
Adopting healthy lifestyle changes can significantly impact both conditions:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Following a balanced diet low in purines and refined sugars
- Regular physical activity
- Limiting alcohol consumption
- Staying properly hydrated
Gender Differences and Risk Patterns
Research suggests that the relationship between gout and diabetes may vary between men and women. Women with gout often face unique challenges, including potentially higher risks for developing diabetes compared to their male counterparts. This difference might be related to hormonal factors and different patterns of inflammation between genders.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the connection between gout and type 2 diabetes?
Gout and type 2 diabetes are connected through shared metabolic pathways involving insulin resistance and uric acid metabolism. People with one condition are at higher risk of developing the other due to these overlapping mechanisms.
How does insulin resistance link gout and diabetes?
Insulin resistance affects how the body processes both glucose and uric acid. When cells become resistant to insulin, it can lead to increased uric acid production and reduced excretion, while also disrupting blood sugar control.
Can managing uric acid levels help prevent diabetes in people with gout?
Research suggests that controlling uric acid levels may help improve insulin sensitivity and potentially reduce diabetes risk. However, this should be part of a comprehensive approach to health management.
What lifestyle changes can reduce the risk of both gout and diabetes?
Key lifestyle modifications include maintaining a healthy weight, following a balanced diet, regular exercise, limiting alcohol intake, and staying hydrated. These changes can help manage both conditions effectively.
Are women with gout more likely to develop diabetes than men?
Some studies indicate that women with gout may have a higher risk of developing diabetes compared to men with gout. This difference may be related to hormonal factors and varying inflammatory responses between genders.