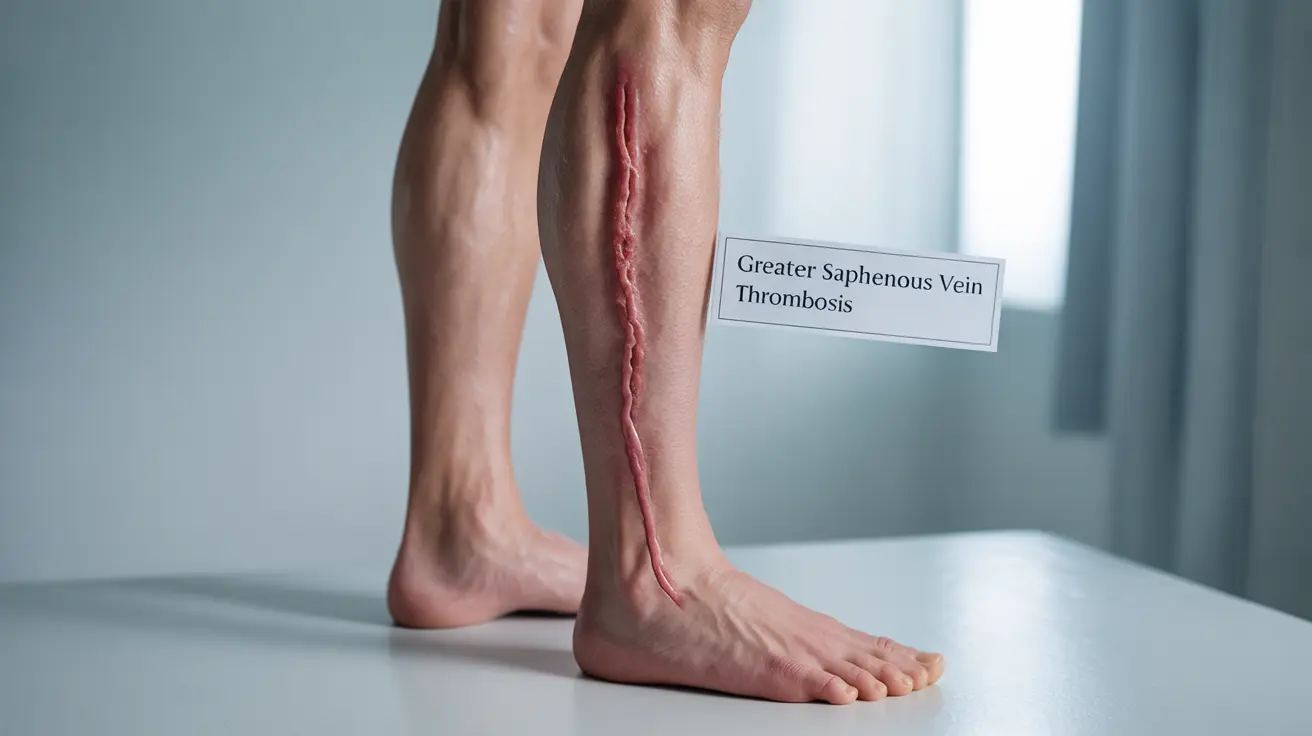
Greater saphenous vein thrombosis is a medical condition where a blood clot forms in the large superficial vein that runs along the inner leg from the ankle to the groin. While less common than deep vein thrombosis (DVT), this condition requires prompt medical attention to prevent potential complications and ensure proper treatment.
Understanding the symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options for greater saphenous vein thrombosis is crucial for early detection and successful management. This comprehensive guide will help you recognize the signs and know when to seek medical care.
Key Symptoms to Watch For
Greater saphenous vein thrombosis typically presents with several distinctive symptoms that can help identify the condition:
- Visible red streak along the inner thigh or leg
- Tenderness or pain along the vein's path
- Warmth in the affected area
- Swelling of the leg
- Hardening or rope-like feeling under the skin
- Skin redness over the affected vein
Diagnosis Process
Healthcare providers use several methods to accurately diagnose greater saphenous vein thrombosis:
Physical Examination
The doctor will carefully examine the affected leg, looking for visible signs of inflammation and feeling for tenderness along the vein's path.
Diagnostic Tests
- Ultrasound imaging (most common method)
- Doppler flow studies
- Blood tests to check for clotting disorders
- Complete medical history review
Treatment Approaches
Treatment for greater saphenous vein thrombosis typically involves multiple strategies:
Conservative Management
- Compression stockings
- Regular walking and movement
- Leg elevation
- Anti-inflammatory medications
Medical Interventions
More intensive treatments may include:
- Anticoagulation therapy
- Blood thinners in specific cases
- Monitoring for potential complications
Risk Factors and Prevention
Several factors can increase your risk of developing greater saphenous vein thrombosis:
- Prolonged immobility
- Recent surgery
- Obesity
- Pregnancy
- Hormone therapy
- Previous history of blood clots
- Varicose veins
Preventive Measures
Taking proactive steps can help reduce your risk:
- Maintaining regular physical activity
- Avoiding prolonged sitting
- Staying well-hydrated
- Managing weight
- Following post-surgery mobility instructions
Complication Prevention
While greater saphenous vein thrombosis is generally less severe than deep vein thrombosis, it's essential to prevent complications:
- Regular monitoring of symptoms
- Adherence to prescribed treatments
- Prompt reporting of worsening symptoms
- Following up with healthcare providers as recommended
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of greater saphenous vein thrombosis?
Common symptoms include a visible red streak along the inner leg, tenderness or pain along the vein's path, warmth in the affected area, swelling, and a rope-like feeling under the skin.
How is greater saphenous vein thrombosis diagnosed by doctors?
Doctors typically diagnose this condition through physical examination, ultrasound imaging, Doppler flow studies, and sometimes blood tests to rule out other clotting disorders.
What treatment options are available for managing greater saphenous vein thrombosis?
Treatment options include compression therapy, anticoagulation medications when necessary, anti-inflammatory drugs, regular walking, and leg elevation. The specific treatment plan depends on the severity and individual patient factors.
What are the risk factors that increase the chance of developing greater saphenous vein thrombosis?
Major risk factors include prolonged immobility, recent surgery, obesity, pregnancy, hormone therapy, previous blood clots, and existing varicose veins.
How can I prevent complications like deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism from greater saphenous vein thrombosis?
Prevent complications by following prescribed treatment plans, maintaining regular movement, wearing compression stockings as directed, and promptly reporting any worsening symptoms to your healthcare provider. Regular monitoring and early intervention are key to preventing serious complications.