Living with eczema can be challenging, especially when dealing with the persistent itching, dryness, and inflammation that characterize this common skin condition. Emollients for eczema represent one of the most fundamental and effective approaches to managing symptoms and maintaining healthier skin. These specialized moisturizing products work by creating a protective barrier on the skin's surface while helping to restore the skin's natural moisture balance.
Understanding how to properly use emollients for eczema can significantly improve your quality of life and reduce the frequency of flare-ups. Whether you're newly diagnosed or seeking better management strategies, learning about these essential skincare products is crucial for long-term eczema control and skin health maintenance.
Understanding Eczema and Skin Barrier Function
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, affects millions of people worldwide and is characterized by a compromised skin barrier. This impaired barrier function allows moisture to escape more easily while permitting irritants and allergens to penetrate the skin more readily. The result is the classic symptoms of dry, itchy, red, and inflamed skin that can appear anywhere on the body.
The skin barrier consists of skin cells held together by lipids, creating a protective seal. In people with eczema, this barrier is naturally weaker, making consistent moisturization with appropriate emollients essential for maintaining skin health and preventing symptom escalation.
What Are Emollients and How Do They Work
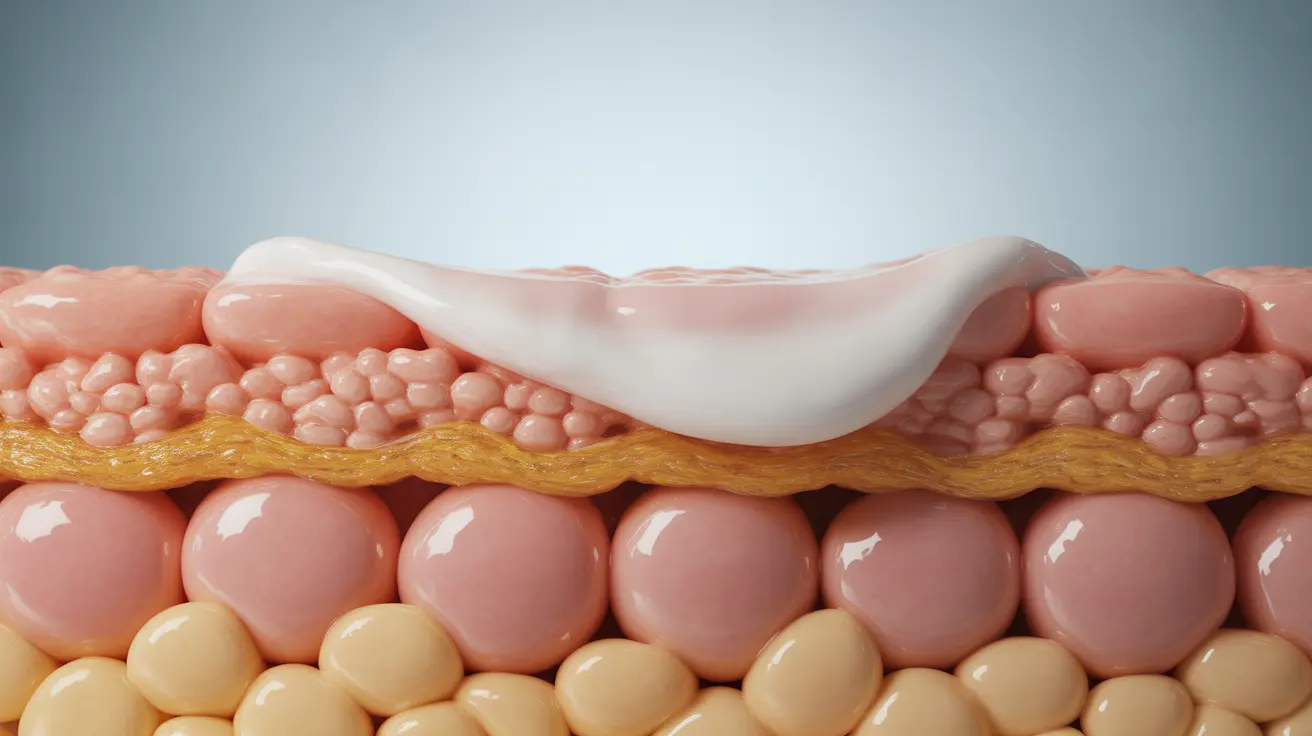
Emollients are specialized moisturizing products designed to soften and smooth the skin by filling in the gaps between skin cells. These products contain ingredients that mimic the skin's natural lipids, helping to restore barrier function and lock in moisture. Unlike regular moisturizers, emollients for eczema are typically formulated without fragrances, dyes, and other potential irritants that could trigger flare-ups.
The mechanism of action involves creating an occlusive layer on the skin's surface that prevents water loss while simultaneously delivering hydrating ingredients into the skin. This dual action helps to reduce dryness, minimize itching, and create an environment where the skin can heal and regenerate more effectively.
Key Ingredients in Effective Emollients
High-quality emollients for eczema typically contain ingredients such as ceramides, which help restore the skin barrier, and humectants like glycerin that draw moisture from the environment into the skin. Occlusive agents such as petrolatum or dimethicone create a protective seal, while emollient ingredients like shea butter and natural oils provide softening properties.
Types of Emollient Formulations
Creams
Emollient creams represent a balanced formulation that combines water and oil components. They provide good moisturization while being less greasy than ointments, making them suitable for daytime use and visible areas of the body. Creams are often well-tolerated and absorb relatively quickly into the skin.
Ointments
Ointments contain a higher concentration of oils and fewer water-based ingredients, making them the most occlusive and longest-lasting option. While they may feel greasy initially, ointments are particularly beneficial for severely dry or thick areas of eczematous skin and are often recommended for nighttime application.
Lotions
Lotions have the highest water content and lightest texture, making them easy to apply over large areas of the body. However, they may not provide sufficient moisture retention for severely affected skin and might require more frequent reapplication compared to creams or ointments.
Application Techniques and Best Practices
Proper application of emollients for eczema is crucial for maximum effectiveness. The technique involves applying the product in downward strokes following the direction of hair growth to avoid blocking follicles and causing irritation. Use gentle, smooth motions rather than rubbing vigorously, which can further irritate sensitive skin.
The amount used should be generous – many people underestimate how much emollient is needed for effective coverage. A good rule of thumb is to apply enough product so that the skin appears shiny initially, then allow it to absorb naturally.
Timing and Frequency Guidelines
The optimal timing for emollient application is immediately after bathing or showering while the skin is still damp. This technique, known as "wet skin application," helps trap additional moisture and enhances the product's effectiveness. For daily maintenance, applying emollients at least twice daily is recommended, with additional applications as needed based on skin dryness and environmental factors.
Selecting the Right Emollient for Your Needs
Choosing appropriate emollients for eczema requires considering factors such as skin sensitivity, severity of symptoms, lifestyle preferences, and seasonal changes. Those with highly sensitive skin should look for products labeled as hypoallergenic and free from common irritants including fragrances, parabens, and harsh preservatives.
Climate and season also influence emollient selection. During dry winter months, heavier ointments may be necessary, while lighter creams or lotions might suffice during humid summer conditions. It's often beneficial to have different formulations available for varying circumstances and body areas.
Long-term Benefits and Prevention Strategies
Consistent use of emollients for eczema provides cumulative benefits beyond immediate symptom relief. Regular application helps strengthen the skin barrier over time, potentially reducing the frequency and severity of flare-ups. This proactive approach can decrease dependence on topical medications and improve overall skin resilience.
Research suggests that maintaining a consistent emollient routine even during clear periods can help prevent eczema recurrence. This preventive strategy is particularly important for children with eczema, as it may help reduce the likelihood of developing associated conditions such as food allergies or asthma.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the best emollients for treating eczema and how do they work?
The best emollients for eczema are those formulated without fragrances, dyes, or harsh chemicals that could irritate sensitive skin. Look for products containing ceramides, hyaluronic acid, or natural oils like coconut or sunflower oil. These ingredients work by creating a protective barrier on the skin's surface while delivering moisture deep into the skin layers. Popular, dermatologist-recommended brands include CeraVe, Eucerin, Aveeno, and Vanicream, though the best choice varies by individual skin needs and preferences.
How often should I apply emollients for eczema and when is the best time?
Emollients for eczema should be applied at least twice daily – once in the morning and once before bed. The optimal time is immediately after bathing while your skin is still damp, as this helps lock in additional moisture. During flare-ups or in dry environments, you may need to apply emollients more frequently, even up to 3-4 times daily. Always reapply after hand washing and whenever your skin feels tight or dry.
What is the difference between emollient creams, ointments, and lotions for eczema?
The main differences lie in their oil-to-water ratios and thickness. Ointments contain the most oil and provide the strongest barrier protection, making them ideal for severe dryness but potentially feeling greasy. Creams offer a balance of moisture and absorption, suitable for most daily use. Lotions are lightest and absorb quickly but may require more frequent application. For eczema, creams and ointments are generally more effective than lotions due to their superior moisturizing and barrier-protecting properties.
Can emollients prevent eczema flare-ups and reduce the need for steroid creams?
Yes, regular use of emollients can significantly help prevent eczema flare-ups and potentially reduce the need for topical steroids. By maintaining skin hydration and barrier function, emollients create an environment less susceptible to irritants and allergens that trigger flare-ups. Studies show that consistent emollient use can extend periods between flare-ups and reduce their severity. However, they should complement, not replace, prescribed medications during active flare-ups. Always consult your healthcare provider before making changes to your treatment regimen.
How do I properly apply emollients for eczema on my face and body?
For body application, use gentle downward strokes following hair growth direction to avoid clogging follicles. Apply generously while skin is damp, using smooth motions rather than rubbing. For facial application, use a gentler, fragrance-free formulation specifically designed for sensitive facial skin. Apply with light upward strokes, avoiding the immediate eye area unless the product is ophthalmologist-tested. Always wash your hands before application and use clean fingers to prevent bacterial contamination. Allow the emollient to absorb naturally rather than wiping excess away immediately.