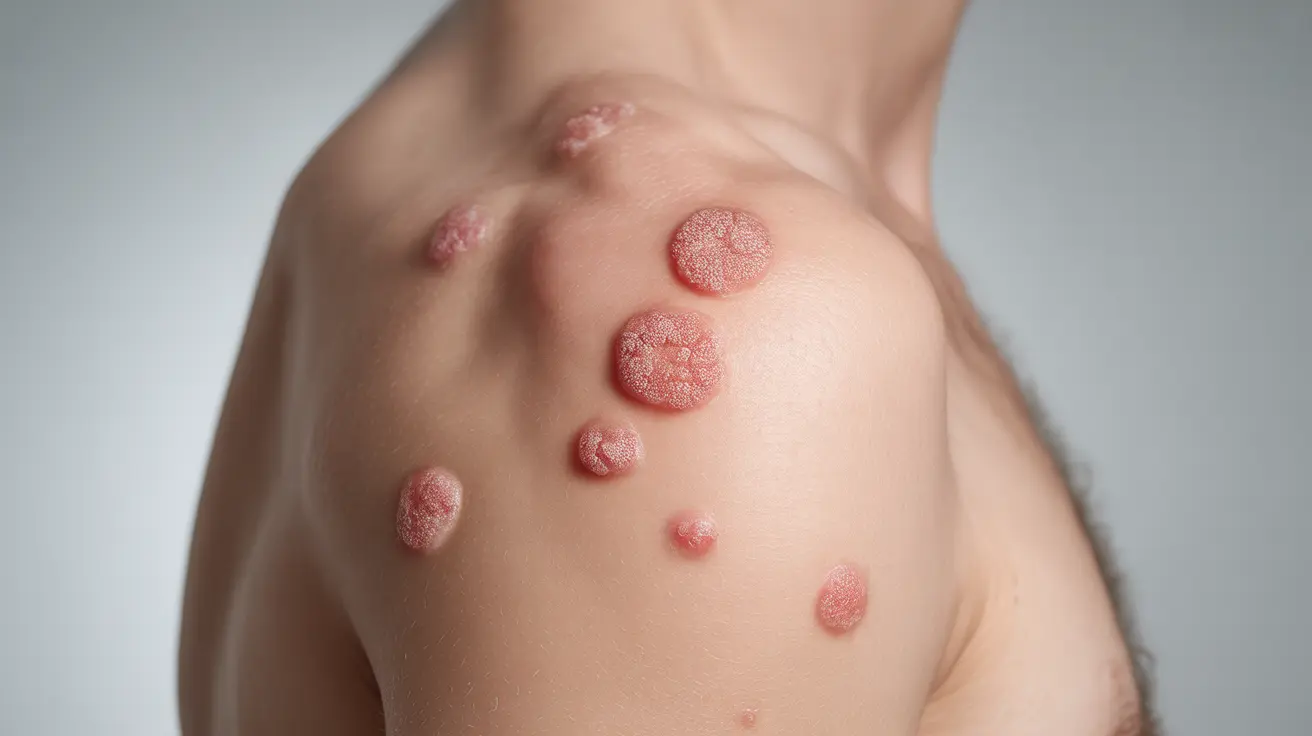
Guttate psoriasis is a distinctive form of psoriasis characterized by small, drop-shaped lesions that typically appear suddenly on the skin. This condition often develops following a streptococcal throat infection or other triggering events that affect the immune system. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options is crucial for proper management and improved quality of life.
While less common than plaque psoriasis, guttate psoriasis can significantly impact individuals of any age, though it frequently occurs in children and young adults. This comprehensive guide will explore the key aspects of guttate psoriasis, from its initial presentation to various treatment approaches.
Identifying Guttate Psoriasis Symptoms
The hallmark signs of guttate psoriasis are quite distinctive and typically develop rapidly. The main characteristics include:
- Small, drop-shaped pink to red spots
- Lesions typically measuring 1-10 millimeters in diameter
- Slight scaling or silvery appearance on the spots
- Spots commonly appearing on the trunk, arms, and legs
- Possible mild itching or discomfort
These symptoms often emerge within a few weeks of a triggering event, such as a throat infection or period of significant stress.
Causes and Triggers
Understanding what triggers guttate psoriasis is essential for both prevention and management. Common triggers include:
- Streptococcal infections (especially strep throat)
- Upper respiratory infections
- Tonsillitis
- Physical trauma to the skin
- Stress
- Certain medications
- Changes in weather or climate
Diagnosis Process
Healthcare providers typically diagnose guttate psoriasis through a combination of physical examination and medical history review. The diagnostic process may include:
Physical Examination
Doctors will carefully examine the size, shape, and distribution of lesions across the body. The characteristic drop-shaped appearance often helps distinguish guttate psoriasis from other skin conditions.
Medical Testing
Additional tests might include:
- Throat culture to check for streptococcal infection
- Skin biopsy in unclear cases
- Blood tests to rule out other conditions
- Review of recent medical history and potential triggers
Treatment Approaches
Treatment for guttate psoriasis often involves a multi-faceted approach, depending on the severity and extent of symptoms:
Topical Treatments
- Corticosteroid creams
- Vitamin D analogues
- Coal tar preparations
- Moisturizers and emollients
Phototherapy
Controlled exposure to UV light, either natural sunlight or artificial UV therapy, can help clear guttate psoriasis lesions in many cases.
Systemic Treatments
In severe cases or when associated with strep infection, healthcare providers might prescribe:
- Antibiotics for underlying infections
- Oral medications for severe cases
- Injectable biologics in resistant cases
Prevention and Management
While not all cases of guttate psoriasis can be prevented, certain strategies may help reduce outbreaks:
- Prompt treatment of strep infections
- Stress management techniques
- Regular skin moisturizing
- Avoiding known triggers
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms and signs of guttate psoriasis?
The main symptoms include small, drop-shaped red spots covered with fine scales, typically appearing on the trunk, arms, and legs. These spots usually develop rapidly and may be accompanied by mild itching or discomfort.
How is guttate psoriasis diagnosed and what tests might a doctor perform?
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination of the skin lesions, medical history review, and possibly a throat culture to check for strep infection. In some cases, a skin biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis.
What treatments are effective for managing guttate psoriasis outbreaks?
Effective treatments include topical medications (corticosteroids, vitamin D analogues), phototherapy, and in some cases, oral medications or antibiotics. The treatment approach depends on the severity of symptoms and presence of underlying infections.
Can guttate psoriasis be triggered or worsened by infections like strep throat?
Yes, strep throat is a common trigger for guttate psoriasis outbreaks. Other infections, stress, skin injury, and certain medications can also trigger or worsen the condition.
What are the chances guttate psoriasis will develop into chronic plaque psoriasis?
While many cases of guttate psoriasis clear up within weeks to months, approximately 40% of people may develop chronic plaque psoriasis later in life. Regular monitoring and proper treatment can help manage this progression.