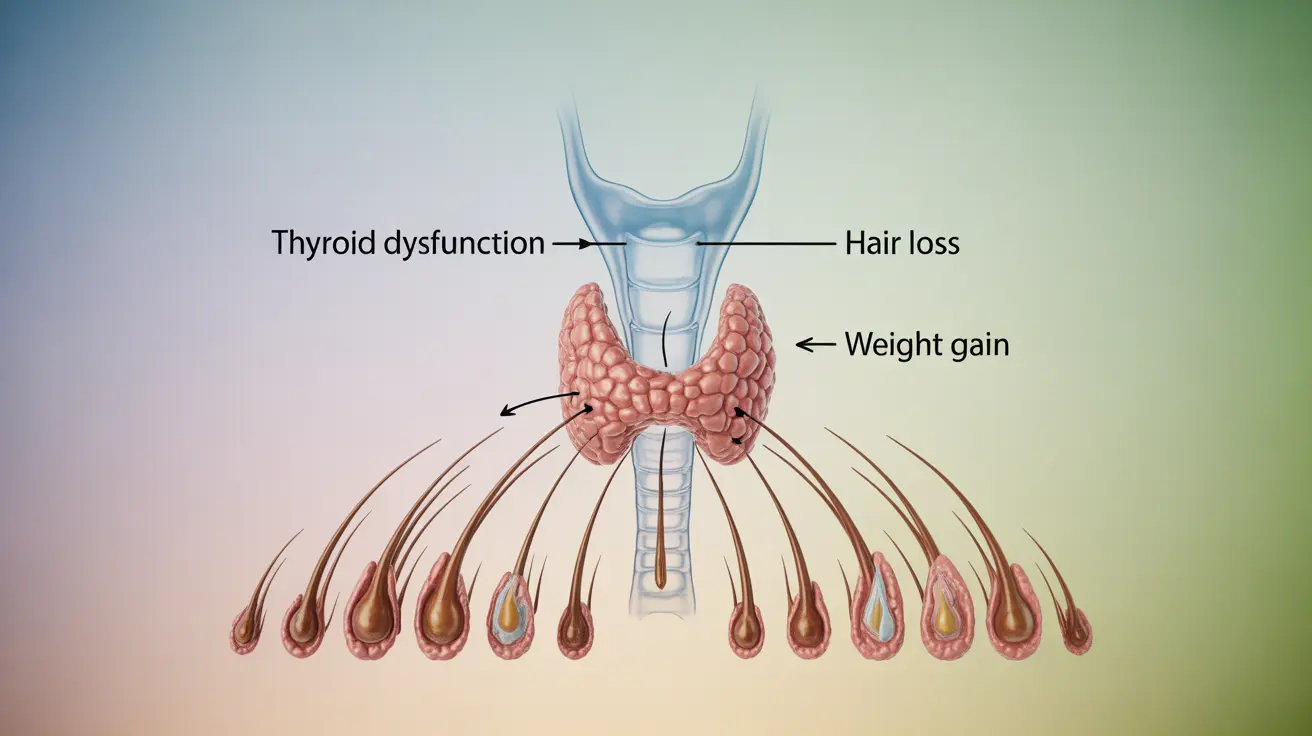
Experiencing simultaneous hair loss and weight gain can be distressing and may signal underlying health issues that require medical attention. These symptoms often occur together due to various medical conditions, hormonal imbalances, or nutritional deficiencies that affect multiple body systems.
Understanding the connection between these symptoms is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. Let's explore the common causes, diagnostic approaches, and available treatment options for concurrent hair loss and weight gain.
Common Medical Conditions Linking Hair Loss and Weight Gain
Several medical conditions can cause both hair loss and weight gain to occur simultaneously. Understanding these conditions is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Thyroid Disorders
Hypothyroidism is one of the most common conditions causing both hair loss and weight gain. When the thyroid gland doesn't produce enough hormones, it can slow down metabolism, leading to weight gain, while also affecting hair follicle health and causing diffuse hair loss.
Hormonal Imbalances
Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and hormonal changes during menopause can trigger both hair thinning and weight gain. These conditions affect the body's hormone balance, particularly androgens and estrogen, which play crucial roles in both weight regulation and hair growth cycles.
Nutritional Deficiencies and Their Impact
Nutritional imbalances can significantly affect both body weight and hair health. Key deficiencies include:
- Iron deficiency anemia
- Vitamin B12 deficiency
- Vitamin D deficiency
- Protein malnutrition
These deficiencies can disrupt normal hair growth cycles while also affecting metabolism and energy levels, potentially leading to weight changes.
Diagnostic Approaches
Healthcare providers typically use a combination of methods to determine the underlying cause of concurrent hair loss and weight gain:
- Comprehensive blood tests
- Thyroid function tests
- Hormone level assessments
- Nutritional deficiency screenings
- Physical examination
- Detailed medical history review
Treatment Strategies
Treatment approaches vary depending on the underlying cause but may include:
Medical Interventions
Doctors may prescribe specific treatments such as thyroid hormone replacement therapy, hormone balancing medications, or supplements to address deficiencies. These treatments target the root cause while addressing both hair loss and weight gain symptoms.
Lifestyle Modifications
Supporting medical treatments with lifestyle changes can improve outcomes:
- Balanced nutrition planning
- Regular physical activity
- Stress management techniques
- Adequate sleep habits
- Proper hair care practices
Frequently Asked Questions
What medical conditions commonly cause hair loss and weight gain together?
The most common conditions causing both symptoms include hypothyroidism, PCOS, hormonal imbalances, and certain nutritional deficiencies. These conditions affect multiple body systems, leading to both hair loss and weight changes.
How does hypothyroidism lead to hair loss and weight gain?
Hypothyroidism slows down the body's metabolism, causing weight gain. It also affects the hair growth cycle by reducing the production of new hair strands and can lead to diffuse hair thinning across the scalp.
Can iron or vitamin B12 deficiencies cause hair loss and affect body weight?
Yes, both iron and vitamin B12 deficiencies can cause hair loss by affecting hair follicle health. These deficiencies can also lead to fatigue and reduced metabolism, which may contribute to weight gain.
What tests do doctors use to diagnose the cause of hair loss and unexplained weight gain?
Doctors typically order comprehensive blood tests, including thyroid function tests, complete blood count, hormone level assessments, and nutritional panels. They also perform physical examinations and review medical history.
What treatment options are available to manage hair loss and weight gain caused by thyroid or nutritional problems?
Treatment options include hormone replacement therapy for thyroid issues, nutritional supplementation for deficiencies, dietary modifications, and lifestyle changes. The specific treatment plan depends on the underlying cause identified through proper diagnosis.