Hashimoto's thyroiditis is an autoimmune disorder where your immune system mistakenly attacks your thyroid gland, leading to inflammation and reduced thyroid hormone production. This condition, also known as chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis, is the most common cause of hypothyroidism in the United States, particularly affecting middle-aged women.
Living with Hashimoto's thyroiditis can significantly impact your daily life, but with proper understanding and management, many people maintain healthy, active lifestyles. Let's explore the essential aspects of this condition, from recognizing early symptoms to understanding treatment options.
Understanding the Impact on Your Thyroid
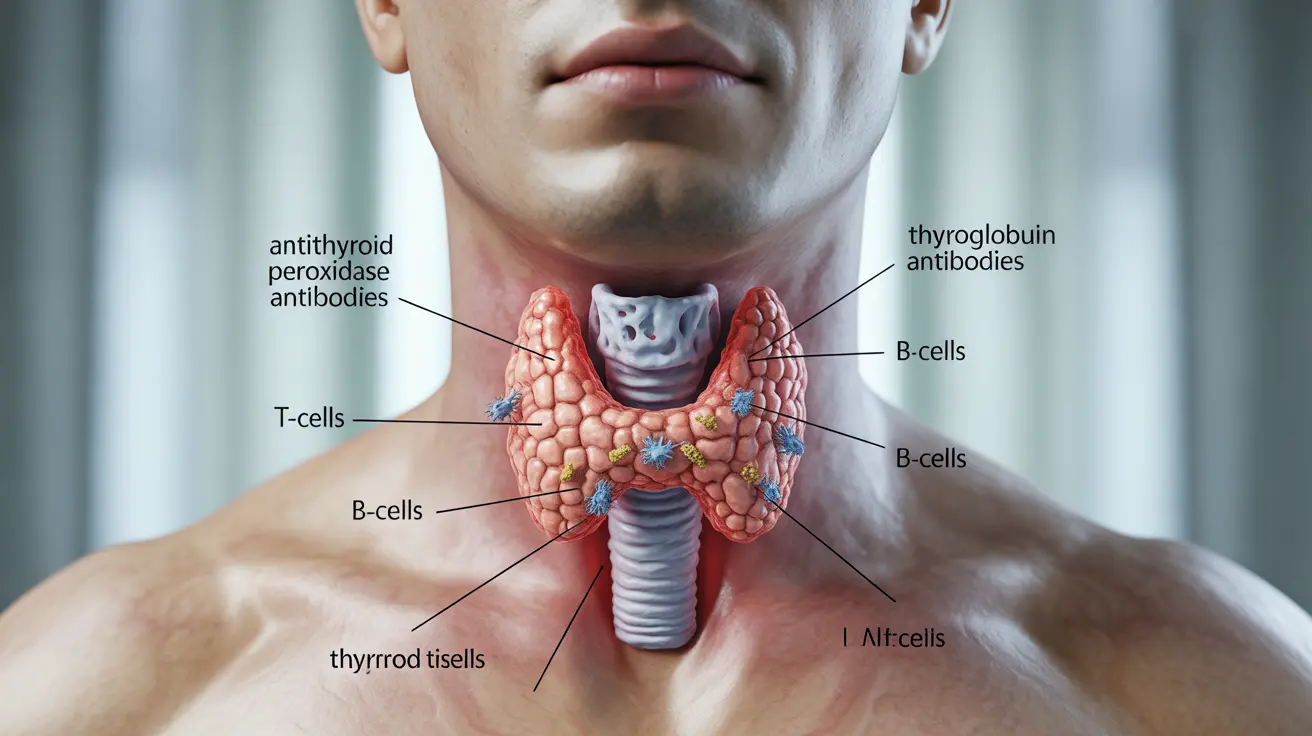
In Hashimoto's thyroiditis, your immune system creates antibodies that gradually damage your thyroid gland. This damage interferes with the gland's ability to produce crucial hormones that regulate various bodily functions, including metabolism, heart rate, and body temperature.
The condition typically develops slowly over years, and symptoms may be subtle at first. As thyroid function decreases, symptoms become more noticeable and can affect multiple body systems.
Common Signs and Symptoms
The symptoms of Hashimoto's thyroiditis often mirror those of hypothyroidism and may include:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Unexplained weight gain
- Cold sensitivity
- Joint and muscle pain
- Depression or mood changes
- Dry skin and brittle nails
- Hair loss or thinning
- Memory problems
- Irregular or heavy menstrual periods
Diagnosis Process
Diagnosing Hashimoto's thyroiditis involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and specific blood tests. Your healthcare provider will typically check for:
- Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) levels
- Free T4 levels
- Thyroid peroxidase antibodies (TPO)
- Thyroglobulin antibodies
Treatment Approaches
Thyroid Hormone Replacement
The primary treatment for Hashimoto's thyroiditis is thyroid hormone replacement therapy, typically with levothyroxine. This medication replaces the natural thyroid hormone your body isn't producing enough of. Finding the right dosage often requires regular monitoring and adjustments.
Lifestyle and Dietary Management
While medication is essential, certain lifestyle changes can help manage symptoms and support overall thyroid health:
- Maintaining a balanced, nutrient-rich diet
- Regular exercise appropriate for your energy levels
- Stress management techniques
- Adequate sleep and rest
- Avoiding excessive iodine intake
- Regular medical check-ups
Managing Complications
Untreated Hashimoto's thyroiditis can lead to various complications, including heart problems, mental health issues, and pregnancy complications. Regular monitoring and proper treatment help prevent these potential complications.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of Hashimoto's thyroiditis and how does it affect the thyroid gland?
Hashimoto's thyroiditis causes the immune system to attack the thyroid gland, leading to inflammation and reduced hormone production. Common symptoms include fatigue, weight gain, cold sensitivity, joint pain, depression, and dry skin. The condition gradually damages the thyroid's ability to produce essential hormones that regulate metabolism and other body functions.
How is Hashimoto's thyroiditis diagnosed and what blood tests are needed?
Diagnosis involves blood tests measuring TSH, Free T4, and thyroid antibodies (TPO and thyroglobulin antibodies). Your healthcare provider will also conduct a physical examination and review your medical history. Regular monitoring through blood tests helps track the condition's progression and adjust treatment as needed.
What treatments are available for Hashimoto's thyroiditis, and how does thyroid hormone replacement therapy work?
The main treatment is thyroid hormone replacement therapy with levothyroxine, which supplements the hormones your thyroid can't produce. The medication dosage is carefully determined based on your specific needs and may require adjustment over time. Regular blood tests help ensure optimal hormone levels.
Can lifestyle changes or supplements help manage Hashimoto's thyroiditis alongside medication?
Yes, lifestyle modifications can support treatment effectiveness. These include maintaining a balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management, and adequate sleep. While supplements may be helpful, they should only be taken under medical supervision and aren't a replacement for prescribed medication.
What are the potential complications if Hashimoto's thyroiditis is left untreated or poorly managed?
Untreated Hashimoto's thyroiditis can lead to serious complications including heart problems, mental health issues, infertility, and pregnancy complications. Other potential risks include goiter development, high cholesterol levels, and decreased cognitive function. Regular treatment and monitoring are essential to prevent these complications.