A headache on the left side of the head can be concerning and may stem from various causes, ranging from common tension headaches to more serious medical conditions. Understanding the potential causes, symptoms, and warning signs can help you determine when to seek medical attention and how to manage your symptoms effectively.
While most left-sided headaches are not life-threatening, being able to recognize different types and their characteristics is crucial for proper treatment and peace of mind. This comprehensive guide will help you understand when to worry about a left-sided headache and what steps to take for relief.
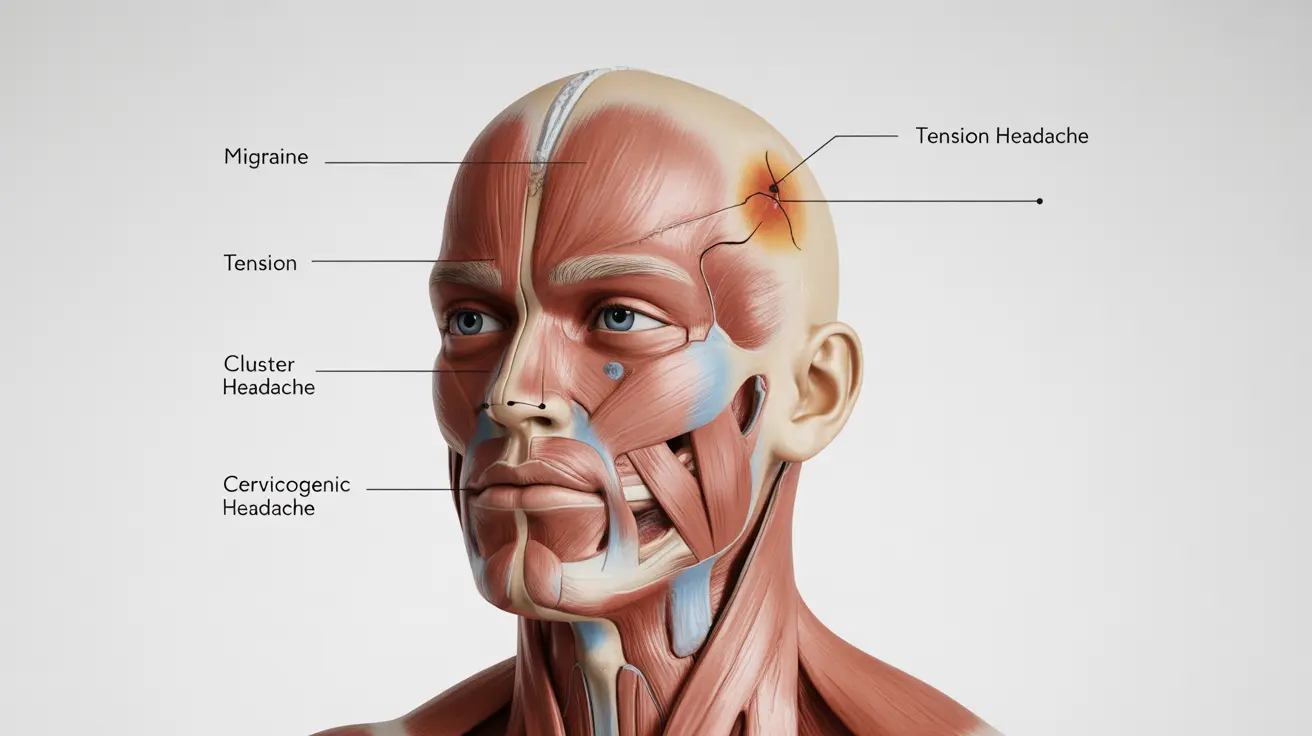
Common Causes of Left-Sided Headaches
Several conditions can trigger headaches specifically on the left side of the head:
- Migraine headaches
- Cluster headaches
- Cervicogenic headaches
- Tension headaches
- Sinus pressure or infection
- Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders
Each type of headache has distinct characteristics that can help identify its cause. For example, migraines often come with sensitivity to light and sound, while cluster headaches typically cause intense pain around one eye.
Warning Signs and Red Flags
Certain symptoms accompanying a left-sided headache warrant immediate medical attention:
- Sudden, severe headache ("thunderclap headache")
- Weakness or numbness on one side of the body
- Slurred speech or confusion
- High fever with neck stiffness
- Vision changes or loss
- Headache following head trauma
These symptoms could indicate serious conditions such as stroke, meningitis, or other neurological emergencies requiring immediate evaluation.
Distinguishing Between Different Types of Headaches
Migraine Characteristics
Migraines often present with:
- Pulsating or throbbing pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Visual disturbances (aura)
- Sensitivity to light, sound, and smells
- Pain lasting 4-72 hours
Cluster Headache Features
Cluster headaches typically involve:
- Severe pain around or behind one eye
- Tearing and redness of the affected eye
- Nasal congestion or runny nose
- Episodes lasting 15-180 minutes
- Attacks occurring in clusters or cycles
Treatment and Management Strategies
Several approaches can help manage left-sided headaches:
Immediate Relief Methods
- Over-the-counter pain relievers
- Cold or hot compresses
- Rest in a quiet, dark room
- Gentle massage of the neck and temples
- Staying hydrated
Preventive Measures
Long-term management strategies include:
- Maintaining regular sleep patterns
- Stress management techniques
- Regular exercise
- Avoiding known triggers
- Proper posture and ergonomics
- Keeping a headache diary
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common causes of a headache on the left side of the head?
The most common causes include migraines, tension headaches, cluster headaches, and cervicogenic headaches. Sinus problems and TMJ disorders can also cause left-sided head pain.
When should I seek emergency medical care for a left-sided headache?
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience a sudden severe headache, accompanied by symptoms like weakness on one side, speech problems, vision changes, high fever with neck stiffness, or confusion.
How can I tell if my left-sided headache is a migraine, cluster headache, or something more serious?
Migraines typically include throbbing pain, nausea, and sensitivity to light and sound. Cluster headaches cause intense pain around one eye with tearing. More serious conditions usually present with additional neurological symptoms or sudden onset of severe pain.
What home treatments or lifestyle changes can help reduce the frequency of left-side headaches?
Regular sleep schedules, stress management, proper hydration, regular exercise, and avoiding triggers can help reduce headache frequency. Over-the-counter pain relievers and cold/hot compresses can provide immediate relief.
Which symptoms accompanying a headache on the left side require prompt doctor evaluation?
Seek prompt medical evaluation for symptoms such as confusion, weakness or numbness, vision changes, fever with neck stiffness, or if the headache occurs after head trauma. Also consult a doctor if headaches become more frequent or severe over time.