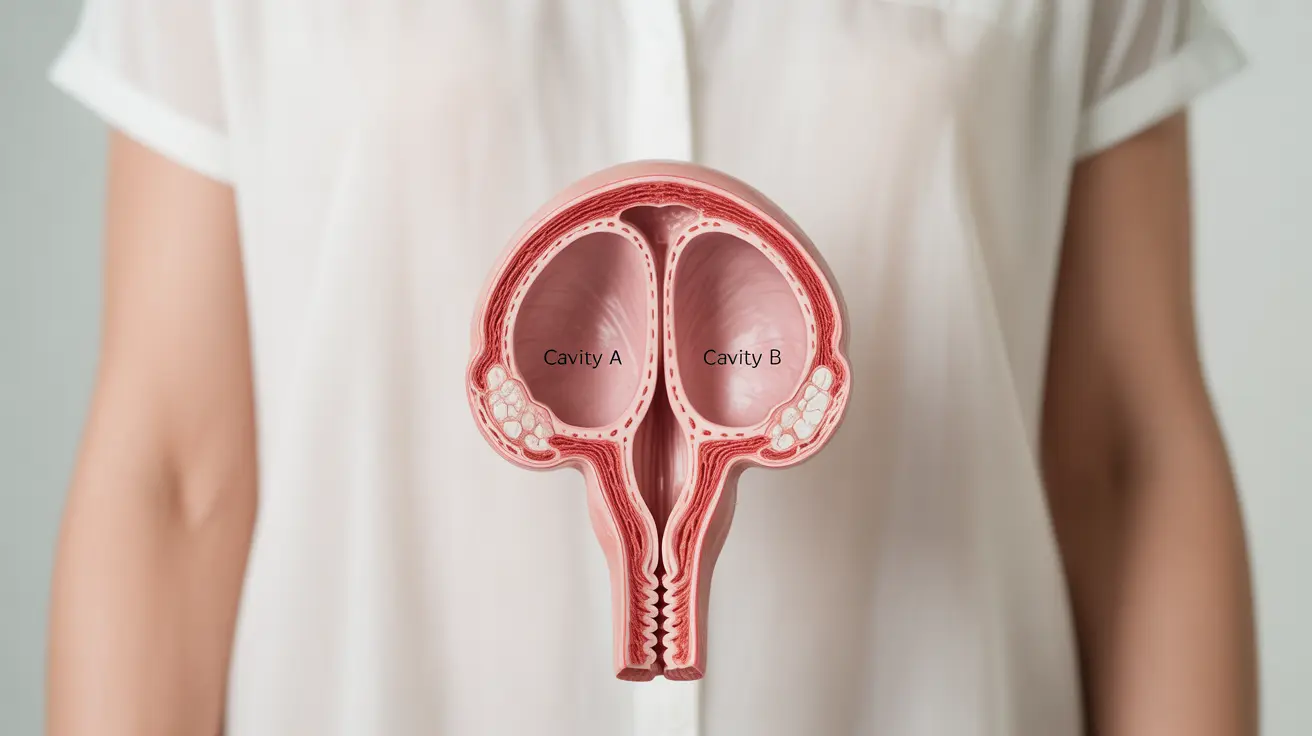
A heart-shaped uterus, medically known as a bicornuate uterus, is a congenital condition where the uterus develops into a distinctive heart shape instead of the typical pear shape. This condition affects approximately 3% of women and can impact fertility and pregnancy outcomes. Understanding this anatomical variation is crucial for women who may have concerns about their reproductive health.
While a heart-shaped uterus doesn't always cause problems, being informed about its potential implications can help women make better decisions about their reproductive health and pregnancy planning. This comprehensive guide explores the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and management options for those with a bicornuate uterus.
Understanding the Heart-Shaped Uterus
A heart-shaped uterus occurs during fetal development when the two parts of the uterus don't fully join together, creating an indentation at the top of the uterus. This anatomical variation results in two separate cavities at the top of the uterus, while the lower portion remains single. The condition is present from birth and is part of a group of conditions known as uterine anomalies.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of a heart-shaped uterus isn't always clear, but several factors may contribute to its development:
- Genetic factors
- Exposure to certain medications during fetal development
- Environmental factors during pregnancy
- Developmental abnormalities during embryonic formation
Signs and Symptoms
Many women with a heart-shaped uterus may not experience any symptoms and only discover the condition during routine gynecological examinations or pregnancy. However, some women might experience:
- Irregular menstrual cycles
- Severe menstrual cramping
- Recurring miscarriages
- Pain during intercourse
- Difficulty conceiving
Diagnosis Methods
Healthcare providers can diagnose a heart-shaped uterus through various imaging techniques:
- 3D ultrasound
- Hysterosalpingogram (HSG)
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- Hysteroscopy
- Saline sonography
Impact on Fertility and Pregnancy
A heart-shaped uterus can affect both fertility and pregnancy outcomes. Women with this condition may experience:
- Increased risk of preterm labor
- Higher likelihood of breech presentation
- Potential need for cesarean delivery
- Slightly reduced fertility rates
- Higher risk of pregnancy loss
Management and Treatment Options
Treatment approaches vary depending on individual circumstances and symptoms:
- Regular monitoring during pregnancy
- Cervical cerclage if necessary
- Surgical correction (metroplasty) in severe cases
- Hormonal therapy for menstrual symptoms
- Additional prenatal care and surveillance
Prevention and Lifestyle Considerations
While you cannot prevent a heart-shaped uterus, certain lifestyle measures can help manage the condition:
- Regular prenatal checkups during pregnancy
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle
- Following medical advice closely
- Being aware of warning signs during pregnancy
- Working with a high-risk pregnancy specialist when necessary
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is a heart-shaped (bicornuate) uterus and how does it affect fertility? A bicornuate uterus is a congenital condition where the uterus develops in a heart shape rather than the typical pear shape. It can affect fertility by potentially making it more difficult to conceive and increasing the risk of pregnancy complications.
2. What symptoms could indicate I have a bicornuate uterus? Common symptoms include irregular menstrual cycles, severe menstrual pain, recurring miscarriages, and pain during intercourse. However, many women may not experience any symptoms at all.
3. How is a bicornuate uterus diagnosed during pregnancy or routine exams? Diagnosis typically involves imaging tests such as 3D ultrasound, MRI, or hysterosalpingogram (HSG). These tests can clearly show the shape of the uterus and confirm the condition.
4. What pregnancy risks and complications are associated with a bicornuate uterus? The main risks include preterm labor, breech presentation, increased chance of cesarean delivery, and a slightly higher risk of pregnancy loss. Close monitoring during pregnancy is essential.
5. What treatment or management options are available for women with a bicornuate uterus? Treatment options include regular monitoring during pregnancy, possible cervical cerclage, surgical correction in severe cases, and working with a high-risk pregnancy specialist. The specific approach depends on individual circumstances and symptoms.