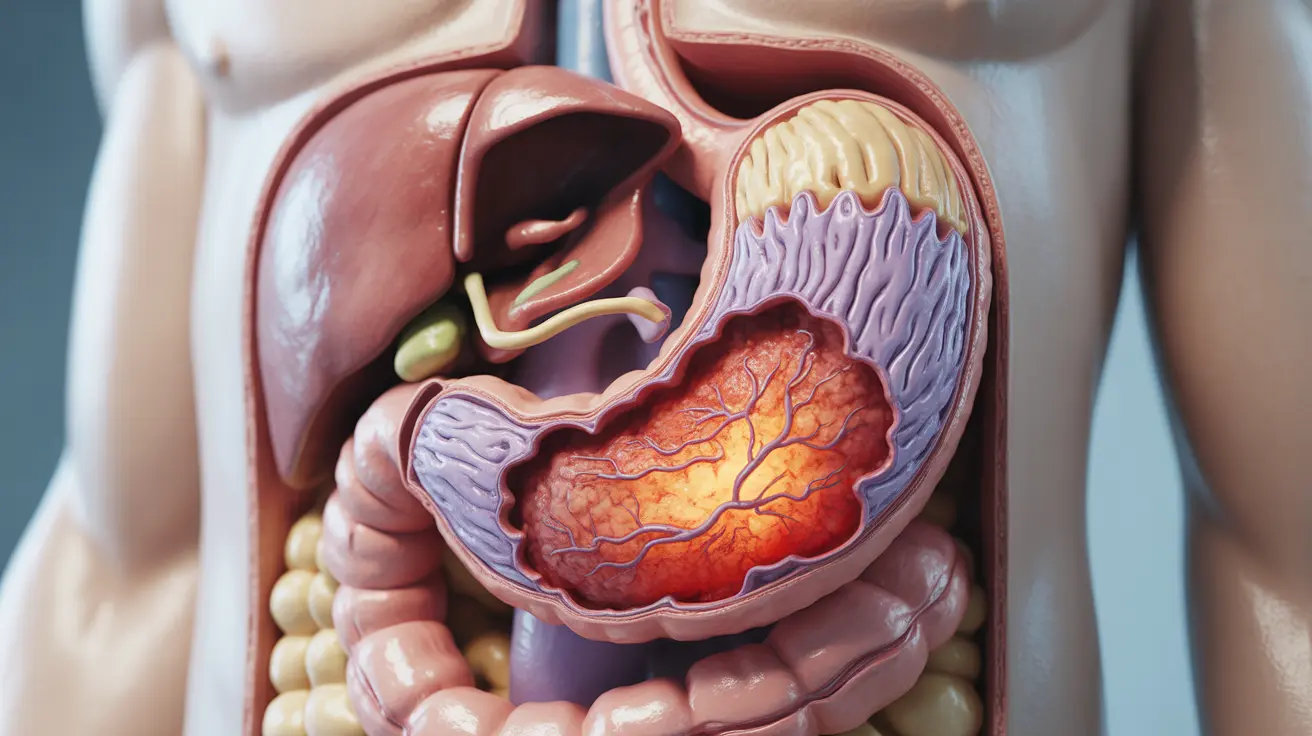
Hemorrhagic gastroenteritis in humans is a serious gastrointestinal condition characterized by bloody diarrhea, severe abdominal pain, and potential complications. This condition requires prompt medical attention and can be caused by various factors, most commonly bacterial infections like E. coli O157:H7. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options is crucial for proper management and prevention.
Understanding the Condition
Hemorrhagic gastroenteritis occurs when the lining of the digestive tract becomes inflamed and begins to bleed. This inflammation can affect both the stomach (gastritis) and intestines (enteritis), leading to potentially severe symptoms and complications if left untreated.
Common Symptoms and Warning Signs
The symptoms of hemorrhagic gastroenteritis typically develop rapidly and can be severe. Recognition of these symptoms is crucial for early intervention:
- Bloody diarrhea
- Severe abdominal cramping
- Vomiting
- Fever
- Dehydration
- Weakness and fatigue
- Loss of appetite
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can contribute to the development of hemorrhagic gastroenteritis:
Bacterial Infections
E. coli O157:H7 is a common bacterial cause, often contracted through:
- Contaminated food
- Unpasteurized dairy products
- Contaminated water
- Direct contact with infected individuals
Other Contributing Factors
Additional causes may include:
- Viral infections
- Certain medications
- Underlying medical conditions
- Stress-related factors
Diagnosis and Treatment Approaches
Healthcare providers typically diagnose hemorrhagic gastroenteritis through a combination of physical examination, patient history, and laboratory tests. Stool samples are often collected to identify the specific cause, particularly when bacterial infection is suspected.
Treatment Options
Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and preventing complications:
- Fluid and electrolyte replacement
- Monitoring for dehydration
- Antibiotics (when bacterial infection is confirmed)
- Supportive care and rest
- Dietary modifications during recovery
Prevention Strategies
Several preventive measures can reduce the risk of developing hemorrhagic gastroenteritis:
- Practice proper hand hygiene
- Cook foods thoroughly
- Avoid cross-contamination during food preparation
- Use safe water sources
- Store food at appropriate temperatures
- Avoid unpasteurized dairy products
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of hemorrhagic gastroenteritis in humans? Common symptoms include bloody diarrhea, severe abdominal pain, vomiting, fever, and signs of dehydration. Symptoms typically develop rapidly and can be severe enough to require immediate medical attention.
How is hemorrhagic gastroenteritis caused by E. coli O157:H7 diagnosed and treated? Diagnosis involves physical examination, stool testing, and blood work. Treatment typically includes fluid replacement, monitoring for complications, and possibly antibiotics when bacterial infection is confirmed. Supportive care and rest are essential components of the treatment plan.
What serious complications can arise from acute hemorrhagic gastroenteritis, such as hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS)? Hemolytic uremic syndrome is a serious complication that can lead to kidney failure, particularly in children and elderly patients. Other complications may include severe dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, and potential organ damage if left untreated.
When should someone with hemorrhagic gastroenteritis seek emergency medical care? Emergency medical care should be sought immediately if there is bloody diarrhea, severe abdominal pain, signs of dehydration (dark urine, decreased urination, extreme thirst), high fever, or persistent vomiting.
What steps can be taken to prevent hemorrhagic gastroenteritis caused by contaminated food or bacteria? Prevention includes proper hand washing, safe food handling practices, thorough cooking of foods, avoiding cross-contamination, proper food storage, and consuming only pasteurized dairy products. Regular cleaning and sanitization of food preparation areas is also crucial.