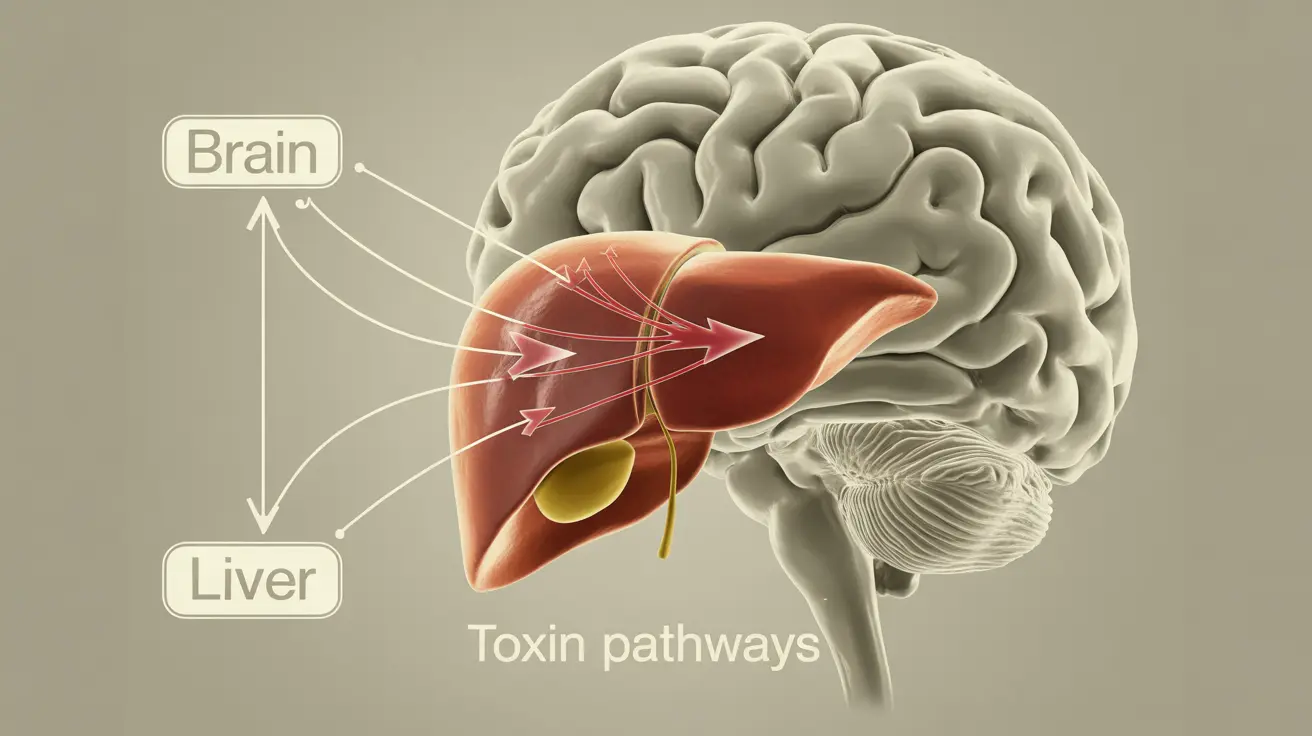
Hepatic encephalopathy is a serious neurological condition that occurs when liver dysfunction leads to toxic substances accumulating in the brain. This complex disorder primarily affects people with severe liver disease or cirrhosis, causing a range of cognitive and physical symptoms that can significantly impact daily life.
Early recognition and proper management of hepatic encephalopathy are crucial for better outcomes. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options can help patients and caregivers take prompt action when signs first appear.
Key Signs and Symptoms
Hepatic encephalopathy presents with various symptoms that typically progress in severity if left untreated. Early recognition of these signs is essential for timely intervention:
- Mild confusion or forgetfulness
- Changes in sleep patterns
- Difficulty concentrating
- Poor coordination
- Changes in personality or behavior
- Hand tremors (asterixis)
- Lethargy or excessive drowsiness
- Slurred speech
- Disorientation
Understanding the Causes and Triggers
The primary cause of hepatic encephalopathy is the liver's inability to effectively filter toxins from the blood, particularly ammonia. Several factors can trigger or worsen this condition:
Common Triggers
- Infections
- Dehydration
- Electrolyte imbalances
- Excessive protein intake
- Gastrointestinal bleeding
- Certain medications
- Constipation
Diagnostic Approaches
Diagnosing hepatic encephalopathy involves several methods and tests:
Physical Examination
Doctors assess mental status, behavior changes, and look for physical signs like asterixis (hand flapping tremors).
Laboratory Tests
- Blood ammonia levels
- Liver function tests
- Complete blood count
- Electrolyte panel
- Kidney function tests
Additional Assessments
Healthcare providers may use cognitive tests, brain imaging, and electroencephalogram (EEG) to rule out other conditions and confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment Strategies
Treatment for hepatic encephalopathy focuses on addressing both immediate symptoms and underlying causes:
Medical Interventions
- Lactulose administration
- Rifaximin or other antibiotics
- Correction of triggering factors
- Management of underlying liver disease
Supportive Care
- Dietary modifications
- Regular monitoring
- Prevention of complications
Prevention and Management
Several strategies can help prevent episodes of hepatic encephalopathy:
- Regular medication compliance
- Proper nutrition management
- Avoiding trigger factors
- Regular medical check-ups
- Maintaining good hydration
- Following dietary restrictions
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms and signs of hepatic encephalopathy that I should watch for? The most common signs include confusion, personality changes, poor concentration, sleep disturbances, and coordination problems. Physical symptoms like hand tremors and slurred speech may also occur.
What causes hepatic encephalopathy and what are the main triggers that worsen it? The condition is caused by liver dysfunction leading to toxin accumulation in the brain. Common triggers include infections, dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, excessive protein intake, and certain medications.
How is hepatic encephalopathy diagnosed and what tests do doctors use to confirm it? Diagnosis involves physical examination, blood tests (particularly ammonia levels), liver function tests, and possibly brain imaging or cognitive assessments. Doctors may also perform tests to rule out other neurological conditions.
What treatments are available to manage hepatic encephalopathy and how do they work? Treatment typically includes medications like lactulose and rifaximin to reduce ammonia levels, dietary modifications, and addressing underlying triggers. The approach is tailored to each patient's specific situation.
How can hepatic encephalopathy be prevented, especially in people with liver disease? Prevention focuses on medication adherence, proper nutrition, avoiding triggers, regular medical monitoring, and maintaining good hydration. Early intervention when symptoms appear is crucial for preventing severe episodes.