For many people experiencing persistent heartburn and acid reflux, understanding the relationship between hiatal hernia and GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease) is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. These two conditions often occur together and can significantly impact quality of life, but knowing their connection can help you better manage your symptoms.
This comprehensive guide explores how these conditions are related, their distinctive symptoms, and effective management strategies that can bring relief.
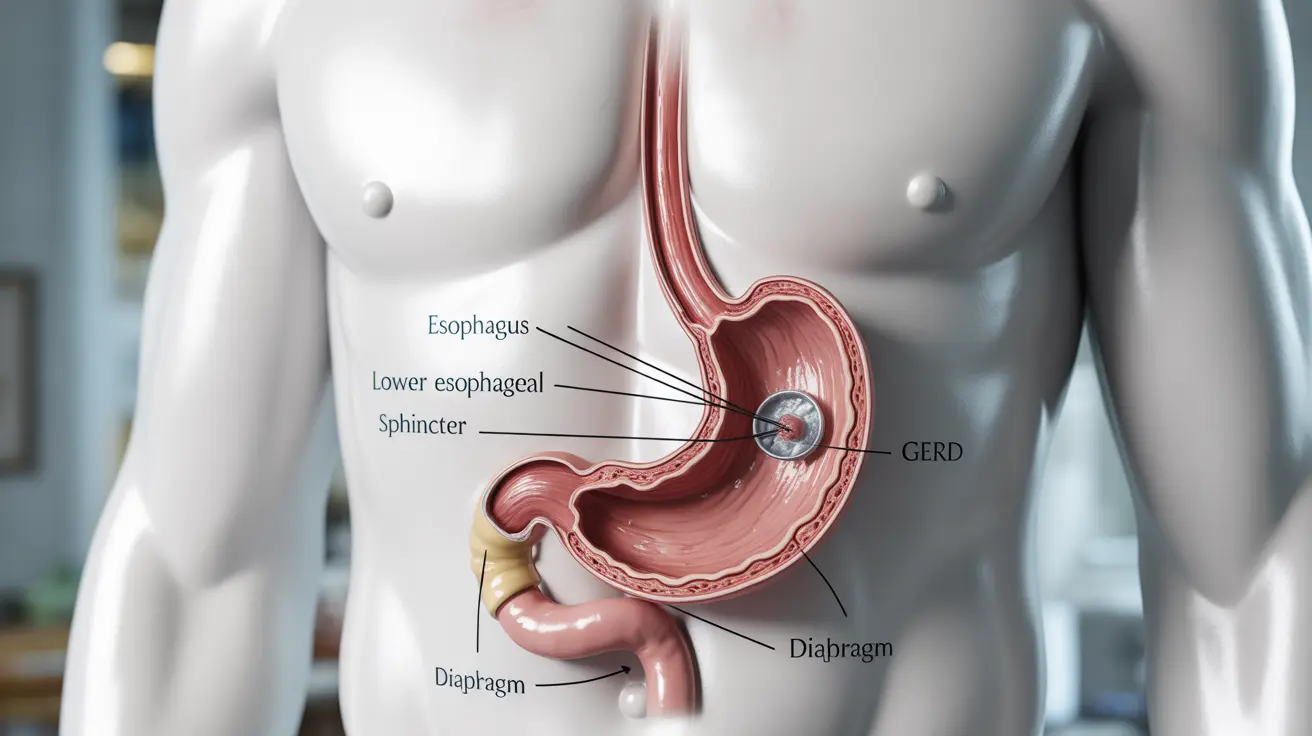
What is a Hiatal Hernia and How Does it Relate to GERD?
A hiatal hernia occurs when part of the stomach pushes upward through the diaphragm, the muscle that separates the chest cavity from the abdomen. This anatomical change can weaken the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), the muscle that normally prevents stomach acid from flowing back into the esophagus.
When the LES doesn't function properly due to a hiatal hernia, it can lead to GERD symptoms. However, it's important to note that not everyone with a hiatal hernia develops GERD, and not all GERD cases are caused by a hiatal hernia.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Common Hiatal Hernia Symptoms
Hiatal hernias often present with these distinctive signs:
- Chest pain or pressure
- Difficulty swallowing
- Feeling unusually full after eating
- Shortness of breath
- Chronic burping or belching
GERD-Specific Symptoms
GERD typically manifests with these symptoms:
- Persistent heartburn
- Regurgitation of food or sour liquid
- Chronic cough
- Difficulty sleeping lying flat
- Frequent throat clearing
Diagnosis and When to Seek Medical Care
If you experience persistent heartburn, difficulty swallowing, or chest pain, it's important to consult a healthcare provider. They may recommend various diagnostic tests, including:
- Upper endoscopy
- Barium swallow study
- pH monitoring
- Esophageal manometry
Treatment Approaches and Management Strategies
Medical Interventions
Treatment options for hiatal hernia and GERD may include:
- Prescription medications to reduce acid production
- Antacids for immediate symptom relief
- Surgery in severe cases
- Endoscopic treatments
Lifestyle Modifications
Several lifestyle changes can help manage symptoms effectively:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Eating smaller, more frequent meals
- Avoiding trigger foods
- Not lying down for 2-3 hours after eating
- Elevating the head of the bed
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common symptoms of a hiatal hernia, and how do they differ from GERD symptoms?
Hiatal hernia symptoms often include chest pressure, difficulty swallowing, and feeling unusually full after meals. GERD symptoms typically focus more on acid-related issues like heartburn, regurgitation, and chronic cough. While these conditions can overlap, hiatal hernia symptoms tend to be more mechanical in nature, while GERD symptoms relate more to acid exposure.
Can a hiatal hernia cause GERD, and how are these two conditions connected?
Yes, a hiatal hernia can cause GERD by compromising the lower esophageal sphincter's function. The hernia changes the normal anatomy of the stomach and diaphragm, which can allow stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus more easily, leading to GERD symptoms.
What lifestyle changes or home remedies can help manage both hiatal hernia and GERD symptoms?
Effective lifestyle changes include maintaining a healthy weight, eating smaller meals, avoiding trigger foods, staying upright after meals, and elevating the head of your bed. Additionally, quitting smoking, limiting alcohol, and wearing loose-fitting clothes can help reduce symptoms of both conditions.
When should someone with acid reflux or heartburn see a doctor about a possible hiatal hernia or GERD?
Seek medical attention if you experience persistent heartburn, difficulty swallowing, chest pain, chronic cough, or if over-the-counter medications aren't providing relief. Also consult a doctor if symptoms interfere with daily activities or sleep, or if you experience unexplained weight loss.
What treatment options are available for a hiatal hernia that is causing persistent GERD-like symptoms?
Treatment options range from medications (such as proton pump inhibitors and H2 blockers) to lifestyle modifications. In severe cases where conservative treatments aren't effective, surgical options like fundoplication or hernia repair may be recommended. Treatment plans are typically customized based on symptom severity and overall health status.