High granulocytes, also known as granulocytosis, occur when there's an elevated level of specific white blood cells in your bloodstream. These specialized immune cells play a crucial role in fighting infections and maintaining your body's defense system. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for high granulocytes is essential for proper medical management.
While some elevation in granulocyte levels can be a normal response to infection or inflammation, persistent high levels may indicate underlying health conditions that require medical attention. This comprehensive guide will help you understand what elevated granulocytes mean for your health and when to seek medical care.
Understanding Granulocytes and Their Function
Granulocytes are white blood cells that contain small granules filled with proteins and enzymes. These cells are vital components of your immune system, helping to fight off bacterial and fungal infections, as well as responding to allergic reactions and inflammation.
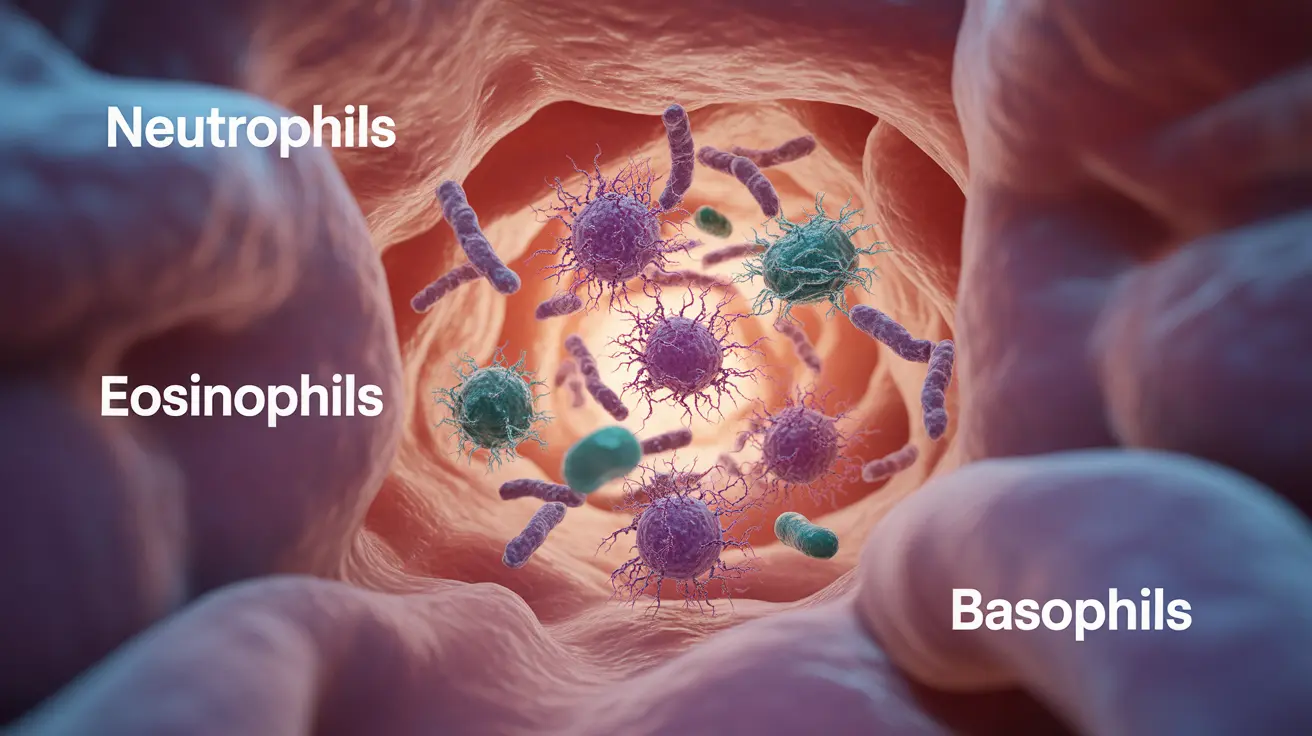
There are three main types of granulocytes:
- Neutrophils (most common, fighting bacterial infections)
- Eosinophils (responding to allergies and parasitic infections)
- Basophils (involved in inflammatory reactions)
Common Causes of High Granulocytes
Several factors can lead to elevated granulocyte levels in your blood:
Infections
Bacterial, viral, or fungal infections often trigger increased production of granulocytes as your body fights off the infection. This is typically a normal immune response.
Inflammatory Conditions
Chronic inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, or vasculitis can cause persistent elevation in granulocyte levels.
Blood Disorders
Certain blood disorders, including some types of leukemia and myeloproliferative disorders, can cause abnormal production of granulocytes in the bone marrow.
Other Causes
Additional factors that may lead to high granulocytes include:
- Severe physical or emotional stress
- Certain medications, including corticosteroids
- Smoking
- Pregnancy
- Recent surgery or trauma
Signs and Symptoms
The symptoms associated with high granulocytes often relate to the underlying condition causing the elevation. Common symptoms may include:
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Night sweats
- Unexplained weight loss
- Frequent infections
- Bone pain or tenderness
- Enlarged lymph nodes
Diagnosis and Testing
Diagnosis of high granulocytes typically involves several steps:
Complete Blood Count (CBC)
This initial blood test measures the levels of different blood cells, including granulocytes. It helps determine if levels are above normal range.
Additional Testing
Your healthcare provider may recommend:
- Bone marrow biopsy
- Blood smear examination
- Genetic testing
- Imaging studies
- Inflammatory marker tests
Treatment Approaches
Treatment for high granulocytes focuses on addressing the underlying cause:
Infection Management
If an infection is present, appropriate antimicrobial therapy will be prescribed based on the type of infection.
Underlying Condition Treatment
For chronic conditions or blood disorders, specific treatment protocols will be developed, which may include:
- Medication adjustments
- Targeted therapy
- Regular monitoring
- Specialist referrals
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common causes of having high granulocytes in my blood? Common causes include infections, inflammatory conditions, blood disorders, stress, certain medications, smoking, pregnancy, and recent surgery or trauma.
What symptoms might indicate that high granulocytes are due to an infection or a serious condition like leukemia? Key symptoms include persistent fever, fatigue, night sweats, unexplained weight loss, frequent infections, bone pain, and enlarged lymph nodes. Serious conditions like leukemia may also present with easy bruising and bleeding.
How is granulocytosis diagnosed and what tests are involved? Diagnosis typically begins with a Complete Blood Count (CBC) test, followed by additional testing such as bone marrow biopsy, blood smear examination, genetic testing, and imaging studies as needed.
What treatments are available to manage high granulocyte levels and their underlying causes? Treatment depends on the underlying cause and may include antimicrobial therapy for infections, specific medications for chronic conditions, targeted therapy for blood disorders, and regular monitoring.
Can lifestyle changes or diet help reduce or manage elevated granulocytes effectively? While lifestyle changes alone cannot treat high granulocytes, maintaining a healthy lifestyle through proper nutrition, regular exercise, stress management, and smoking cessation can support overall immune system function and help manage underlying conditions.