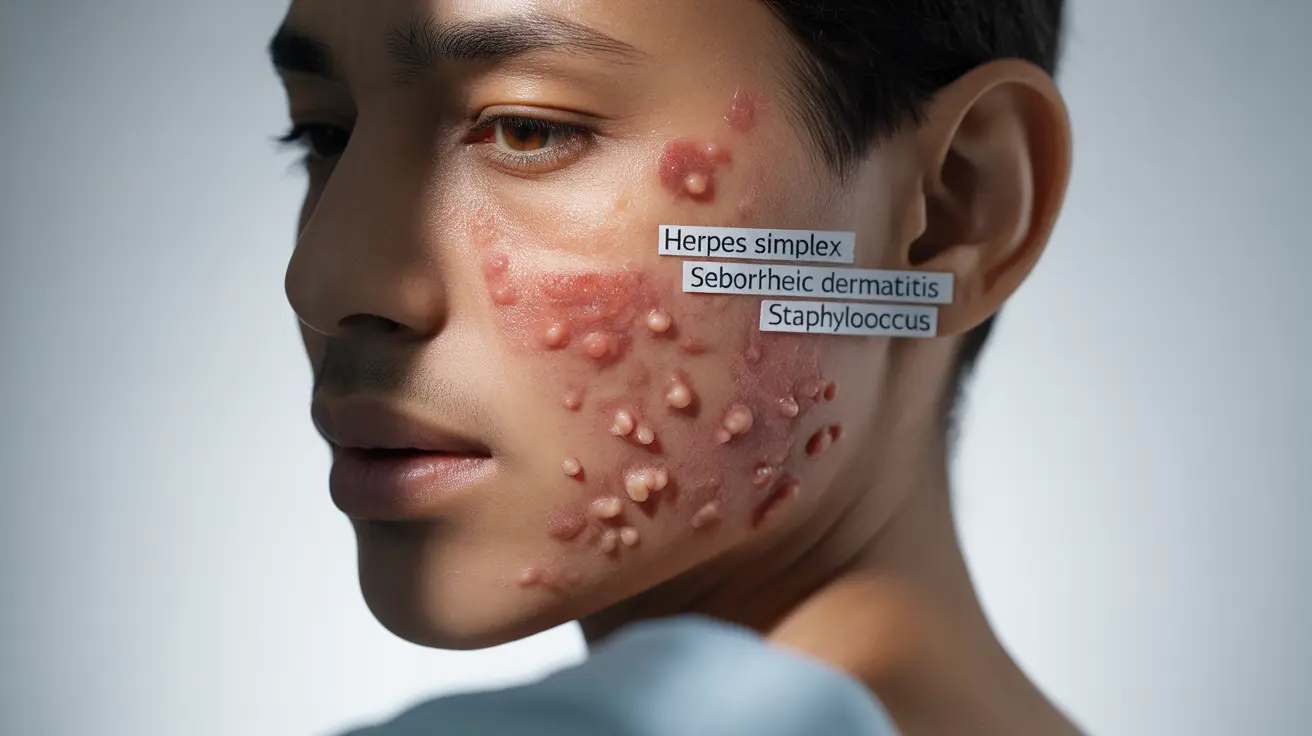
Skin lesions are common manifestations in people living with HIV, affecting up to 90% of individuals during the course of their infection. These skin changes can range from mild to severe and often serve as important clinical indicators of the disease's progression. Understanding these skin manifestations is crucial for both healthcare providers and individuals living with HIV to ensure proper management and care.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the various types of HIV-related skin lesions, their significance in disease progression, and available treatment options. We'll also discuss how to differentiate HIV-related skin changes from other skin conditions and the role of antiretroviral therapy in managing these symptoms.
Common Types of HIV-Related Skin Lesions
HIV-related skin lesions can manifest in various forms, each with distinct characteristics and implications for health:
Viral-Related Lesions
Common viral-induced skin lesions include herpes simplex outbreaks, shingles (herpes zoster), and molluscum contagiosum. These typically appear as clustered blisters or raised bumps on the skin and can be more severe and frequent in HIV-positive individuals.
Fungal Infections
Candidiasis and other fungal infections often present as red, scaly patches that may be itchy or painful. These infections commonly affect the mouth, groin area, and skin folds.
Bacterial Infections
Bacterial skin infections may manifest as folliculitis, impetigo, or cellulitis. These conditions can cause redness, swelling, and sometimes pus-filled lesions.
Significance in HIV Progression
Skin lesions can serve as important markers of HIV disease progression and immune system function:
- Early-stage manifestations typically include seborrheic dermatitis and viral infections
- Mid-stage symptoms might include more severe fungal infections
- Late-stage manifestations often include opportunistic infections and certain types of cancers
Treatment Approaches
Treatment for HIV-related skin lesions typically involves a multi-faceted approach:
Specific Treatments
Different types of lesions require specific treatments:
- Antiviral medications for viral infections
- Antifungal treatments for fungal infections
- Antibiotics for bacterial infections
- Topical treatments for inflammatory conditions
Preventive Measures
Maintaining good skin health through proper hygiene and preventive care is essential. This includes:
- Regular skin examination
- Prompt treatment of any new lesions
- Protection from sun exposure
- Maintaining good overall hygiene
Role of Antiretroviral Therapy
Antiretroviral therapy (ART) plays a crucial role in managing HIV-related skin conditions by:
- Strengthening the immune system
- Reducing the frequency and severity of skin lesions
- Preventing opportunistic infections
- Improving overall skin health
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common types of skin lesions caused by HIV and how do they appear?
HIV-related skin lesions commonly include viral infections (like herpes and shingles), fungal infections (such as candidiasis), and bacterial infections. They can appear as blisters, rashes, bumps, or scaly patches, varying in severity and appearance depending on the specific condition.
How can HIV-related skin lesions indicate the stage or severity of HIV infection?
Skin lesions often correlate with immune system function and HIV progression. More frequent and severe skin problems typically indicate a weakened immune system and potentially advanced HIV disease, while mild and occasional lesions may occur in earlier stages.
What treatments are available for managing skin lesions caused by HIV?
Treatments depend on the specific type of lesion and may include antiviral medications, antifungal treatments, antibiotics, or topical medications. Antiretroviral therapy is fundamental in preventing and managing skin conditions by supporting immune function.
How can I tell if a skin lesion is related to HIV or another condition?
While certain skin conditions are more common in HIV-positive individuals, definitive diagnosis requires medical evaluation. Healthcare providers consider factors such as appearance, duration, and response to treatment to determine if lesions are HIV-related.
Can antiretroviral therapy (ART) help prevent or improve HIV-related skin problems?
Yes, ART can significantly help prevent and improve HIV-related skin problems by strengthening the immune system and reducing viral load. This leads to fewer opportunistic infections and better overall skin health.